LLM之RAG实战(五十三)| 微调Embedding模型:终极指南
使用nltk进行切块,这样便于llm更好的处理。我们配置了 Matryoshka 损失函数 ,指定了用于截断嵌入的维度。内部损失函数 MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(可参考:https://sbert.net/examples/sentence_transformer/training/matryoshka/README.html) 可帮助模型
假设您正在为医疗领域构建一个问答系统,并希望确保它可以在用户提出问题时准确检索相关的医学文章。但是,通用嵌入模型可能难以处理高度专业化的词汇和医学术语的细微差别。
这就是微调的用武之地 !!
在这篇博文中,我们将深入探讨为特定领域(如医学、法律或金融)微调嵌入模型的过程。我们将专门为您的领域生成一个数据集,并使用它来训练模型,以更好地理解您选择的领域中微妙的语言模式和概念。
一、Embedding概念理解
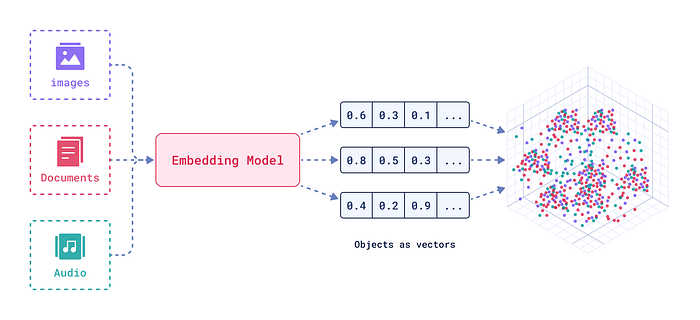
嵌入是文本或图像的强大数字表示形式,用于捕获语义关系。将文本或音频想象成多维空间中的一个点,其中相似的单词或短语比不同的单词或短语更靠近。
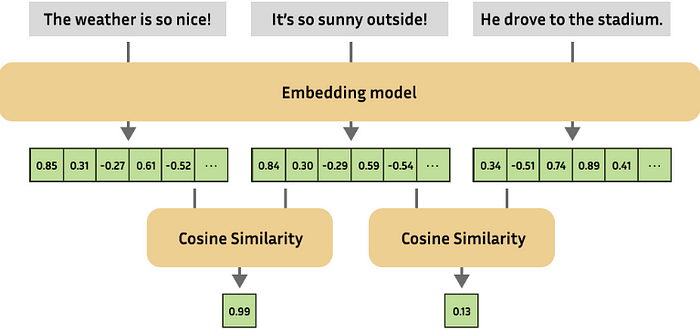
嵌入对于许多 NLP 任务至关重要,例如:
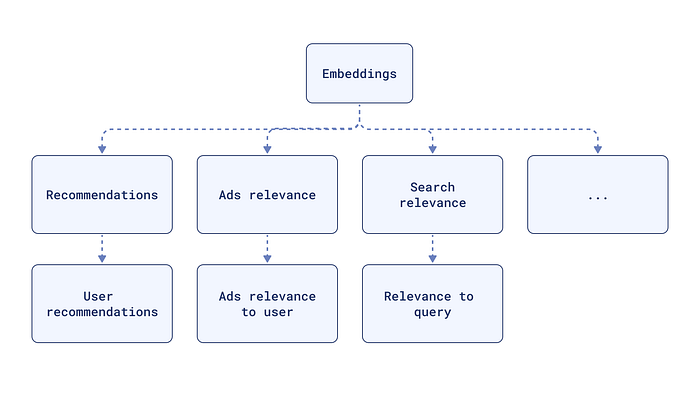
Semantic Similarity(语义相似性): 查找两个图像或文本的相似程度。
Text Classification(文本分类): 根据数据的含义将数据分组到各个类别中。
Question Answering(问答): 查找最相关的文档来回答问题。
RAG (检索增强生成): 将用于检索的嵌入模型与用于文本生成的语言模型相结合,以提高生成文本的质量和相关性。
二、BGE-base-en向量模型
BAAI/bge-base-en-v1.5 模型由 BAAI(北京人工智能研究院)开发,是一个强大的文本嵌入模型。它擅长各种 NLP 任务,并已被证明在 MTEB 和 C-MTEB 等基准测试中表现良好。bge-base-en 模型对于计算资源有限的应用程序(如我的情况)来说是一个不错的选择。
三、为什么要微调嵌入 ?
针对特定域微调嵌入模型对于优化 RAG 系统至关重要。此过程可确保模型对相似性的理解与域的特定上下文和语言细微差别保持一致。经过微调的嵌入模型可以更好地检索与问题最相关的文档,最终从 RAG 系统获得更准确、更相关的响应。
四、微调数据集格式
常见的数据格式如下:
-
Positive Pair: 一对相关句子(例如,questions , answers)。
-
Triplets: (锚点、正、负)三元组,其中锚点与正值相似,与负值不同。
-
Pair with Similarity Score(与相似性分数配对 ): 一对具有相似性分数的句子,指示它们之间的关系。
-
Texts with Classes(带类的文本 ): 带有相应类标签的文本。
在这篇博文中,我们将创建一个 questions 、 answers 对的数据集,以微调我们的 bge-base-en-v1.5 模型。
五、损失函数
损失函数对于训练嵌入模型至关重要。它们测量模型的预测与实际标签之间的差异,为模型提供调整其权重的信号。
不同的损失函数适用于不同的数据集格式:
-
三元组损失: 与 (anchor, positive, negative) 三元组一起使用,以鼓励模型将相似的句子放在更近的位置,将不同的句子放在更远的位置。
-
对比损失: 与正负对一起使用,鼓励相似的句子接近,鼓励不同的句子保持距离。
-
余弦相似度损失: 与句子对和相似性分数一起使用,鼓励模型生成与提供的分数匹配的余弦相似性的嵌入。
-
俄罗斯套娃损失(Matryoshka Loss): 一种专门的损失函数,旨在创建 Matryoshka 嵌入,其中嵌入是可截断的。
六、微调示例代码
6.1 安装依赖项
我们从安装基本库开始。我们将使用 datasets、sentence-transformers 和 google-generativeai 来处理数据集、嵌入模型和文本生成。
apt-get -qq install poppler-utils tesseract-ocrpip install datasets sentence-transformers google-generativeaipip install -q --user --upgrade pillowpip install -q unstructured["all-docs"] pi_heifpip install -q --upgrade unstructuredpip install --upgrade nltk
我们还将安装 unstructured 用于 PDF 解析,安装 nltk 用于文本处理。
6.2 PDF 解析和文本提取
我们将使用unstructured库从 PDF 文件中提取文本和表格。
import nltkimport os from unstructured.partition.pdfimport partition_pdffrom collections import Counternltk.download('punkt')nltk.download('averaged_perceptron_tagger')nltk.download('punkt_tab')def process_pdfs_in_folder(folder_path):total_text = [] # To accumulate the text from all PDFs# Get list of all PDF files in the folderpdf_files = [f for f in os.listdir(folder_path) if f.endswith('.pdf')]for pdf_file in pdf_files:pdf_path = os.path.join(folder_path, pdf_file)print(f"Processing: {pdf_path}")# Apply the partition logicelements = partition_pdf(pdf_path, strategy="auto")# Display the types of elementsdisplay(Counter(type(element) for element in elements))# Join the elements to form text and add it to total_text listtext = "\n\n".join([str(el) for el in elements])total_text.append(text)# Return the total concatenated textreturn "\n\n".join(total_text)folder_path = "data"all_text = process_pdfs_in_folder(folder_path)
我们浏览指定文件夹中的每个 PDF,并将内容划分为文本、表格和图形。
然后,我们将文本元素组合成单个文本表示形式。
6.3 自定义文本分块
使用nltk进行切块,这样便于llm更好的处理。
import nltknltk.download('punkt')def nltk_based_splitter(text: str, chunk_size: int, overlap: int) -> list:"""Splits the input text into chunks of a specified size, with optional overlap between chunks.Parameters:- text: The input text to be split.- chunk_size: The maximum size of each chunk (in terms of characters).- overlap: The number of overlapping characters between consecutive chunks.Returns:- A list of text chunks, with or without overlap."""from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize# Tokenize the input text into individual sentencessentences = sent_tokenize(text)chunks = []current_chunk = ""for sentence in sentences:# If the current chunk plus the next sentence doesn't exceed the chunk size, add the sentence to the chunkif len(current_chunk) + len(sentence) <= chunk_size:current_chunk += " " + sentenceelse:# Otherwise, add the current chunk to the list of chunks and start a new chunk with the current sentencechunks.append(current_chunk.strip()) # Strip to remove leading spacescurrent_chunk = sentence# After the loop, if there is any leftover text in the current chunk, add it to the list of chunksif current_chunk:chunks.append(current_chunk.strip())# Handle overlap if it's specified (overlap > 0)if overlap > 0:overlapping_chunks = []for i in range(len(chunks)):if i > 0:# Calculate the start index for overlap from the previous chunkstart_overlap = max(0, len(chunks[i-1]) - overlap)# Combine the overlapping portion of the previous chunk with the current chunkchunk_with_overlap = chunks[i-1][start_overlap:] + " " + chunks[i]# Append the combined chunk, making sure it's not longer than chunk_sizeoverlapping_chunks.append(chunk_with_overlap[:chunk_size])else:# For the first chunk, there's no previous chunk to overlap withoverlapping_chunks.append(chunks[i][:chunk_size])return overlapping_chunks # Return the list of chunks with overlap# If overlap is 0, return the non-overlapping chunksreturn chunkschunks = nltk_based_splitter(text=all_text,chunk_size=2048,overlap=0)
6.4 数据集生成
在本节中,我们定义了两个函数:
prompt 函数为 Google Gemini 创建一个提示,用于根据提供的文本块请求问答对。
import google.generativeai as genaiimport pandas as pd# Replace with your valid Google API keyGOOGLE_API_KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxx"# Prompt generator with an explicit request for structured outputdef prompt(text_chunk):return f"""Based on the following text, generate one Question and its corresponding Answer.Please format the output as follows:Question: [Your question]Answer: [Your answer]Text: {text_chunk}"""# Function to interact with Google's Gemini and return a QA pairdef generate_with_gemini(text_chunk:str, temperature:float, model_name:str):genai.configure(api_key=GOOGLE_API_KEY)generation_config = {"temperature": temperature}# Initialize the generative modelgen_model = genai.GenerativeModel(model_name, generation_config=generation_config)# Generate response based on the promptresponse = gen_model.generate_content(prompt(text_chunk))# Extract question and answer from response using keywordtry:question, answer = response.text.split("Answer:", 1)question = question.replace("Question:", "").strip()answer = answer.strip()except ValueError:question, answer = "N/A", "N/A" # Handle unexpected format in responsereturn question, answer
generate_with_gemini 函数与 Gemini 模型交互,并使用创建的提示生成 QA 对。
6.5 生成QA对
使用 process_text_chunks 函数,我们使用 Gemini 模型为每个文本块生成 QA 对。
def process_text_chunks(text_chunks:list, temperature:int, model_name=str):"""Processes a list of text chunks to generate questions and answers using a specified model.Parameters:- text_chunks: A list of text chunks to process.- temperature: The sampling temperature to control randomness in the generated outputs.- model_name: The name of the model to use for generating questions and answers.Returns:- A Pandas DataFrame containing the text chunks, questions, and answers."""results = []# Iterate through each text chunkfor chunk in text_chunks:question, answer = generate_with_gemini(chunk, temperature, model_name)results.append({"Text Chunk": chunk, "Question": question, "Answer": answer})# Convert results into a Pandas DataFramedf = pd.DataFrame(results)return df# Process the text chunks and get the DataFramedf_results = process_text_chunks(text_chunks=chunks,temperature=0.7,model_name="gemini-1.5-flash")df_results.to_csv("generated_qa_pairs.csv", index=False)
然后,这些结果将存储在 Pandas DataFrame 中。
6.6 加载数据集
接下来,我们将生成的 QA 对从 CSV 文件加载到 HuggingFace 数据集中 。我们确保数据的格式正确,以便进行微调。
from datasets import load_dataset# Load the CSV file into a Hugging Face Datasetdataset = load_dataset('csv', data_files='generated_qa_pairs.csv')def process_example(example, idx):return {"id": idx, # Add unique ID based on the index"anchor": example["Question"],"positive": example["Answer"]}dataset = dataset.map(process_example,with_indices=True ,remove_columns=["Text Chunk", "Question", "Answer"])
6.7 加载模型
我们从 HuggingFace 加载 BAAI/bge-base-en-v1.5 模型,确保选择合适的设备进行执行(CPU 或 GPU)。
import torchfrom sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformerfrom sentence_transformers.evaluation import (InformationRetrievalEvaluator,SequentialEvaluator,)from sentence_transformers.util import cos_simfrom datasets import load_dataset, concatenate_datasetsfrom sentence_transformers.losses import MatryoshkaLoss, MultipleNegativesRankingLossmodel_id = "BAAI/bge-base-en-v1.5"# Load a modelmodel = SentenceTransformer(model_id, device="cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
6.8 定义损失函数
我们配置了 Matryoshka 损失函数 ,指定了用于截断嵌入的维度。
# Important: large to smallmatryoshka_dimensions = [768, 512, 256, 128, 64]inner_train_loss = MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(model)train_loss = MatryoshkaLoss(model, inner_train_loss, matryoshka_dims=matryoshka_dimensions)
内部损失函数 MultipleNegativesRankingLoss(可参考:https://sbert.net/examples/sentence_transformer/training/matryoshka/README.html) 可帮助模型生成适合检索任务的嵌入。
6.9 定义训练参数
我们用来 SentenceTransformerTrainingArguments 定义训练参数。这包括输出目录、纪元数、批量大小、学习率和评估策略。
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformerTrainingArgumentsfrom sentence_transformers.training_args import BatchSamplers# define training argumentsargs = SentenceTransformerTrainingArguments(output_dir="bge-finetuned", # output directory and hugging face model IDnum_train_epochs=1, # number of epochsper_device_train_batch_size=4, # train batch sizegradient_accumulation_steps=16, # for a global batch size of 512per_device_eval_batch_size=16, # evaluation batch sizewarmup_ratio=0.1, # warmup ratiolearning_rate=2e-5, # learning rate, 2e-5 is a good valuelr_scheduler_type="cosine", # use constant learning rate scheduleroptim="adamw_torch_fused", # use fused adamw optimizertf32=True, # use tf32 precisionbf16=True, # use bf16 precisionbatch_sampler=BatchSamplers.NO_DUPLICATES, # MultipleNegativesRankingLoss benefits from no duplicate samples in a batcheval_strategy="epoch", # evaluate after each epochsave_strategy="epoch", # save after each epochlogging_steps=10, # log every 10 stepssave_total_limit=3, # save only the last 3 modelsload_best_model_at_end=True, # load the best model when training endsmetric_for_best_model="eval_dim_128_cosine_ndcg@10", # Optimizing for the best ndcg@10 score for the 128 dimension)
注意 :如果您正在使用 Tesla T4 并在训练期间遇到错误,请尝试注释掉 tf32=True 和 bf16=True 行以禁用 TF32 和 BF16 精度。
6.10 创建Evaluator
我们创建一个评估器来衡量模型在训练期间的性能。评估器使用 InformationRetrievalEvaluator 评估俄罗斯套娃损失中每个维度的模型的检索性能。
corpus = dict(zip(dataset['train']['id'],dataset['train']['positive'])) # Our corpus (cid => document)queries = dict(zip(dataset['train']['id'],dataset['train']['anchor'])) # Our queries (qid => question)# Create a mapping of relevant document (1 in our case) for each queryrelevant_docs = {} # Query ID to relevant documents (qid => set([relevant_cids])for q_id in queries:relevant_docs[q_id] = [q_id]matryoshka_evaluators = []# Iterate over the different dimensionsfor dim in matryoshka_dimensions:ir_evaluator = InformationRetrievalEvaluator(queries=queries,corpus=corpus,relevant_docs=relevant_docs,name=f"dim_{dim}",truncate_dim=dim, # Truncate the embeddings to a certain dimensionscore_functions={"cosine": cos_sim},)matryoshka_evaluators.append(ir_evaluator)# Create a sequential evaluatorevaluator = SequentialEvaluator(matryoshka_evaluators)
6.11 在微调之前评估模型
在微调之前,我们会评估基本模型以获得基准性能。
results = evaluator(model)for dim in matryoshka_dimensions:key = f"dim_{dim}_cosine_ndcg@10"print(f"{key}: {results[key]}")
6.12 定义Trainer
我们创建一个 SentenceTransformerTrainer 对象,指定模型、训练参数、数据集、损失函数和计算器。
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformerTrainertrainer = SentenceTransformerTrainer(model=model, # our embedding modelargs=args, # training arguments we defined abovetrain_dataset=dataset.select_columns(["positive", "anchor"]),loss=train_loss, # Matryoshka lossevaluator=evaluator, # Sequential Evaluator)
6.13 开始微调
trainer.train() 方法启动微调过程,使用提供的 data 和 loss 函数更新模型的权重。
# start trainingtrainer.train()# save the best modeltrainer.save_model()
训练完成后,我们将性能最佳的模型保存到指定的输出目录中。
6.14 微调后评估
最后,我们加载微调后的模型,并使用相同的评估器对其进行评估,以衡量微调后的性能改进。
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformerfine_tuned_model = SentenceTransformer(args.output_dir, device="cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")# Evaluate the modelresults = evaluator(fine_tuned_model)# Print the main scorefor dim in matryoshka_dimensions:key = f"dim_{dim}_cosine_ndcg@10"print(f"{key}: {results[key]}")

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献25条内容
已为社区贡献25条内容





所有评论(0)