大模型笔记9 Data Synthesis相关论文
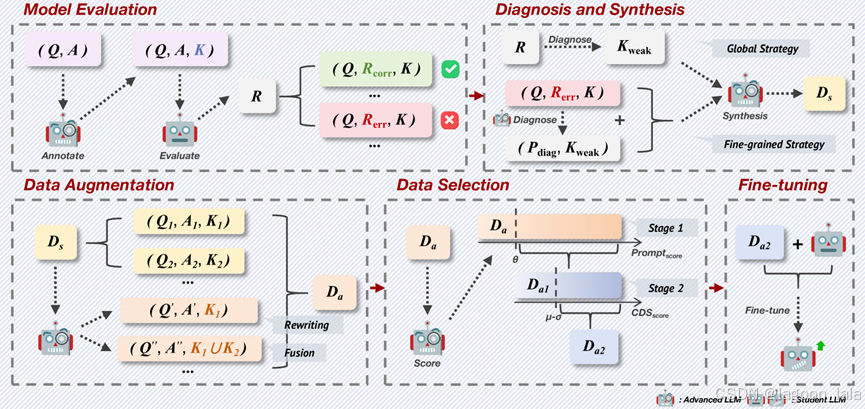
CDS: Knowledge Component-Driven Data Synthesis Guided by Cognitive Diagnosis TheoryCDTKCsCDS方法流程1.模型评估KC标注流程第一步Prompt第二步Prompt构建Q-KC矩阵模型评估与错误案例收集2.诊断与数据合成全局策略细粒度策略全局合成的prompt细粒度策略prompt3.数据增强+数据选择数据增强
目录
CDS: Knowledge Component-Driven Data Synthesis Guided by Cognitive Diagnosis Theory
CDS: Knowledge Component-Driven Data Synthesis Guided by Cognitive Diagnosis Theory
认知诊断驱动的数据合成方法 (CDS)
CDS: Knowledge Component-Driven Data Synthesis Guided by Cognitive Diagnosis Theory
CDT
将CDT(认知诊断理论)应用于LLM:从将LLM的错误仅仅视为统计偏差,转变为将其解读为类似于人类学习过程中特定“知识缺口”的指标。传统上,LLM的改进可能侧重于架构调整或大规模、未经区分的数据。CDT则引入了一种更结构化,近乎“教学法”的途径 。如果一个LLM因为对“分数”(一个KC)理解不足而在数学问题上失败,CDS的目标是提供关于分数的有针对性的“课程”(合成数据),而不是仅仅提供更多笼统的数学问题。这是一种更具可解释性,也可能更高效的模型改进方式。虽然教育中的CDT通常处理概率性的掌握程度,但该论文在全局策略中初步采用了简化的确定性模型(DINA假设),这对于将这些概念应用于LLM是一个务实的选择,因为LLM的真实“认知状态”是未知的。DINA模型的二元掌握假设(对一个项目的正确回答意味着掌握了该项目相关的所有KCs,错误回答则意味着未掌握任何相关KCs )简化了LLM的诊断过程。尽管这可能过分简化了真实的“理解”,但它为识别在数据集中持续存在问题的KCs提供了一种计算上可行的方法,使得CDT框架能够在这个新情境下得以应用。
KCs
知识组件 (KCs) 在细粒度模型画像中的关键作用
知识组件(KCs)被定义为执行任务所需的特定子技能、概念或能力 。在CDS的框架下,LLM所犯的错误被归因于一个或多个这些KCs的缺陷 。KCs使得我们能够对模型能力进行细致的刻画,而不是给出一个笼统的“好”或“坏”的评价 。
论文强调了KC粒度的重要性:它们不应过于宽泛(这将缺乏信息量),也不应过于狭窄(这可能导致KC数量爆炸和每个KC的数据稀疏)。理想的KC应具备“相互独立、完全穷尽且粒度适中”的特性 。论文的表4( P13)为编码、数学以及学术考试中的多个科目提供了丰富的KC示例,直观地展示了这一概念的实际应用。例如,“数学”领域的KCs包括“基本算术运算”、“代数表达式”、“面积”、“概率”等。
KCs的定义和质量可以说是实现CDS最关键(也最具挑战性)的方面。定义不佳的KCs将导致有缺陷的诊断和无效的合成数据。整个CDS流程(诊断、合成、选择)都依赖于KCs 。
CDS方法流程
步骤:
模型评估、诊断与数据合成、数据增强和数据选择
1.模型评估
使用更高级的“教师”LLM (Ma)标注相关KCs的基准数据集来评估“学生”LLM (Ms)。
KC标注流程
1. 粗略标注与KC集合优化
首先,Ma 对目标数据集 Dtarget 进行初步的粗略KC标注。
从所有样本中聚合初始的KC标签集合(不同样本会获得不同的知识点label, 这些label可以组成一个集合)。然后,这个集合会由 Ma 进行优化,以确保KCs“相互独立、完全穷尽且粒度适中”。由此产生最终的KC集合 K 。
2. 约束性标注
Ma 重新对数据集进行标注,但这次是有约束的:每个问题 q 所标注的KCs集合 Kq 必须来源于阶段1优化后的KC集合 K。这样就得到了标注好的基准数据集 Dtarget∗={d∗∣d∗=(q,a_ref,Kq),Kq⊊K} 。
第一步Prompt
原始数据集进行知识点粗标记
|
prompt4extract = """You are an educational AI designed to help students improve their math skills. Your task is categorizing the math problem based on the primary knowledge points it assesses. Please keep the following requirements in mind: ### Requirements: 1. The knowledge points should be as independent as possible, without overlapping. 2. The knowledge points should not be too granular; maintain a reasonable level of generalization. 3. Each problem should be labeled with no more than 4 primary knowledge points. 4. Use simple noun phrases to summarize the knowledge points. 5. The format for returning the knowledge points should be in the form of a list, e.g., [Addition, Multiplication]. ### Example Knowledge Points: - Addition - Subtraction - Multiplication - Division - Mixed Operations - Algebraic Expressions - Linear Equations - Inequalities - Area - Perimeter - Volume - Angles - Properties of Shapes - Prime and Composite Numbers - Factors and Multiples - Mean, Median, Mode - Probability - Data Analysis - Permutations and Combinations - Length Units - Volume Units - Weight Units - Time Units - Ratios and Proportions ### Math Problem {QUESTION} {ANSWER} Please categorize the math problem according to these requirements.""" |
第二步Prompt
原始数据集进行知识点细标记
|
template4tagging = Template( """You are an educational AI designed to help students improve their math skills. Your task is categorizing the math problem based on the primary knowledge points it assesses. Please keep the following requirements in mind: ### Requirements: 1. Select the appropriate knowledge points from the list provided under ### Knowledge Points. 2. Label each problem with no more than 4 primary knowledge points. 3. Return the knowledge points in a list format, e.g., [Addition, Multiplication]. ### Knowledge Points: {% for KNOWLEDGE_POINT in KNOWLEDGE_POINTS %}- {{ KNOWLEDGE_POINT }} {% endfor %} ### Math Problem {{ QUESTION }} {{ ANSWER }} Please categorize the math problem according to these requirements.""") |
构建Q-KC矩阵
(Question-Knowledge Component Matrix)
Dtarget∗ 被标注了KCs -> Q-KC矩阵: 用于全局策略中计算KC准确率和频率
Q⋅KC∈{0,1}^∣Dtarget∣×∣K∣
矩阵中的一个元素 Q⋅KC[i,j] 如果问题 qi 评估了知识组件 kcj (即 kcj∈Kqi),则为1,否则为0 。
模型评估与错误案例收集
使用标注好的基准数据集 Dtarget∗ 来评估学生模型 Ms。关键在于收集所有错误的案例 Derr={(q,rerr,Kq)},其中 rerr 是模型对问题 q 的错误回答 。
这些错误的回答及其相关的KCs是诊断策略的输入。收集所有错误案例而非仅仅抽样,能够实现全面的诊断,特别是对于在单个错误上操作的细粒度策略而言。
2.诊断与数据合成
诊断过程旨在分析从评估结果中得出的KC掌握情况画像。
两种从不同诊断角度出发的诊断-合成策略:
1. 全局策略:数据集层面的KC掌握度视图
全局策略的优势在于识别广泛的、系统性的弱点或对某些KCs的接触不足。虽然一个问题包含有多个知识点, 对不同知识点掌握可能不同, 但对于全局视角,这种聚合可能会平滑掉个体案例的复杂性,从而揭示整体趋势。
2. 细粒度策略:问题层面的错误分析与CoT增强合成
全局策略
诊断:
遵循DINA认知诊断框架的假设:对问题 qi 的正确回答意味着掌握了其所有相关的KCs,而错误的回答则意味着未掌握任何相关的KCs 。
基于此,计算KC特定的指标如准确率, 准确率低于阈值 δa 或频率低于阈值 δf 的KCs被识别为薄弱掌握的KCs (Kw) 。
合成:
高级模型 Ma 针对 Kw 中的每一个薄弱KC生成新的数据 (q,a,Kq={kc}) 。合成时prompt中避免使用原始问题,仅将目标KC作为输入。
细粒度策略
诊断
该策略针对 Derr 中的每一个错误案例,在单个问题层面进行详细诊断 。
高级模型 Ma 充当“诊断器”,分析错误并列出未掌握的KCs。
分析学生模型在特定问题上的解决过程 (rerr),以识别由此特定案例暴露出的潜在薄弱KCs (Kw)。这个诊断分析过程本身被记录为 Pdiag 。此诊断步骤的prompt
合成
生成合成数据的prompt包括诊断分析 (Pdiag) 与原始问题 (q)、错误回答 (rerr) 以及识别出的薄弱KCs (Kw)
它们相结合,形成一个长的思维链 (Chain-of-Thought, CoT) 提示,用于在合成阶段指导 Ma 。这旨在激发 Ma 进行更深层次的推理,从而生成更高质量和更具针对性的合成数据 。此合成步骤的提示明确包含了一个“{{ process of diagnosis }}”(诊断过程)的占位符。
细粒度策略利用了高级LLM的分析能力,而不仅仅是数据生成能力。
全局合成的prompt
诊断部分未使用llm, 合成部分prompt:
|
prompt4kps = """Based on the given knowledge points, create new, more challenging math questions that emphasize understanding and applying these knowledge points. ### Given Knowledge Points {kps} ### Requirements: - Create clear and high-quality questions. - Ensure that the new questions comprehensively cover all the given knowledge points. - Provide accurate mathematical calculations and detailed steps in your samples. - Ensure that the difficulty level of the new questions is appropriate for {DIFFICULTY} mathematics. - Ensure the final answer is explicitly presented with "So, the final answer is [NUMBER]". ### Return Format: Return your samples in the following format: **Question**: [QUESTION] **Answer**: >> [ANSWER] << Please follow the requirements and generate {X} samples.""" |
细粒度策略prompt
诊断
|
template4cognitive = Template( """You are an educational AI designed to help students improve their math skills by performing cognitive diagnosis on their incorrect answers and identifying their knowledge mastery levels. ### Knowledge Points: {% for KNOWLEDGE_POINT in KNOWLEDGE_POINTS %}- {{ KNOWLEDGE_POINT }} {% endfor %} ### Return Format: Return your cognitive diagnosis results in the following format: - Unmastered Knowledge Points: [UNMASTERED_KNOWLEDGE_POINTS] - Mastered Knowledge Points: [MASTERED_KNOWLEDGE_POINTS] e.g.: - Unmastered Knowledge Points: [Equations, Unit Conversion] - Mastered Knowledge Points: [Addition, Multiplication] ### Question given to the student: {{ QUESTION }} ### Student's incorrect answer: {{ WRONG_ANSWER }} ### Requirements: - Perform a clear and detailed cognitive diagnosis. - Diagnose the student's incorrect answer step-by-step. - Ensure the identified knowledge points are from those provided in the ### Knowledge Points. - Do not include knowledge points that are not involved in the question in the Unmastered Knowledge Points. Please follow the requirements and generate your cognitive diagnosis.""") |
合成
|
template4cogsynthesis = Template("""Based on the results of the previous cognitive diagnosis, create new, more challenging questions focusing on the student's unmastered knowledge points to reinforce their understanding. ### Requirements: - Create clear and high-quality questions. - Provide accurate mathematical calculations and detailed steps in your samples. - Ensure that the new questions have a greater focus on the unmastered knowledge points. - Ensure that the difficulty level of the new questions is appropriate for {{ DIFFICULTY }} mathematics. {% if UNMASTERED %} ### Unmastered Knowledge Points: {{ UNMASTERED }} {% endif %} ### Return Format: Return your samples in the following format: **Question**: [QUESTION] **Answer**: >> [ANSWER] << Please follow the requirements and generate {{ X }} samples.""") |
3.数据增强+数据选择
增强与筛选合成数据 – 最大化质量与多样性
数据增强技术
1. KC约束的重写 (KC-Constrained Rewriting):传统的数据重写方法+约束:重写后的数据必须覆盖与原始合成样本相同的KCs 。
2. 多KC融合 (Multi-KC Fusion):选取成对的合成数据样本,并提示 Ma 生成包含两个原始样本中KCs的新数据 。
这旨在增加数据的复杂性和全面性,模拟需要多种技能协同解决的问题。为了避免过度复杂,对每个融合样本中的最大KC数量进行了限制 。
两阶段数据选择流程
阶段1:高级LLM过滤
评分低于阈值过滤掉
Ma 根据多个标准(如正确性(最高优先级)、KC相关性(次高优先级)、清晰度、简洁性和结构等)对每个合成样本进行评分 。低于某个质量阈值的样本将被过滤掉。
阶段2:CDSscore筛选高影响力数据
CDSscore 来选择最有可能解决学生LLM弱点的数据
包含更多KCs(复杂度更高)的数据,以及包含学生LLM初始准确率 (Acc(kcj)) 较低或在增强合成集中频率 (Freqs(kcj)) 较低的KCs的数据,更为有效 。
一个KC的“显著性”V(kcj) 计算如下:
V(kcj)=w1log(Acc(kcj)+ϵ)+w2log(Freqs(kcj)+ϵ) (公式5)
其中 w1 和 w2 是平衡权重,ϵ 是一个避免对数零的小常数。
一个数据样本 da 的 CDSscore 是其包含的所有KCs的 V(kcj) 之和:
CDSscore(da)=∑kcj∈KqV(kcj) (公式6)
最终保留 CDSscore(di)>μ−σ (均值减一倍标准差)的样本用于微调 。
数据增强prompt
KC约束的prompt
|
prompt4kps = """Based on the given knowledge points, create new, more challenging math questions that emphasize understanding and applying these knowledge points. ### Given Knowledge Points {kps} ### Requirements: - Create clear and high-quality questions. - Ensure that the new questions comprehensively cover all the given knowledge points. - Provide accurate mathematical calculations and detailed steps in your samples. - Ensure that the difficulty level of the new questions is appropriate for {DIFFICULTY} mathematics. - Ensure the final answer is explicitly presented with "So, the final answer is [NUMBER]". ### Return Format: Return your samples in the following format: **Question**: [QUESTION] **Answer**: >> [ANSWER] << Please follow the requirements and generate {X} samples.""" |
KC融合的prompt(数学任务图13,编码任务图14 )
|
prompt4more = """Based on the provided math question example, create new, more challenging math questions. ### Requirements: - Create clear and high-quality questions. - Provide accurate mathematical calculations and detailed steps in your samples. - Generate questions with varying difficulty levels (e.g., junior high, senior high). - Ensure that the generated question examine the same knowledge points as the example math question, but avoid simple variable replacement. ### Example: **Question**: {question} **Answer**: {answer} **Knowledge Points**: {label} ### Return Format: Return your samples in the following format: **Question**: [QUESTION] **Answer**: >> [ANSWER] << Please follow the requirements and generate {X} samples.""" |
数据选择prompt
评分prompt
|
prompt4filter = """Here are the math problem and the answer in a question-answer format. **Question**: {question} **Answer**: {answer} **Knowledge Points**: {label} As a strict evaluator, please follow these steps when scoring: ## Correctness of the Answer (Top Priority 1): If the answer is incorrect, assign a score of 0 and briefly explain. No further evaluation is needed. If the answer is correct, proceed to the next step. ## Relevance to Knowledge Points (Top Priority 2): Does the problem assess the specified knowledge points? If no, assign a score of 0 with an explanation. If yes, continue. ## Evaluation of Other Dimensions: ### Clarity: Is the reasoning clear and easy to follow? ### Conciseness: Is the explanation succinct without unnecessary details? ### Format and Structure: Is the response well-structured and correctly formatted? After considering these factors, provide a single score (0-10) for the overall quality, with correctness and knowledge point relevance as the highest priorities. Use the format: Score: <score>||<explanation>.""" |
实验设置
任务、数据集与模型
CDS方法在三个不同的任务上进行了评估:数学推理、编码和学术考试 。
1.数据集
为每个任务都使用了领域内(In-Domain, ID)和领域外(Out-of-Domain, OOD)数据集,以评估模型的泛化能力:
数学:GSM8k (ID), GSM8k-PLUS (OOD)。
编码:MBPP (ID), HumanEval (OOD)。
学术考试:GAOKAO-Bench (ID), GAOKAO-Bench-Updates (OOD)。
对于GAOKAO任务,KC标注来源于教学大纲的章节标题 。
高考数据集:
https://github.com/OpenLMLab/GAOKAO-Bench-Updates
GitHub中3个文件夹包含data:
work_on_coding, work_on_fact, work_on_math
2.模型
学生LLM(待提升的模型):Llama3-8B-Instruct 和 Qwen1.5-7B-Chat。
高级LLM(用于诊断、合成、阶段1评分):Qwen2-72B-Instruct 。
3.训练/推理设置
实验采用了标准的训练和推理设置,包括使用LoRA进行微调,AdamW优化器,特定的批量大小、序列长度,以及解码策略(评估时使用贪婪解码,生成时使用温度和top-p采样)。所有推理均在0-shot设置下进行。
KC表
表 4 中所示的以下知识组件 (KC) 用于各种任务:
|
Task |
Knowledge Components |
|
Coding |
Basic Data Types, Bitwise Operations, Boolean Logic, Class Definitions, Comparison Operators, Conditional Statements, Copying and Deep Copying, Dictionary Operations, Dynamic Programming, Exception Handling, Finding Min and Max, Heap Operations, Importing Libraries and Modules, Indexing and Slicing, Lambda Functions, List and Array Operations, Looping, Map Function, Recursion, Regular Expressions, Search Algorithms, Sorting Algorithms, Stacks and Queues, String Operations, Summation, Tree Structures, Tuple Operations, Type Checking and Conversion |
|
Math |
Basic Arithmetic Operations, Decimal and Fraction Operations, Mixed Operations, Prime and Composite Numbers, Factors and Multiples, GCD and LCM, Algebraic Expressions, Equations, Inequalities, Basic Geometry, Area, Perimeter, Volume, Angles, Coordinates, Mean, Median, Mode, Probability, Permutations, Combinations, Financial Calculations, Unit Conversion, Time and Date Calculations, Speed, Distance, and Time, Measurement, Money, Ratio and Proportion, Bar Graphs, Line Graphs, Number Sequences, Word Problems, Linear Equations, Simple Algebra, Pattern Recognition, Mathematical Logic, Shapes and Spatial Understanding, Symmetry, Congruence, Units of Measurement, Temperature, Length, Mass, Capacity |
|
Exams |
Biology: Protein and Nucleic Acid Structure, Sugar and Lipid Types and Functions, Water and Inorganic Salts, Cell Theory, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, Cell Membrane Structure, Organelles Structure and Function, Nucleus Structure and Function, Substance Transport Across Cell Membrane, Enzyme Role in Metabolism, ATP Metabolism, Photosynthesis Process, Environmental Impact on Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration, Cell Growth and Division, Cell Differentiation, Cell Aging and Apoptosis, Cancer Cells and Prevention, Meiotic Division, DNA Structure and Replication, Gene Transcription and Translation, Mendel’s Laws, Sex-linked Inheritance, Gene Mutation, Transgenic Food Safety, Human Genetic Diseases, Evolution Theory, Plant Hormones, Nervous and Hormonal Regulation, Nerve Impulse Transmission, Homeostasis, Immune System Role, Population and Community, Ecosystem Structure and Function, Ecosystem Stability, Biodiversity Conservation, Plant Growth Regulators, Yeast Respiration.Chemistry: Physical vs Chemical Changes, Acids, Bases, Salts and Oxides, Element Symbols, Valency and Formulas, Atomic and Molecular Masses, Law of Mass Conservation, Chemical Reactions, Molar Mass and Volume Calculations, Solubility and Concentration, Colloids and Solutions, Periodic Table Structure, Element Trends, Chemical Bonds, Oxidation-Reduction Reactions, Heat of Reactions, Electrochemistry, Reaction Rate and Activation Energy, Chemical Equilibrium, Electrolytes and Conductivity, pH Calculation, Ionization and Hydrolysis, Organic Compounds, Polymer Chemistry, Laboratory Safety, Gas Production and Separation, Chemical Analysis, Concentration Calculations.Geography: Earth’s Position in Space, Solar Influence, Earth’s Movements and Seasons, Earth’s Layers, Earth Material Cycles, Surface Changes, Atmospheric Heating, Wind and Pressure Systems, Climate and Weather Systems, Water Cycle, Ocean Currents, Geography and Environment, Climate Change, Natural Resources, Natural Disasters, Population Growth, Migration, Urbanization, Agricultural and Industrial Location, Environmental Impact, Geography of Resources, Transportation Systems, Human-Earth Relationships, Sustainability, Green Development, Remote Sensing, Geographic Information Systems, GPS and Navigation, Digital Earth.History: Ancient Chinese Political Systems, Shang and Zhou Dynasties, Qin Centralization, Han to Yuan Political Evolution, Ming and Qing Monarchy, Ancient Chinese Economy, Agricultural Systems, Handicraft and Commerce, Capitalism Emergence, Cultural Evolution, Hundred Schools of Thought, Confucianism, Neo-Confucianism, Chinese Scientific and Technological Achievements, Ancient Greek and Roman Political Systems, Athenian Democracy, Roman Law, Renaissance, Enlightenment, Industrial Revolution, World War Effects, Cold War and Bipolarity, Globalization, WTO and China’s Role, Modern Chinese Politics, Reform and Opening-up, Scientific and Technological Development in China, Modern Chinese Education and Culture. Math: Basic Arithmetic Operations, Decimal and Fraction Operations, Prime and Composite Numbers, Factors and Multiples, GCD and LCM, Algebraic Expressions, Equations, Inequalities, Geometry, Area, Perimeter, Volume, Angles, Coordinates, Mean, Median, Mode, Probability, Permutations, Combinations, Financial Calculations, Unit Conversion, Time and Date Calculations, Speed, Distance, Time, Measurement, Fractions, Decimals, Ratio, Proportion, Bar Graphs, Line Graphs, Probability Theory, Number Sequences, Word Problems, Time Tables, Integer Operations, Linear Equations, Simple Algebra, Pattern Recognition, Mathematical Logic, Shapes and Spatial Understanding, Symmetry, Congruence, Binomial Theorem, Conic Sections.Physics: Motion of Particles, Newton’s Laws, Mechanical Energy, Projectile and Circular Motion, Law of Gravitation, Electric Field, Circuits, Magnetic Field, Electromagnetic Induction, AC, Kinetic Theory of Gases, States of Matter, Thermodynamics, Vibration and Waves, Electromagnetic Waves, Light, Relativity, Reference Frames, Linear Motion, Friction, Hooke’s Law, Scalars and Vectors, Force Composition, Equilibrium, Energy Conservation, Momentum, Collision Theory, Universal Gravitation, Satellite Motion, Electric Potential, Capacitors, Ohm’s Law, Electric Resistance, Magnetic Forces, Lorentz Force, Spectroscopy, Nuclear Physics, Radiation, Energy Loss, Fission and Fusion Reactions, Photoelectric Effect, Einstein’s Equation. |
对比baseline
微调方法对比
Prompt (vanilla):直接提示,无微调。
IFT:在领域内训练数据上进行标准微调。
LEC:使用SentenceBERT嵌入错误案例,以找到相似的正面示例进行合成。
AugGPT:从未使用的领域内指令中抽样,由高级LLM进行合成。
LLM2LLM:使用高级LLM从错误示例中生成数据。
MUSTARD:从种子概念生成问题,然后由高级LLM生成答案并进行过滤。
所有基线方法使用了相同数量的合成数据(数学2k,代码/考试0.5k)。
其中AugGPT, MUSTARD使用合成数据
LEC, LLM2LLM使用错误分析的方法
这使得我们能够更细致地理解CDS为何可能更优——是因为诊断、合成策略、选择,还是这些因素的组合?
数据选择对比(用于评估 CDSscore):
CBS(聚类)、Coreset(聚类)、Diversity(基于ROUGE)、Length、Perplexity、AlpaGasus(LLM评分)、Random。
其中Length使用简单启发式数据选择
CBS, Coreset使用复杂嵌入/聚类
AlpaGasus使用基于LLM评分
实验结果
CDS比基线方法效果更好
模型(Qwen1.5-7B-Chat)
数据集MBPP (P@1)GSM8k (Acc)GAOKAO (Acc)
对域外 (OOD) 任务的强大泛化能力
尽管CDS是在基于ID任务生成的合成数据上训练的,但经过CDS改进的模型在OOD任务上也表现良好。
例如,Qwen1.5-7B在HumanEval(OOD编码)上提升了4.27%,Llama3-8B在GAOKAO-Bench-Updates(OOD考试)上提升了5.43% 。这与某些基线方法(如AugGPT和LEC)形成对比,后者未能持续提升OOD性能,有时甚至导致性能下降 。
KC标注的灵活性
对来源不同KC,CDS都带来了性能提升。
对于GAOKAO-Bench,KCs来源于官方教学大纲的章节标题;而对于MBPP和GSM8k,则使用了第3.1节中描述的更通用的标注方法(受MOOC启发,由Ma优化)。
CDSscore指标在数据选择中的有效性
CDSscore(数据选择的第二阶段)在数学和编码任务上均取得了最佳的平均指标,优于其他七种选择策略,包括Random、Perplexity和AlpaGasus 。
验证了其设计背后的假设:优先选择复杂(更多KCs)且针对已识别弱点
消融研究的启示
1.全局和细粒度双重策略优于单一策略效果
2.数据增强方法(重写与融合)双重>单一
单一增强策略(如仅“重写”)有时会在某个OOD任务上导致轻微性能下降,可能是由于对相似合成数据过拟合;而双重增强则未观察到此现象,表明双重策略通过多样性和复杂性提高了鲁棒性 。
MathGenie: Generating Synthetic Data with Question Back-translation for Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning of LLMs
不足: 此处的代码比较是大模型自己比较, 仍然可能有幻觉, 可以通过agent调用代码实际验证
论文《MathGenie: Generating Synthetic Data with Question Back-translation for Enhancing Mathematical Reasoning of LLMs》提出了一种名为 MathGenie 的新方法 。其核心目标是通过一种成本效益高且可扩展的开源方法生成高质量的合成数据,从而增强大语言模型的数学推理能力
MathGenie 的意义不仅在于提升模型本身的数学技能,更在于通过赋能开源模型,使更广泛的研究者和开发者能够接触并利用先前主要由资源密集型闭源模型所主导的高级数学推理能力
MathGenie 的总体目标是从一个相对小规模的种子数据集出发,创建一个大规模、多样化且可靠的,包含数学问题及代码集成解答的数据集 。
MathGenie框架
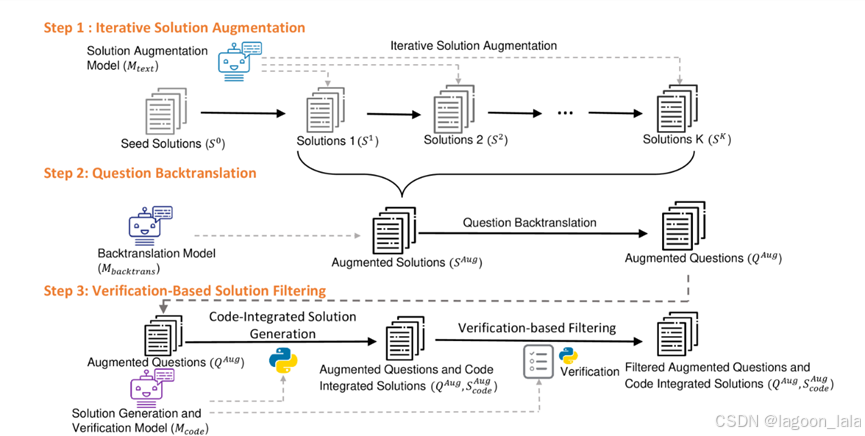
步骤 1:迭代式解题方案增强 (Iterative Solution Augmentation)
论文提出首先增强现有解题方案,而非直接增强问题本身。这种策略旨在更好地约束问题生成过程,并提升机器生成问题的可靠性 。与直接增强问题相比,这种方法更能保留问题的逻辑一致性和可解性。
迭代性:初始的人工标注解题方案集合 S0 经过 Mtext 增强后产生 S1,S1 再作为输入产生 S2,以此类推,直至 SK 。迭代式地应用解题方案增强(S0→S1→⋯→SK)不仅仅是为了增加数量,更是一种逐步增大与原始种子数据语义距离的机制,从而促进了更大的多样性 。
“通过迭代式解题方案增强,每一轮都会产生一组与前一轮不同的解题方案,使得这些解题方案逐渐偏离原始解题方案”。
步骤 2:问题反向转换 (Question Back-translation) – 从解题方案到问题
接收增强后的解题方案集合 S^Aug 作为输入,并生成一组新的问题集合
这种方法利用解题方案中固有的逻辑结构和约束关系,来创建可靠且可解的新问题 。如图 2 所示,与直接增强问题(可能破坏问题内部条件间的隐藏约束,导致问题无解)相比,问题反向翻译考虑了解题方案,能够正确地增强问题 。
步骤 3:基于验证的解题方案筛选 (Verification-Based Solution Filtering) – 确保质量与可靠性
通过反向翻译新生成的问题缺乏真实的解题方案。此步骤为这些新问题生成准确的代码集成解题方案并确保其可靠性。
筛选流程如下:
1.Mcode 为 QAug 中的问题生成候选的代码集成解题方案。
2.通过答案一致性进行初步筛选(如果多个解题方案得出不同答案,则移除该问题)。
3.然后,Mcode 为每个剩余的问题-解题方案对生成一个代码集成的验证推理过程。
4.被验证为错误的解题方案将被丢弃 。附录 G 中的表 13 和表 14 展示了验证推理过程的示例 。
数学解题方案具有固有的逻辑结构和约束。在保持有效性的前提下修改这些内容,然后提出“什么问题会导致这个解题方案?”对于 LLM 来说是一个定义明确的问题。这种“解题方案优先”的方法自然地将可解性和逻辑一致性嵌入到生成的问题中。这一原则对于在其他需要复杂、多步推理的领域(如法律推理、科学假说生成或复杂规划任务)生成合成数据可能非常有效。
使用代码进行验证(如附录 G 所示 )提供了一种比单独比较最终数值答案更客观的正确性检查方法,因为它可以审查解题方法本身。这种严格的方法确保了合成数据不仅数量充足,而且值得信赖,这对于有效训练大语言模型以完成像数学这样精确的任务至关重要。这也凸显了在技术领域合成数据生成的一个最佳实践:以易于自动验证的格式生成解题方案,并实施强大的验证循环。Mcode 模型生成验证推理过程的能力也是向可解释人工智能迈出的一步。
例子
引导模型使用代码来检查一个解题方案,使验证过程更加透明。代码生成prompt:
|
问题:<br>(问题内容)<br>解题方案:<br>[解题方案内容]<br>以上是一个数学问题及其解题方案。请使用代码验证上述解题方案。 |
|
Prompt |
|
**Question**:{question}**Solution**:{solution}Above is a math problem and its solution. Please use code to verify the solution above. |
Appendix G Examples of Code-Integrated Verification Rationales
Two examples of code-integrated verification rationales are presented in Tab. 13 and Tab. 14. In Tab. 13, the solution is verified as correct by using the answer to calculate the condition and comparing it with the actual condition.
1. 答案->条件
2. 条件值是否正确
In Tab. 14, the solution is verified as incorrect by solving the question through an alternative method and comparing the answers.
1. 问题->答案
2. 答案是否正确
|
Input: |
|
*Question**: Express 0.54 as a fraction in lowest terms. 将 0.54‾ 化为最简分数。(其中‾表示循环小数) *Solution**: To express the repeating decimal 0.54 as a fraction in lowest terms, we can use algebraic manipulation. 要将循环小数 0.54(即 0.54‾0.\overline{54}0.54)表示为最简分数,可以使用代数变形。 Let x=0.54. Step 1: Multiply x by 100 to shift the decimal point. …… Therefore, 0.54¯ can be expressed as 611 in lowest terms. Above is a math problem and its solution. Please use code to verify the solution above. |
|
Output: |
|
Now, let’s verify the answer by converting 6/11 back to a decimal. # Convert the fraction 6/11 to a decimal decimal_value = float(simplified_fraction) decimal_value Result: 0.5454545454545454 The decimal representation of 611 is approximately 0.5454545454545454, which matches the repeating decimal 0.54¯ Thus, our answer is verified and correct. |
Table 13:An example of code-integrated verification rationale in which the solution is verified as correct.
|
Input: |
|
*Question**: What is 2121_3−212_3? Express your answer in base 3. *Solution**: Alright, let’s solve this step by step. To subtract these numbers, we’ll start from the rightmost digit (least significant) and move to the left, just like we do in base 10 subtraction. …… The result of 21213−2123 is 2223. Above is a math problem and its solution. Please use code to verify the solution above. |
|
Output: |
|
Now, let’s verify our answer by converting both numbers to base 10, performing the subtraction, and then converting the result back to base 3 to see if it matches our answer. 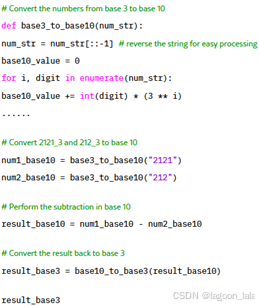
Result: 1202 It seems there was an error in our calculations. The correct result for 21213−2123 is 12023, not 2223. I apologize for the oversight. |
Table 14:An example of code-integrated verification rationale in which the solution is verified as wrong.
实验
生成了包含 17 万个问题和代码集成解题方案对的 AugData(其中 11 万样本来自 GSM8K 增强,6 万来自 MATH 增强)。结合用于训练 Mcode 的种子数据 SeedData,形成了最终的数据集 MathGenieData 。
多数投票对比, MathGenieLM 生成的解题方案不仅平均准确率高,而且其多样性也足以使多数投票发挥效用。
增强数据量消融实验
不同数量增强数据对模型性能的影响 。通过使用 {0, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2,1} 倍数量的增强数据进行训练,结果显示,随着增强数据量的增加,模型在所有五个数据集上的性能都持续提升,鲜有例外。这证明了 MathGenieData 具有很高的扩展质量,即增加更多的这类合成数据通常能带来更好的模型性能。
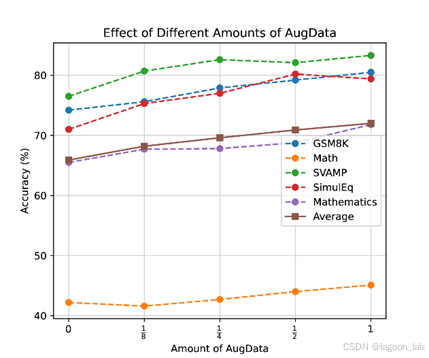
图3
过滤消融实验
与使用未经过滤的数据进行微调相比,使用经过验证筛选的增强问答对进行微调,在 GSM8K 和 MATH 数据集上均带来了显著的准确率提升(GSM8K 提升 1.2%,MATH 提升 1.3%)。这突显了筛选过程在提高数据质量方面的有效性。
代码集成的解题方案暴露了推理步骤,验证可以检查这些步骤是否合乎逻辑并正确执行,而不仅仅是最终数字是否正确(这可能仅仅是巧合)。因此,筛选过程实际上是在选择那些在方法论上可被证明是正确的解题方案。在这些经过更严格审查的解题路径上进行训练,很可能教会了模型更稳健和可靠的推理策略。这强调了在合成数据生成中,“可解释”或“可检查”的解题方案格式(如代码)的价值,因为它们允许进行超越表面答案检查的更有意义的质量控制,这是一种对推理步骤的自动化质量保证。
其他增强方法
现有的解题方案格式,如纯文本的思维链(CoT)和纯代码的程序思想(PoT)
|
增强方法 |
GSM8K |
MATH |
SVAMP |
Simuleq |
Mathematics |
平均 |
|
MetaMath |
79.5 |
44.6 |
78.4 |
79.6 |
67.9 |
70.0 |
|
直接问题增强 (无解题方案) Direct question augmentation (w/o sol.) |
78.8 |
43.0 |
84.0 |
77.0 |
70.2 |
70.6 |
|
直接问题增强 (有解题方案) Direct question augmentation (w/ sol.) |
79.2 |
44.2 |
83.6 |
72.0 |
68.6 |
69.5 |
|
MathGenie (本文方法) |
80.5 |
45.1 |
83.3 |
79.4 |
71.8 |
72.0 |
效率
“验证两次”的平均成本为 2.3x,而 3 路径投票的成本为 3x。每次验证算作一次生成,一次重新解决算作另一次生成。这意味着模型通常只需一到两个额外的生成步骤(一次用于验证,可能一次用于重新解决)就能发现并纠正自身的错误,这比总是生成三个完整的解题方案效率更高。

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容





所有评论(0)