Spring处理请求的过程详细版
Target表示该注解的作用范围,此处指作用于方法上@Retention表示该注解在什么时候对程序可见,此处是运行时@Document表示该注解会出现在JavaDoc中@Override//1.判断是否Handler类方法if(!LOGGER.info("不是HandlerMethod类型,则无需检查");//2.强制转型//3.判断该Handler的方法上是否存在注解if(!//不存在Login
目录
2、SpringMVC首先通过对Dispatcher配置,处理"/"的请求
5、HandlerExectionChain便利interceptor[]
7、根据Handler获取对应的HandlerAdapter
为什么不直接用Handler而是包一层HandlerAdapter(从反射的角度理解)?
Spring总体结构(简述)
spring处理结构
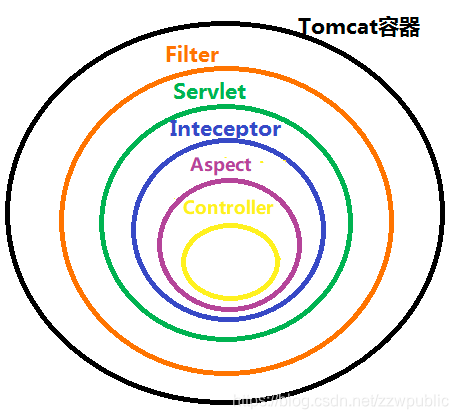
- Filter(过滤器):属于Servelt规范,最早被触发,用于全局请求预处理,常用跨域处理、日志打印、请求加密解密,权限校验。
- Servlet(DispatcherServlet):SpringMVC的所有请求会转到这里,用doDispatch()方法找到适配器等
- Interceptor(拦截器):不依赖Servlet容器,处理链的一部分(HandlerExecutionChain),可以在Controller前后进行处理。
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { public boolean preHandle(...) // 请求前(可中断) public void postHandle(...) // Controller 返回后 public void afterCompletion(...)// 完成后(资源清理) } - Aspect(切面):基于动态代理,横切增强任何Bean的方法调用,包括Controller、Service等,常用于日志、权限、事务等。
@Aspect @Component public class LogAspect { @Before("execution(* com.xxx.controller..*(..))") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("切面:调用前"); } } - Controller(控制器):执行业务逻辑的地方,被HandlerAdapter调用。
- 特别注意易搞混!:Handler是被@GetMapping等注解标注的一个方法,而不是整个Controller类,HandlerMapping是将对应的方法转为已给HandlerMethod的对象并与url进行映射。但调用对应HandlerMethod的时候是需要拿到对应Controller的实例的。
路径匹配规则
1、精准匹优先(/user/list)
2、路径变量其次(/user/{id})
3、单通配符(/user/*)
4、双通配符(/user/**)
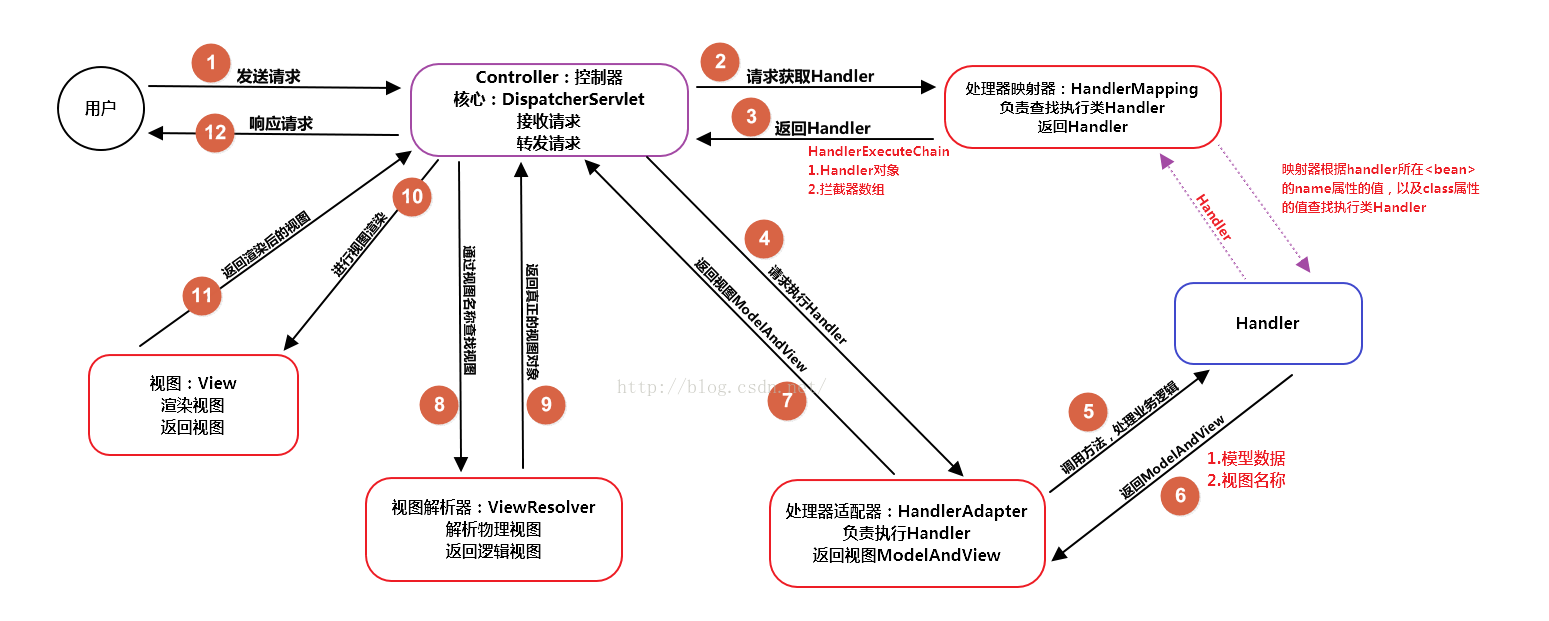
Spring处理Http请求流程(代码详述)
1、Filter过滤器
由Servlet容器执行,例如Tomcat。例如下述自定义过滤器。
@WebFilter("/*")
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("👉 Filter before DispatcherServlet");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
System.out.println("👈 Filter after DispatcherServlet");
}
}
2、SpringMVC首先通过对Dispatcher配置,处理"/"的请求
spring.mvc.servlet.path=/之后SpringBoot的配置类 DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@Conditional({DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class})
@ConditionalOnClass({ServletRegistration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class})
@Import({DispatcherServletConfiguration.class})
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
protected DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration() {
}
@Bean(
name = {"dispatcherServletRegistration"}
)
@ConditionalOnBean(
value = {DispatcherServlet.class},
name = {"dispatcherServlet"}
)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet, WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet, webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName("dispatcherServlet");
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
Objects.requireNonNull(registration);
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
}
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@Conditional({DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class})
@ConditionalOnClass({ServletRegistration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class})
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
protected DispatcherServletConfiguration() {
}
@Bean(
name = {"dispatcherServlet"}
)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
this.configureThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties, dispatcherServlet);
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(webMvcProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
private void configureThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) {
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean({MultipartResolver.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
name = {"multipartResolver"}
)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
return resolver;
}
}上述语句使得所有的请求都打到DispatcherServlet上:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
3、进入DispatcherServlet处理请求
DispatcherServlet#doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 检查是否是Multipart请求
processedRequest = this.checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = processedRequest != request; // 标记是否为multipart请求
// 获取请求的处理器
mappedHandler = this.getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
this.noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 获取处理器适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 处理GET或HEAD请求的缓存
String method = request.getMethod();
if (HttpMethod.GET.matches(method) || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if ((new ServletWebRequest(request, response)).checkNotModified(lastModified) && HttpMethod.GET.matches(method)) {
return; // 如果缓存未修改,直接返回
}
}
// 执行前置处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 执行请求处理并返回视图
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 检查是否为异步请求
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 设置视图名称并执行后置处理
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
} catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new ServletException("Handler dispatch failed: " + err, err);
}
// 处理请求结果
this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
} finally {
// 异步请求的后续操作
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
asyncManager.setMultipartRequestParsed(multipartRequestParsed);
} else if (multipartRequestParsed || asyncManager.isMultipartRequestParsed()) {
this.cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}处理流程简述
- 判断是否multipart请求:multipart请求通常包含文件数据 需要较大的内存和处理能力 尤其是当文件很大时。因此,提前检查是否是multipart请求可以避免不必要的解析操作,节省系统资源。
- 获取处理器Handler,从HandlerMapping中获取执行链,包括1、Handler对象 2、拦截器数组Interceptor[]
- 获取适配器HandlerAdapter
- 处理GET或HEAD请求。因为这两类请求通常用于获取数据而不做什么改动,因此对这两种请求进行缓存,有效提高请求效率。
- 利用处理器适配器HandlerAdapter来执行Handler方法并返回ModelAndView给前端
4、根据HandlerMapping#getHandler()来找到对应的执行链(HandlerExecutionChain),包括Handler和Interceptor[]数组,(Interceptor[]是通过InterceptorRegistry类维护的,并根据HandlerMethod的url返回对应匹配的Interceptor[])
首先Spring启动时会扫描所有@Controller,将所有带有@RequestMapping注解的方法扫描出来建立一张URL->HandlerMethod的映射表。
注意,每个HandlerMethod对应的HandlerExecutionChain下的Interceptor[]是不一样的。可以参考下面的自定义注解实现登录认证的实例。因为每个Interceptor都可以被指定需要拦截的路径和不需要拦截的路径。
InterceptorRegistry会根据当前HandlerMethod对应的url去match出对应的Interceptor[]。
特别注意:Handler(HandlerMethod)是被@GetMapping等注解标注的一个方法,而不是整个Controller类,HandlerMapping是将对应的方法转为已给HandlerMethod的对象并与url进行映射。但调用对应HandlerMethod的时候是需要拿到对应Controller的实例的。
路径匹配规则
1、精准匹优先(/user/list)
2、路径变量其次(/user/{id})
3、单通配符(/user/*)
4、双通配符(/user/**)
注意单通配符只能匹配单层路径,比如(/user/*)能匹配(/user/abc)但不能匹配(/user/a/b),双通配符可以匹配任意层请求。
5、HandlerExectionChain便利interceptor[]
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
this.applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);首先mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)这个方法,调用所有拦截器的preHandle(),运行所有拦截器的方法,只要其中一个返回了false,Controller就不会执行。例如,登录拦截器发现未登录。
public boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); // 执行 afterCompletion()
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
接着ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())执行Handle的业务方法。
最后mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv),调用所有interceptor的postHandle()方法。
6、关于切面@Aspect
与interceptor和HandlerAdapter不同,切面基于动态代理实现,实在方法层面实现的拦截。例如:
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Before method");
Object result = pjp.proceed(); // 执行目标方法
System.out.println("After method");
return result;
}
}
Spring 会为目标类生成一个代理类(JDK 动态代理或 CGLIB 子类),在调用该方法时会先进入代理类然后在执行方法。
7、根据Handler获取对应的HandlerAdapter
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
//用来判断能否处理某个请求
@Override
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return handler instanceof HandlerMethod;
}
//用来处理请求
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
// 强转为 HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
// 通过反射调用 controller 方法
Object result = handlerMethod.getMethod().invoke(handlerMethod.getBean());
// 封装为 ModelAndView 返回
return new ModelAndView("viewName", "data", result);
}
}HandlerAdapter主要实现#supports和#handler方法。
利用support方法的InstanceOf来找对应的HandlerAdapter,然后调用方法返回ModelAndView
一些问题
为什么不直接用Handler而是包一层HandlerAdapter(从反射的角度理解)?
首先利用HanlerMapping根据路径获取到了Handler,然后用instanceOf来找对应的HandlerAdapter。
下面为简单的代码逻辑。
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
//用来判断能否处理某个请求
@Override
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return handler instanceof HandlerMethod;
}
//用来处理请求
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
// 强转为 HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
// 通过反射调用 controller 方法
Object result = handlerMethod.getMethod().invoke(handlerMethod.getBean());
// 封装为 ModelAndView 返回
return new ModelAndView("viewName", "data", result);
}
}
上述为一个HandlerAdapter的简单代码。现在假设我们有两个HandlerAdapter,分别是MyControllerHandlerAdapter和MyHttpHandlerAdapter,他们两个都被注册到DispatcherSimulator方法的HandlerAdapters数组中。
public class DispatcherSimulator {
// 模拟注册的适配器(像 Spring 一样有多个适配器)
private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>();
public DispatcherSimulator() {
handlerAdapters.add(new MyControllerHandlerAdapter());
handlerAdapters.add(new MyHttpHandlerAdapter());
}
// 核心调度逻辑
public void dispatch(Object handler) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
adapter.handle(handler);
return;
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("❌ 没有找到合适的 HandlerAdapter");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DispatcherSimulator dispatcher = new DispatcherSimulator();
// 模拟两种请求类型
Object controllerHandler = new MyControllerHandler();
Object httpHandler = new MyHttpHandler();
dispatcher.dispatch(controllerHandler); // 👉 MyControllerHandler: 处理请求
dispatcher.dispatch(httpHandler); // 👉 MyHttpHandler: 执行 service()
}
}
从上面的代码可以看到,在有新请求到达时,会依次调用HandlerAdapters数组中每个HandlerAdapter的support方法来判断是否能处理该请求(),如果能处理则调用对应HandlerAdapter的handle方法。
Filter,Interceptor和Aspect的区别?
|
机制 |
执行层面 |
拦截方式 |
作用域 |
常见用途 |
|
Filter |
Servlet容器(Tomcat) |
doFilter()+chain.doFilter() |
所有请求 |
权限、跨域、编码、日志 |
|
Interceptor |
SpringMVC(DispatcherServlet) |
HandlerExectionChain内数组遍历 |
Handler请求,如Controller |
登录校验、权限控制、计时 |
|
Aspect |
Spring Bean |
生成目标方法和类的代理类 |
代理的方法 |
日志,事务,统一异常处理 |
示例:自定义注解实现登录认证(通过Interceptor)
1、首先自定义出注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface LoginRequired {
boolean required() default false;
}
@Target表示该注解的作用范围,此处指作用于方法上
@Retention表示该注解在什么时候对程序可见,此处是运行时
@Document表示该注解会出现在JavaDoc中
2、定义Interceptor
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor{
private static final Logger LOGGER= LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoginInterceptor.class);
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//1.判断是否Handler类方法
if(!(handler instanceof HandlerMethod)){
LOGGER.info("不是HandlerMethod类型,则无需检查");
return true;
}
//2.强制转型
HandlerMethod method = (HandlerMethod)handler;
//3.判断该Handler的方法上是否存在注解
boolean hasLoginAnnotation=method.getMethod().isAnnotationPresent(LoginRequired.class);
if(!hasLoginAnnotation){
//不存在LoginRequired注解,则直接通过
LOGGER.info("不存在LoginRequired注解,则直接通过");
return true;
}
LoginRequired loginRequired=method.getMethod().getAnnotation(LoginRequired.class);
//2.required=false,则无需检查是否登录
if(!loginRequired.required()){
LOGGER.info("required=false,则无需检查是否登录");
return true;
}
//3.登录状态检查,使用response返回指定信息
LOGGER.info("required=true,需检查是否登录");
response.getWriter().append("you need login!");
return false;
}
}
- 首先,判断当前传入的handler是否是HandlerMethod(即是否是Controller类中被指定了url的方法,用@GetMapping等注解了的方法会被HandlerMapping封装为一个HandlerMethod对象)。(例如,存在静态资源,Spring处理器等,这些的Handler也可能为其他类型,比如 ResourceHttpRequestHandler,则会直接跳出 )。
- 判断handler为HandlerMethod类型后,将传入的Object类型的handler转为HandlerMethod类型。
- 利用反射机制,method.getMethod()返回一个Java.lang.reflect.Method的对象,用于获取方法的元信息(包括注解、参数、返回值类型等),之后判断我们写的注解是否在方法上出现。
- 若出现了我们的注解,则走一遍登录认证的逻辑。
3、将定义的Interceptor注册到InterceptorRegistry 中。InterceptorRegistry 会负责将这些拦截器注册到请求的 HandlerExecutionChain的Interceptor[] 中
@Configuration
public class LoginConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
.addPathPatterns("/**") // 拦截所有路径
.excludePathPatterns("/login", "/register"); // 排除登录/注册接口
}
}
4、使用上自定义注解
@RestController
public class LoginAction {
private static final Logger LOGGER= LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoginAction.class);
/**
* 首页数据接口,无需登录
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
/**
* 签到接口(需要在登录状态下)
* @param request
* @return
*/
@LoginRequired(required = true)
@RequestMapping("signIn")
public String signIn(HttpServletRequest request){
//进行签到逻辑
return "success";
}
}

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容





所有评论(0)