WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第四部分-NetEQ核心原理
音频模块是WebRTC非常重要的部分,音频模块中的NetEq是WebRTC的三大核心技术(NetEq/GCC/音频3A)之一,我们分七部分介绍该模块,本文是第四部分(NetEq核心原理)。这个专题包括:音频播放设备的播放线程定时触发音频获取、解码和播放操作,播放线程每10ms通过GetAudioInternal()接口从NetEq读取10ms长度的音频数据,并决策操作类型(正常、加速、减速、融合、
1. 前言
音频模块是WebRTC非常重要的部分,音频模块中的NetEq是WebRTC的三大核心技术(NetEq/GCC/音频3A)之一,我们分七部分介绍该模块,本文是第四部分(NetEq核心原理)。这个专题包括:
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第一部分-整体介绍
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第二部分-发送端
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第三部分-接收端
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第四部分-NetEq核心原理
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第五部分-NetEq音频决策
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第六部分-NetEq数字信号处理
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第七部分-体验保障
2. 音频播放流程&调用堆栈介绍
音频播放设备的播放线程定时触发音频获取、解码和播放操作,播放线程每10ms通过GetAudioInternal()接口从NetEq读取10ms长度的音频数据,并决策操作类型(正常、加速、减速、融合、拉伸(PLC)、生成舒适噪音),然后根据决策结果处理PCM数据,包括后续的解码、音画同步、播放。整个过程封装在结构体NetEqImpl中。
音频播放流程的具体调用堆栈如下:
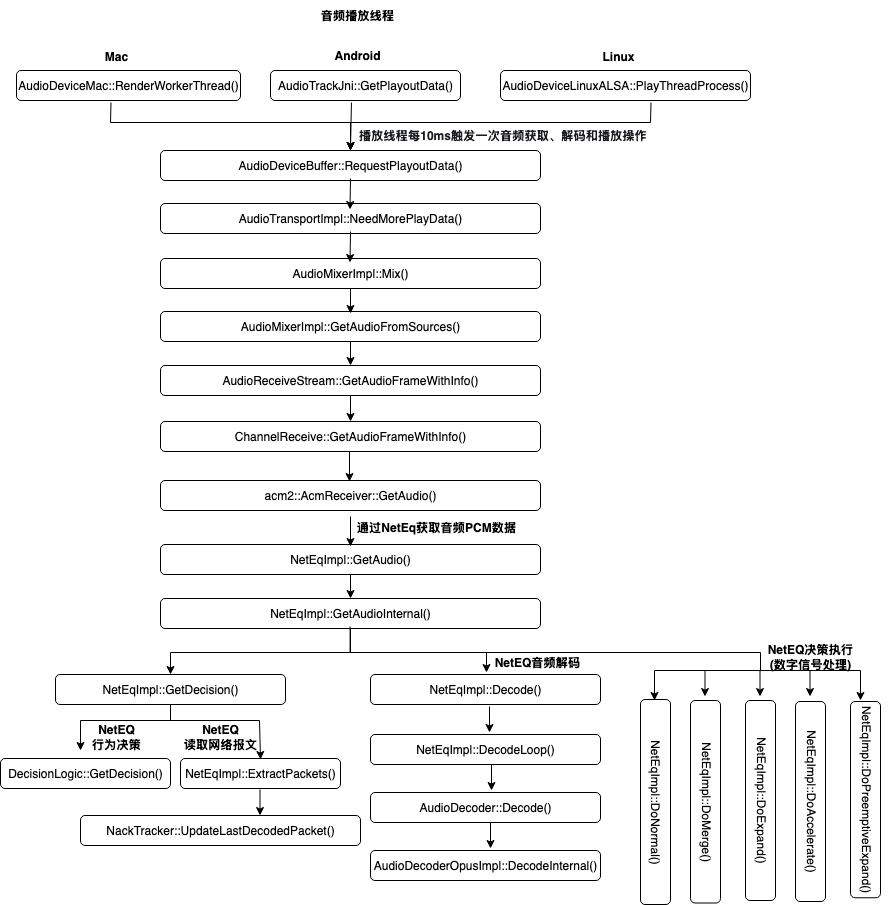
3. NetEq核心原理&关键缓冲区&主流程介绍
3.1. NetEq的核心原理
NetEq是WebRTC最具有技术含量的3个模块(NetEq/GCC/音频3A)之一,最初由GIPS公司(Global IP Sound)开发,专为实时语音通信设计,旨在解决网络抖动、丢包等导致的音频质量问题。GIPS在实时通信领域深耕多年,其NetEq模块以 低延迟 和 高鲁棒性著称,成为行业标杆。2011年,Google收购GIPS,并将其核心技术(包括NetEq)整合进WebRTC项目中,WebRTC于同年开源。NetEq作为其核心音频模块,成为实时音视频通信的基石之一,负责网络抖动缓冲、丢包补偿和音频同步。
NetEq(Network Echo Canceler)作为WebRTC音频引擎的核心模块,是实时音视频通信的基石之一,旨在解决网络抖动、丢包和延迟问题,确保音频传输的稳定性和低延迟,并实现音频同步。其核心原理主要围绕抖动控制(Jitter Control)和丢包隐藏(Packet Loss Concealment, 又称为error concealment)展开,正如官网文档介绍(http://www.gipscorp.alcatrazconsulting.com/files/english/datasheets/NetEq.pdf),两者的结合是NetEq表现出色的关键:
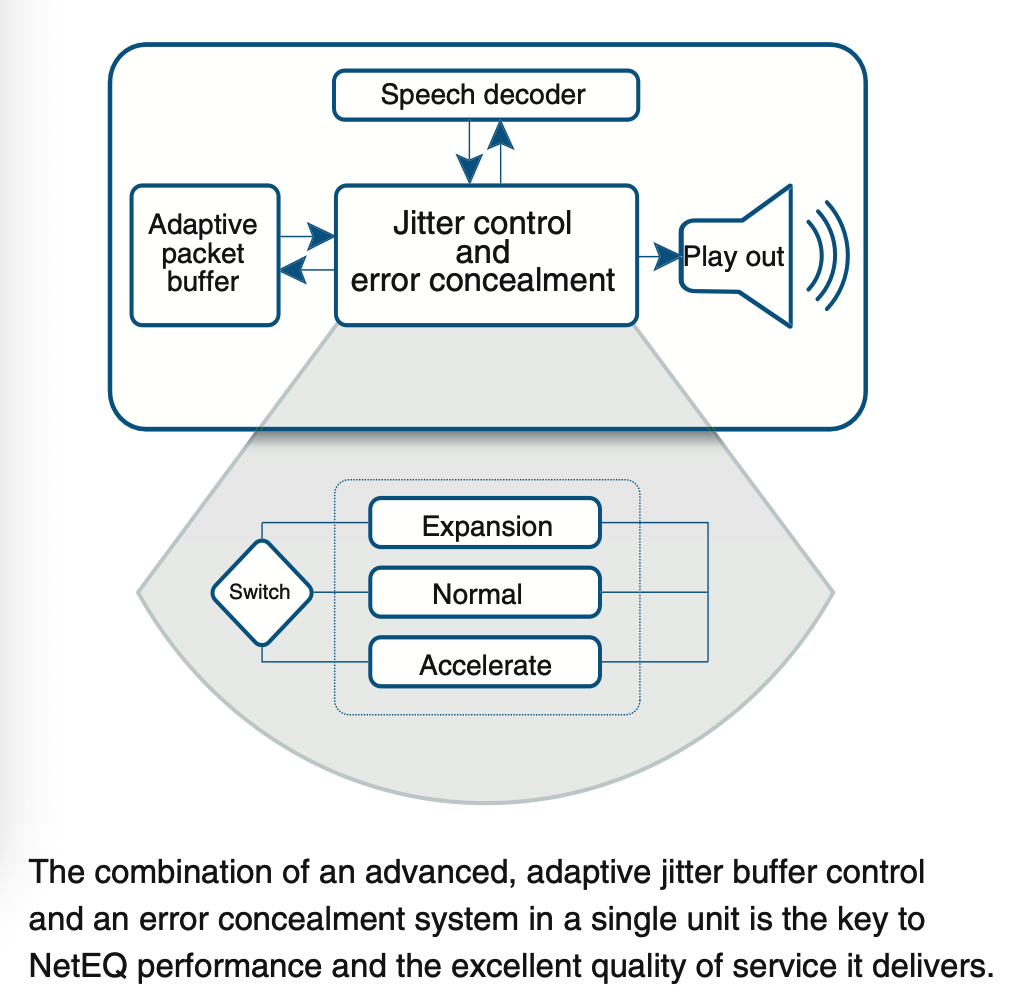
NetEq的抖动控制(Jitter Control)通过动态调整抖动缓冲区(packet_buffer_)的大小(深度),并基于该缓冲区的当前水位灵活处理数字信号(加速、减速、正常播放等),再按固定时间间隔(如10ms)提取数据播放,从而平滑网络抖动,实现对实时性和稳定性的平衡。
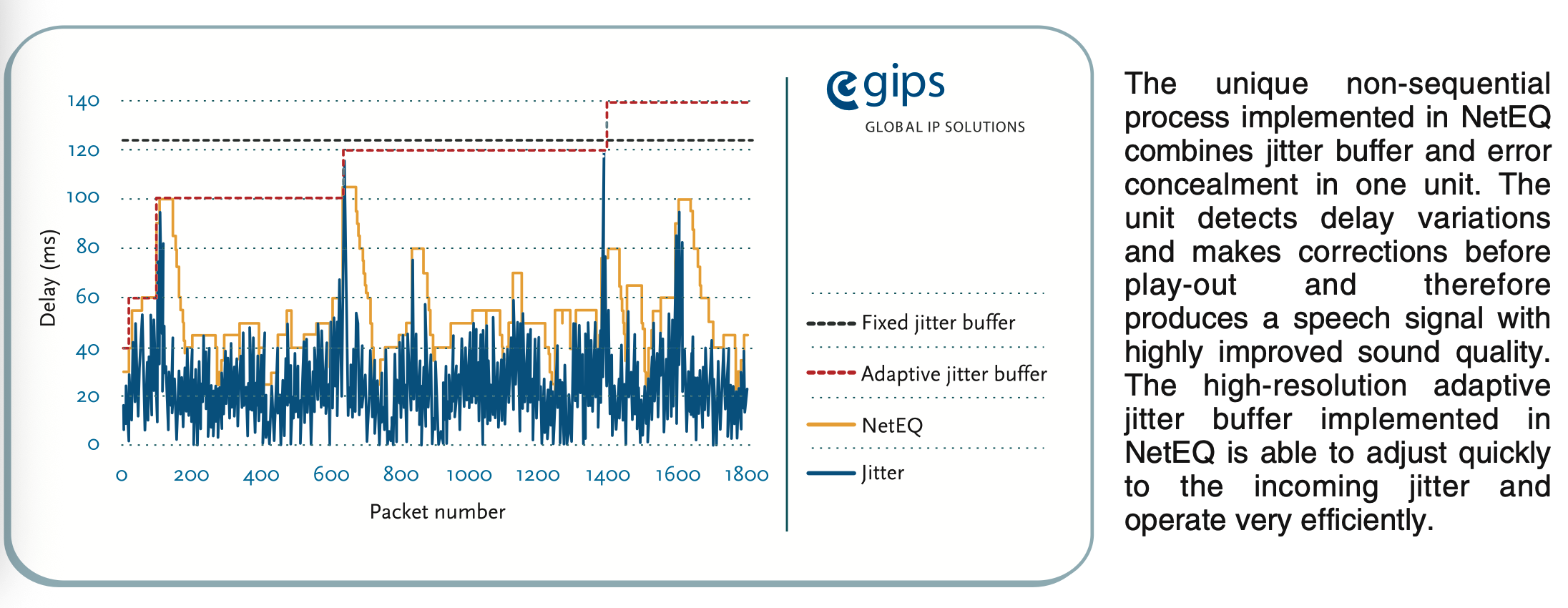
NetEq根据网络状况动态调整缓冲区大小(抖动增加时增大缓冲区,反之减小),将NetEq的延迟目标控制在80ms~200ms之间。抖动缓冲区最大可缓存4秒的音频数据(200个20ms包),确保在网络抖动较大时仍能维持播放。下图同样来自官网,从这张图可以看到对比其他Jitter Buffer的视线,NetEq在延迟优化上非常有竞争力。
当网络丢包发生时,NetEq通过以下技术生成音频的替代数据,避免静音或卡顿(缺点是如果音频的填充数据),此项技术称为丢包隐藏(PLC)或错误隐藏(Packet Loss Concealment, 又称为error concealment):
- 插值补偿:利用前一帧或后一帧的音频信号进行插值,生成丢失帧的近似数据。
- 静音填充:在连续丢包或无法补偿的情况下,填充短暂静音(通常为10ms~20ms),避免完全中断播放。
- 多帧补偿:对于连续丢包,NetEq会逐帧递减补偿增益,避免失真累积。例如,连续丢包时,后续帧的补偿强度逐渐降低,以平滑过渡。
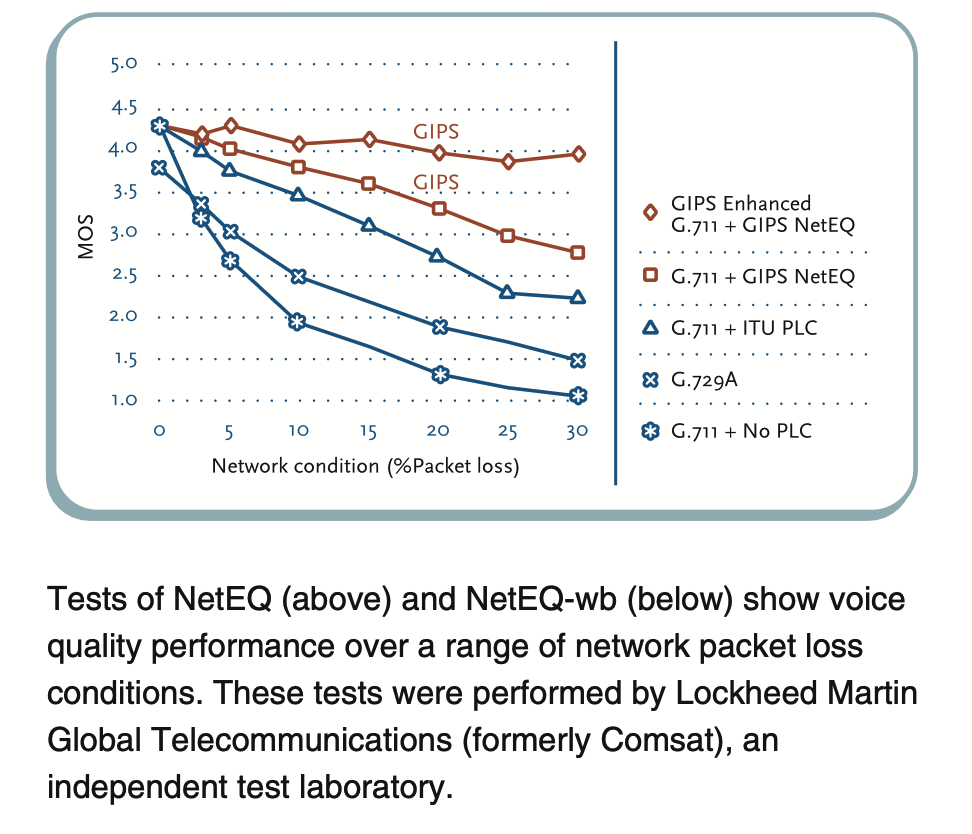
通过独立的评测机构的对比测试,可以发现NetEq对比传统的PLC,以及没有PLC时的音质表现(MOS),确实非常亮眼。
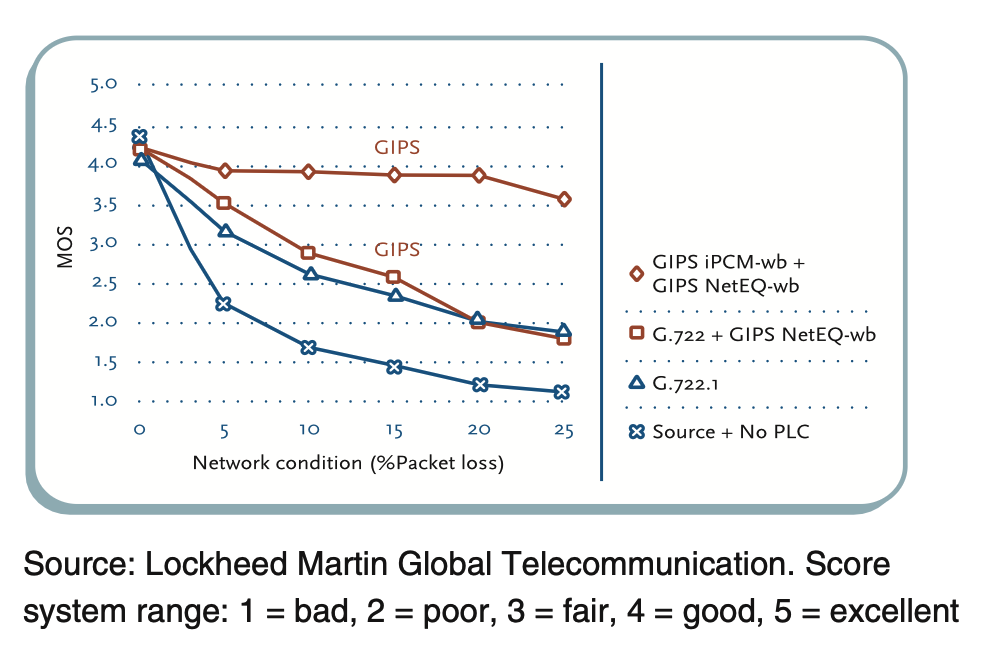
NetEq支持多种音频编解码器(如Opus、G.711),在代码层面做了不同音频编码器的Adapter(适配层),并以统一的逻辑处理网络报文和PCM数据。此外,NetEq和信道层面包括RED/NACK在内的QoS技术相互协同,共同为保障接收端兼顾延迟、流畅度和音质的音频播放体验。
最后,我们要看到NetEq的一些局限性,包括:
- 高丢包率下的音质下降:连续丢包超过10帧时,PLC补偿效果显著下降。在通话过程中,偶尔会听到吱嘎吱嘎的机械声,就是因为连续丢包导致PLC无法补偿相对保真的音频数据。
- 计算资源消耗:WSOLA等插值算法对CPU要求较高,可能影响移动端性能。
3.2. 工业界对NetEq表现的指标评价
工业界用音频卡顿率来衡量NetEq及整个音频模块在对抗网络时的整体表现,音频卡顿率的计算公式为:
音频卡顿率 = (卡顿时长 / 总音频时长) × 100%
具体地说,音频卡顿率是音频卡顿的总时长与音频总播放时长的比值。通常我们以200ms为阈值,单次卡顿时长超过200ms的片段会被记为一次音频卡顿。由于NetEq PLC的存在,播放线程始终可以从缓冲区中取到数据(包括PLC生成的伪造数据),所以我们无法根据播放器是否播放了音频作为卡顿的依据。在工业界,音频卡顿率是通过检测NetEq有没有触发PLC来统计的,每触发一次PLC,我们就做一次统计,如果该次PLC的持续时长超过200ms,我们就记一次卡顿。
以此为标准,在中国的网络环境下,音频卡顿率当前的(截至2025年8月)最优值为0.2%,这个值很难被突破。
3.3. 关键缓冲区介绍
为更好地理解NetEq的整体设计,我们给出NetEq的核心数据结构及它们之间数据流转的关系图:
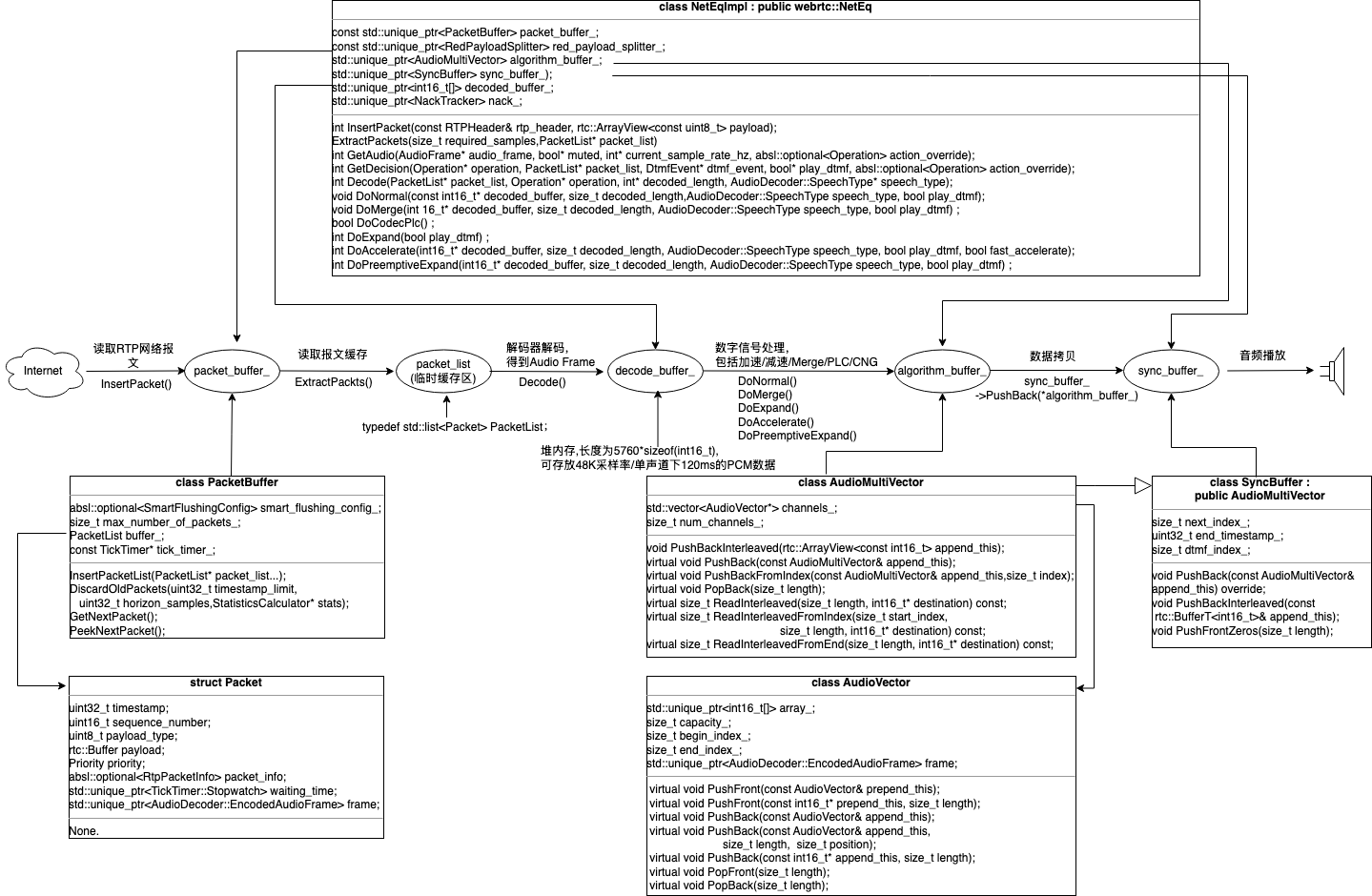
NetEq内部包含四个核心缓冲区,按照流程处理的先后顺序整理如下:
|
缓冲区 |
功能 |
容量 |
|
const std::unique_ptr<PacketBuffer> packet_buffer_; |
存储接收到的RTP数据包,通过调整缓冲区的大小(深度)平滑网络抖动 |
最大4秒(200包音频报文,每个报文的编码周期为20ms),同时会主动丢弃5秒前的报文,避免过时数据占用资源 |
|
std::unique_ptr<int16_t[]> decoded_buffer_; |
存储解码后的音频数据(PCM格式) |
最大120ms,48kHz采样率下可存放5760个采样点 |
|
std::unique_ptr<AudioMultiVector> algorithm_buffer_; |
NetEq根据packet_buffer_的水位决定需要执行的动作,包括加速、减速、融合、PLC、生成舒适噪音,处理之后的音频数据存入algorithm_buffer_中 |
动态清空 |
|
std::unique_ptr<SyncBuffer> sync_buffer_); |
存储最终待播放的音频数据。sync_buffer_为循环缓冲区,播放线程每10ms从该缓冲区中提取数据送入声卡播放。 |
最大180ms |
接下来对这几个缓冲区对应的数据结构做详细介绍。
3.3.1. PacketBuffer
class PacketBuffer {
...
private:
absl::optional<SmartFlushingConfig> smart_flushing_config_;
size_t max_number_of_packets_;
PacketList buffer_;
const TickTimer* tick_timer_;
};
typedef std::list<Packet> PacketList;PacketBuffer接收来自网络中的报文,它维护了一个缓存列表buffer_,里面的每个元素都是Packet类型,Packet中存有该报文对应的时戳、序号、Payload等。PacketBuffer提供了报文插入(包括单个报文和批量操作)/淘汰/读取的能力。
3.3.1.1. 向Buffer中插入报文
PacketBuffer::InsertPacketList()尝试将packet_list指向的所有报文全部加入到缓存中。加入的过程中会做两个判断:
- 缓存是否已满或是否需要智能刷新,若为前者则将当前缓存全部清空后继续往里面加报文,若为后者则在完成智能刷新后丢弃packet_list中的剩余报文;
- 检查当前报文的时间戳和buffer中已有报文的时间戳是否一致,若一致则判断为同一个报文,此时需要丢弃其中一个报文。
int PacketBuffer::InsertPacketList(
PacketList* packet_list,
const DecoderDatabase& decoder_database,
absl::optional<uint8_t>* current_rtp_payload_type,
absl::optional<uint8_t>* current_cng_rtp_payload_type,
StatisticsCalculator* stats,
size_t last_decoded_length,
size_t sample_rate,
int target_level_ms) {
bool flushed = false;
for (auto& packet : *packet_list) {
...
int return_val =
InsertPacket(std::move(packet), stats, last_decoded_length, sample_rate,
target_level_ms, decoder_database);
if (return_val == kFlushed) {
// The buffer flushed, but this is not an error. We can still continue.
flushed = true;
} else if (return_val != kOK) {
// An error occurred. Delete remaining packets in list and return.
/*kPartialFlush也会在这里处理,
*也就是在出现智能刷新时也会将原本需要加入到buffer中的报文全部丢弃
*/
packet_list->clear();
return return_val;
}
}
packet_list->clear();
return flushed ? kFlushed : kOK;
}InsertPacket()向buffer中插入报文,插入之前先检查是否需要淘汰老的数据以腾出空间,同时检查该报文是否和buffer中已有报文是否属于同一个报文(例如RED机制允许对同一个包多发几次)。
int PacketBuffer::InsertPacket(Packet&& packet,
StatisticsCalculator* stats,
size_t last_decoded_length,
size_t sample_rate,
int target_level_ms,
const DecoderDatabase& decoder_database) {
if (packet.empty()) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "InsertPacket invalid packet";
return kInvalidPacket;
}
int return_val = kOK;
packet.waiting_time = tick_timer_->GetNewStopwatch();
/*如果当前buffer中的数据量已到达上限则淘汰buffer中的老数据
*如果需要智能刷新,则至少淘汰到buffer中有容量上限一半以上的空间可用
*如果是因为buffer已满,则将buffer中的报文全部淘汰
*/
// Perform a smart flush if the buffer size exceeds a multiple of the target
// level.
const size_t span_threshold =
smart_flushing_config_
? smart_flushing_config_->target_level_multiplier *
std::max(smart_flushing_config_->target_level_threshold_ms,
target_level_ms) *
sample_rate / 1000
: 0;
const bool smart_flush =
smart_flushing_config_.has_value() &&
GetSpanSamples(last_decoded_length, sample_rate, false) >= span_threshold;
if (buffer_.size() >= max_number_of_packets_ || smart_flush) {
size_t buffer_size_before_flush = buffer_.size();
if (smart_flushing_config_.has_value()) {
// Flush down to the target level.
/*淘汰buffer的老数据,保证在buffer中有至少一半的空间可用*/
PartialFlush(target_level_ms, sample_rate, last_decoded_length, stats);
return_val = kPartialFlush;
} else {
// Buffer is full.
/*Flush the buffer. All packets in the buffer will be destroyed.*/
Flush(stats);
return_val = kFlushed;
}
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Packet buffer flushed, "
<< (buffer_size_before_flush - buffer_.size())
<< " packets discarded.";
}
/*如果在原有buffer中出现和当前时戳一致的报文,
*则根据优先级要么丢弃当前报文,要么丢弃原有报文
*/
// Get an iterator pointing to the place in the buffer where the new packet
// should be inserted. The list is searched from the back, since the most
// likely case is that the new packet should be near the end of the list.
PacketList::reverse_iterator rit = std::find_if(
buffer_.rbegin(), buffer_.rend(), NewTimestampIsLarger(packet));
// The new packet is to be inserted to the right of `rit`. If it has the same
// timestamp as `rit`, which has a higher priority, do not insert the new
// packet to list.
if (rit != buffer_.rend() && packet.timestamp == rit->timestamp) {
LogPacketDiscarded(packet.priority.codec_level, stats);
return return_val;
}
// The new packet is to be inserted to the left of `it`. If it has the same
// timestamp as `it`, which has a lower priority, replace `it` with the new
// packet.
PacketList::iterator it = rit.base();
if (it != buffer_.end() && packet.timestamp == it->timestamp) {
LogPacketDiscarded(it->priority.codec_level, stats);
it = buffer_.erase(it);
}
/*插入一个新的报文*/
buffer_.insert(it, std::move(packet)); // Insert the packet at that position.
return return_val;
}
3.3.1.2. 主动丢弃旧的报文
PacketBuffer::DiscardOldPackets()&PacketBuffer::DiscardAllOldPackets()用来淘汰过旧的报文,前者要求报文时戳落在一个区间里面才会被删除,后者只要报文时戳小于指定值就会直接删掉。
/*遍历缓存中的所有报文,如果一个报文的时间戳太小,
*则认为该报文已过期,则将其删除
*/
void PacketBuffer::DiscardOldPackets(uint32_t timestamp_limit,
uint32_t horizon_samples,
StatisticsCalculator* stats) {
/*遍历缓存中的所有报文,如果一个报文的时间戳太小,则认为该报文已过期,则将其删除*/
buffer_.remove_if([timestamp_limit, horizon_samples, stats](const Packet& p) {
if (timestamp_limit == p.timestamp ||
!IsObsoleteTimestamp(p.timestamp, timestamp_limit, horizon_samples)) {
return false;
}
LogPacketDiscarded(p.priority.codec_level, stats);
return true;
});
}
/*遍历缓存中的所有报文,如果一个报文的时间戳太小,
*则认为该报文已过期,则将其删除
*这个函数和DiscardOldPackets()不同的地方在于
*前者只要报文时戳小于timestamp_limit就会直接删掉,
*后者要求报文时戳落在一个区间里面才会被删除
*/
void PacketBuffer::DiscardAllOldPackets(uint32_t timestamp_limit,
StatisticsCalculator* stats) {
DiscardOldPackets(timestamp_limit, 0, stats);
}
// Static method returning true if `timestamp` is older than `timestamp_limit`
// but less than `horizon_samples` behind `timestamp_limit`. For instance,
// with timestamp_limit = 100 and horizon_samples = 10, a timestamp in the
// range (90, 100) is considered obsolete, and will yield true.
// Setting `horizon_samples` to 0 is the same as setting it to 2^31, i.e.,
// half the 32-bit timestamp range.
/*若timestamp落在(timestamp_limit - horizonz_samples,timestamp_limit)或者
*timestamp < timestamp_list且horizon_samples为零时
*我们认为该时戳对应的报文已过期
*/
static bool IsObsoleteTimestamp(uint32_t timestamp,
uint32_t timestamp_limit,
uint32_t horizon_samples) {
return IsNewerTimestamp(timestamp_limit, timestamp) &&
(horizon_samples == 0 ||
IsNewerTimestamp(timestamp, timestamp_limit - horizon_samples));
}3.3.1.3. 获取下一个报文
GetNextPacket()从buffer_头部取走一个Packet,PeekNextPacket()只读取头部的Packet但并不真实取走。
absl::optional<Packet> PacketBuffer::GetNextPacket() {
if (Empty()) {
// Buffer is empty.
return absl::nullopt;
}
absl::optional<Packet> packet(std::move(buffer_.front()));
// Assert that the packet sanity checks in InsertPacket method works.
RTC_DCHECK(!packet->empty());
buffer_.pop_front();
return packet;
}const Packet* PacketBuffer::PeekNextPacket() const {
return buffer_.empty() ? nullptr : &buffer_.front();
}3.3.2. AudioMultiVector
AudioMultiVector可以理解为一个二维向量channels_,每一维存放音频的一个通道的数据。如果为单通道,num_channels为1,如果为双通道,num_channels_为2。
class AudioMultiVector {
...
protected:
std::vector<AudioVector*> channels_;
size_t num_channels_;
};下面介绍几个典型函数。
PushBackInterleaved()将一维向量append_this中的每个元素按序插入到二维向量channels_中,具体插入方法为:按序取出length_per_channel个元素,插入到channels_[0],再按序取出length_per_channel个元素,插入到channels_[1],直至取完。
void AudioMultiVector::PushBackInterleaved(
rtc::ArrayView<const int16_t> append_this) {
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(append_this.size() % num_channels_, 0);
if (append_this.empty()) {
return;
}
if (num_channels_ == 1) {
// Special case to avoid extra allocation and data shuffling.
channels_[0]->PushBack(append_this.data(), append_this.size());
return;
}
size_t length_per_channel = append_this.size() / num_channels_;
int16_t* temp_array = new int16_t[length_per_channel]; // Temporary storage.
for (size_t channel = 0; channel < num_channels_; ++channel) {
// Copy elements to `temp_array`.
for (size_t i = 0; i < length_per_channel; ++i) {
temp_array[i] = append_this[channel + i * num_channels_];
}
channels_[channel]->PushBack(temp_array, length_per_channel);
}
delete[] temp_array;
}ReadInterleavedFromIndex()将channels_[]每一维向量从start_index开始的length个元素,依次拷贝到destination一维向量中。
size_t AudioMultiVector::ReadInterleavedFromIndex(size_t start_index,
size_t length,
int16_t* destination) const {
RTC_DCHECK(destination);
size_t index = 0; // Number of elements written to `destination` so far.
RTC_DCHECK_LE(start_index, Size());
start_index = std::min(start_index, Size());
if (length + start_index > Size()) {
length = Size() - start_index;
}
if (num_channels_ == 1) {
// Special case to avoid the nested for loop below.
(*this)[0].CopyTo(length, start_index, destination);
return length;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
for (size_t channel = 0; channel < num_channels_; ++channel) {
destination[index] = (*this)[channel][i + start_index];
++index;
}
}
return index;
}3.3.3. SyncBuffer
SyncBuffer继承自AudioMultiVector,内部同样维护了一个二维向量channels_,每个向量存放一个声道的音频数据。
class SyncBuffer : public AudioMultiVector {
...
private:
size_t next_index_;
uint32_t end_timestamp_; // The timestamp of the last sample in the buffer.
size_t dtmf_index_; // Index to the first non-DTMF sample in the buffer.
};下面介绍几个典型函数。
PushBackInterleaved()将入参append_this的每个元素插入到SyncBuffer的尾部,同时删除SyncBuffer的头部数据以保持整个Buffer Size不变。
void SyncBuffer::PushBackInterleaved(const rtc::BufferT<int16_t>& append_this) {
const size_t size_before_adding = Size();
AudioMultiVector::PushBackInterleaved(append_this);
const size_t samples_added_per_channel = Size() - size_before_adding;
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(samples_added_per_channel * Channels(), append_this.size());
AudioMultiVector::PopFront(samples_added_per_channel);
next_index_ -= std::min(next_index_, samples_added_per_channel);
dtmf_index_ -= std::min(dtmf_index_, samples_added_per_channel);
}ReplaceAtIndex()将SyncBuffer中每个声道特定区间的音频数据用入参insert_this对应位置的音频数据替换。
void SyncBuffer::ReplaceAtIndex(const AudioMultiVector& insert_this,
size_t length,
size_t position) {
position = std::min(position, Size()); // Cap `position` in the valid range.
length = std::min(length, Size() - position);
AudioMultiVector::OverwriteAt(insert_this, length, position);
}GetNextAudioInterleaved()将当前buffer的数据最多拷贝requested_len字节至output中。
void SyncBuffer::GetNextAudioInterleaved(size_t requested_len,
AudioFrame* output) {
RTC_DCHECK(output);
/*计算当前buffer中剩余字节数,取该值和实际要读取的字节数之间的较小值*/
const size_t samples_to_read = std::min(FutureLength(), requested_len);
output->ResetWithoutMuting();
/*将当前buffer中的数据拷贝至output中*/
const size_t tot_samples_read = ReadInterleavedFromIndex(
next_index_, samples_to_read, output->mutable_data());
const size_t samples_read_per_channel = tot_samples_read / Channels();
next_index_ += samples_read_per_channel;
output->num_channels_ = Channels();
output->samples_per_channel_ = samples_read_per_channel;
}The End.
3.4. NetEqImpl整体流程
具体到NetEq的内部机制,音频数据在NetEq内部的流转分为4个阶段:
- 从网络中收取音频报文,对RTP报文解封装后存入NetEqImpl::packet_buffer_,网络传输中遇到丢包问题由RED、Nack模块来补偿,Opus编码还自带了FEC,也可以用来对抗丢包;
- 对音频数据解码,解码后的PCM数据存入decode_buffer_中;
- NetEq基于历史状态、当前水位等因子决策当前行为,包括加速、减速、融合、PLC(丢包补偿)、生成舒适噪音、正常播放或重置NetEq,根据不同的行为做不同的数字信号处理,处理后的数据存入algorithm_buffer_;
- 将algorithm_buffer_中的音频数据拷贝到sync_buffer,后者被当前的音频播放线程取走,送入扬声器播放。
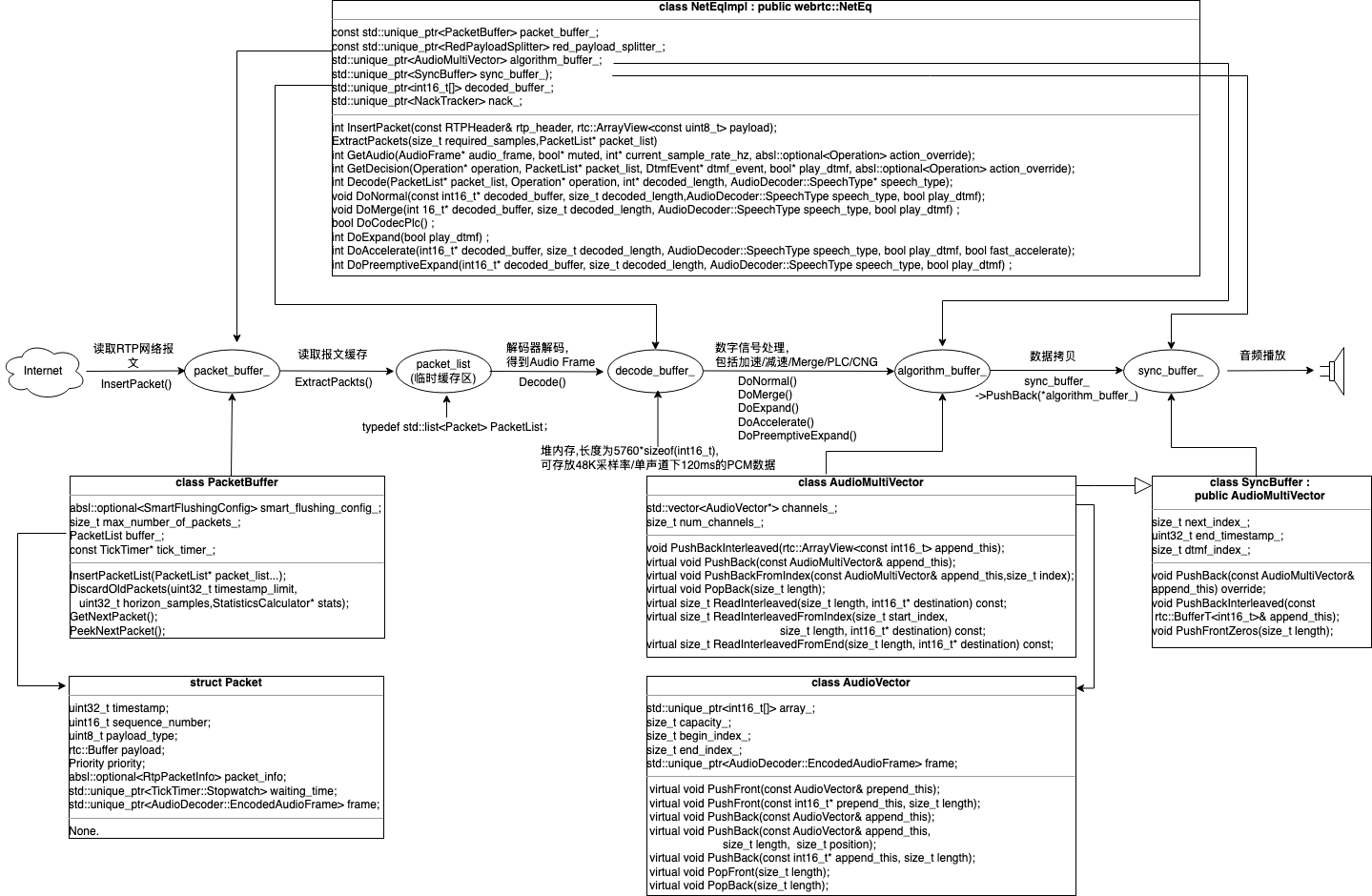
对于NetEqImpl关键的4个缓存区,以下表格做了详细介绍:
|
缓存区名称 |
缓存区作用 |
工作流程 |
|
packet_buffer_ |
存储从网络接收到的原始音频数据包,解决网络传输中的抖动、数据包丢失和乱序问题。 |
网络层将接收到的音频数据包放入 packet_buffer_中,packet_buffer_对数据包进行排序,以确保后续处理的有序性。同时packet_buffer_还会做丢包确认,并启动Nack模块触发发送端重传报文。 |
|
decode_buffer_ |
存储从packet_buffer_中提取并解码后的音频帧。 |
NetEq调用解码模块并指定解码的目标地址为decode_buffer_中的一段连续内存,将编码后的数据转换为原始音频帧(PCM Frame)。 |
|
algorithm_buffer_ |
从decode_buffer_中提取音频帧,根据DecisionLogic模块给出的指令执行对应的数字信号处理,algorithm_buffer_存储经过信号处理后的音频数据。algorithm_buffer_是播放缓存区新数据补充的来源。 |
NetEq从decode_buffer_中取出音频帧之后,执行CNG、加速、减速、Merge、PLC这些数字信号处理,用以提高音频播放的连续性和质量。数字信号处理完毕之后,NetEq将algorithm_buffer_的音频数据放入 sync_buffer_中。 |
|
sync_buffer_ |
播放缓存区,储存从algorithm_buffer_中处理完成的音频帧,并送入到音频设备播放。 播放缓存区是声卡端播放数据的缓存区,从语音缓冲区取出的10ms数据全在此处被播放。 |
NetEq从algorithm_buffer_中提取处理好的音频帧,放入 sync_buffer_中,再以音频播放的时间戳,将音频帧稳定地输出到音频设备进行播放。 |
以上4个阶段对应的代码在NetEqImpl::GetAudio()中,该函数的主体是第6行GetAudioInternal()。
int NetEqImpl::GetAudio(AudioFrame* audio_frame,
bool* muted,
int* current_sample_rate_hz,
absl::optional<Operation> action_override) {
MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
if (GetAudioInternal(audio_frame, muted, action_override) != 0) {
return kFail;
}
...
return kOK;
}GetAudioInternal()这个函数很长,我们把握住关键函数:
- GetDecision()。该函数执行了两个关键动作:
-
- 行为决策,决定对音频PCM数据的信号处理方式,包括加速、减速、融合、PLC(丢包补偿)、生成舒适噪音、正常播放,以及在必要的时候重置NetEq的状态;
- 基于该行为决策决定从音频报文缓存中取多少数据出来,并将该数据从packet_buffer_移到临时变量packet_list中;
- Decode()。基于Opus解码器对音频报文做解码,得到PCM格式的Audio Frame,数据存入decode_buffer_中;
- 基于1得到的信号处理方式执行对应的动作,包括DoNormal()/DoMerge()/DoExpand()/DoAccelerate()/DoPreemptiveExpand()/CNG,数据存入algorithm_buffer_;
- 将algorithm_buffer_的数据拷贝到sync_buffer_中,后者会被最终送至扬声器播放。
接下来的章节会详细分析以上4部分中的1/2/3。
int NetEqImpl::GetAudioInternal(AudioFrame* audio_frame,
bool* muted,
absl::optional<Operation> action_override) {
PacketList packet_list;
...
int return_value = GetDecision(&operation, &packet_list, &dtmf_event,
&play_dtmf, action_override);
if (return_value != 0) {
last_mode_ = Mode::kError;
return return_value;
}
AudioDecoder::SpeechType speech_type;
int length = 0;
const size_t start_num_packets = packet_list.size();
int decode_return_value =
Decode(&packet_list, &operation, &length, &speech_type);
if (length > 0) {
last_decoded_type_ = speech_type;
}
RTC_DCHECK(vad_.get());
bool sid_frame_available =
(operation == Operation::kRfc3389Cng && !packet_list.empty());
vad_->Update(decoded_buffer_.get(), static_cast<size_t>(length), speech_type,
sid_frame_available, fs_hz_);
...
algorithm_buffer_->Clear();
switch (operation) {
case Operation::kNormal: {
DoNormal(decoded_buffer_.get(), length, speech_type, play_dtmf);
if (length > 0) {
stats_->DecodedOutputPlayed();
}
break;
}
case Operation::kMerge: {
DoMerge(decoded_buffer_.get(), length, speech_type, play_dtmf);
break;
}
case Operation::kExpand: {
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(return_value, 0);
if (!current_rtp_payload_type_ || !DoCodecPlc()) {
return_value = DoExpand(play_dtmf);
}
RTC_DCHECK_GE(sync_buffer_->FutureLength() - expand_->overlap_length(),
output_size_samples_);
break;
}
case Operation::kAccelerate:
case Operation::kFastAccelerate: {
const bool fast_accelerate =
enable_fast_accelerate_ && (operation == Operation::kFastAccelerate);
return_value = DoAccelerate(decoded_buffer_.get(), length, speech_type,
play_dtmf, fast_accelerate);
break;
}
case Operation::kPreemptiveExpand: {
return_value = DoPreemptiveExpand(decoded_buffer_.get(), length,
speech_type, play_dtmf);
break;
}
case Operation::kRfc3389Cng:
case Operation::kRfc3389CngNoPacket: {
return_value = DoRfc3389Cng(&packet_list, play_dtmf);
break;
}
case Operation::kCodecInternalCng: {
// This handles the case when there is no transmission and the decoder
// should produce internal comfort noise.
// TODO(hlundin): Write test for codec-internal CNG.
DoCodecInternalCng(decoded_buffer_.get(), length);
break;
}
case Operation::kDtmf: {
// TODO(hlundin): Write test for this.
return_value = DoDtmf(dtmf_event, &play_dtmf);
break;
}
case Operation::kUndefined: {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "Invalid operation kUndefined.";
RTC_DCHECK_NOTREACHED(); // This should not happen.
last_mode_ = Mode::kError;
return kInvalidOperation;
}
} // End of switch.
last_operation_ = operation;
if (return_value < 0) {
return return_value;
}
if (last_mode_ != Mode::kRfc3389Cng) {
comfort_noise_->Reset();
}
// We treat it as if all packets referenced to by `last_decoded_packet_infos_`
// were mashed together when creating the samples in `algorithm_buffer_`.
RtpPacketInfos packet_infos(last_decoded_packet_infos_);
// Copy samples from `algorithm_buffer_` to `sync_buffer_`.
//
// TODO(bugs.webrtc.org/10757):
// We would in the future also like to pass `packet_infos` so that we can do
// sample-perfect tracking of that information across `sync_buffer_`.
sync_buffer_->PushBack(*algorithm_buffer_);
// Extract data from `sync_buffer_` to `output`.
size_t num_output_samples_per_channel = output_size_samples_/*10ms时间的采样点个数*/;
size_t num_output_samples = output_size_samples_ * sync_buffer_->Channels();
if (num_output_samples > AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeSamples/*192*2*20=7680*/) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Output array is too short. "
<< AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeSamples << " < "
<< output_size_samples_ << " * "
<< sync_buffer_->Channels();
num_output_samples = AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeSamples;
num_output_samples_per_channel =
AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeSamples / sync_buffer_->Channels();
}
/*将当前buffer的数据最多拷贝
*(num_output_samples_per_channel*2*通道数)至audio_frame中
*/
sync_buffer_->GetNextAudioInterleaved(num_output_samples_per_channel,
audio_frame);
audio_frame->sample_rate_hz_ = fs_hz_;
audio_frame->packet_infos_ = std::move(packet_infos);
...
audio_frame->timestamp_ =
first_packet_
? 0
: timestamp_scaler_->ToExternal(playout_timestamp_) -
static_cast<uint32_t>(audio_frame->samples_per_channel_);
...
return return_value;
}3.4.1. NetEqImpl::GetDecision
NetEqImpl::GetDecision()的函数很长,但核心代码是这里的第12行和第45行,前者确定NetEq接下来的动作,后者从packet_buffer_中取出报文用于解码、播放,而后者要读取多少音频报文,需要根据前者给出的动作做调整(默认读取10ms的音频报文,在一些情况下,如加速、减速时需要读取该值的2倍)。
第12行代码controller_->GetDecision()将结果存入入参operation中,指导NetEq接下来的动作,包括加速、减速、融合、PLC(丢包补偿)、生成舒适噪音、正常播放或重置NetEq,这部分的细节请参考DecisionLogic::GetDecision()的详细解释。
int NetEqImpl::GetDecision(Operation* operation,
PacketList* packet_list,
DtmfEvent* dtmf_event,
bool* play_dtmf,
absl::optional<Operation> action_override) {
...
const Packet* packet = packet_buffer_->PeekNextPacket();
...
NetEqController::NetEqStatus status;
...
/*Call DecisionLogic::GetDecision()*/
*operation = controller_->GetDecision(status, &reset_decoder_);
...
size_t required_samples = output_size_samples_/*10ms时间的采样点个数*/;
...
switch (*operation) {
...
case Operation::kAccelerate:
case Operation::kFastAccelerate: {
...
required_samples = 2 * output_size_samples_;
...
break;
}
case Operation::kPreemptiveExpand: {
...
required_samples = 2 * output_size_samples_;
// Move on with the preemptive expand decision.
break;
}
case Operation::kMerge: {
required_samples =
std::max(merge_->RequiredFutureSamples(), required_samples);
break;
}
default: {
// Do nothing.
}
}
...
// Get packets from buffer.
int extracted_samples = 0;
if (packet) {
sync_buffer_->IncreaseEndTimestamp(packet->timestamp - end_timestamp);
extracted_samples = ExtractPackets(required_samples, packet_list);
if (extracted_samples < 0) {
return kPacketBufferCorruption;
}
}
...
return 0;
}3.4.2. NetEqImpl::ExtractPackets
音频播放线程从NetEq的Packet Buffer中取出RTP报文并做解码,这部分内容和音频网络报文接收的章节相对应,后者向Packet Buffer中存入RTP报文。
NetEqImpl::ExtractPackets()尝试着从RTP报文缓存packet_buffer_中读取报文并插入到入参packet_list的尾部。
该函数在执行时,会尝试着尽可能多地将报文读取出来,直至想要读取的下一个报文的时戳达到或超过设定的上限(required_samples)。结合NetEqImpl::GetDecision()的分析,我们发现,required_samples默认值为10ms采样周期下的样本个数(采样周期*采样率),在加速、减速的某些条件下该值调整为默认值的2倍。
ExtractPackets()存入packet_list的音频报文是严格时戳递增的(相邻报文的时戳相差一个编码的采集周期),且所有报文都是一种编码格式,如都为Opus编码。函数在取出最后一个音频报文之后,会将Packet Buffer中时戳小于该报文的缓存全部清理掉。
值得注意的是,本函数除了读取音频报文之外,还做了两件事:
- nack_->UpdateLastDecodedPacket
- stats_->JitterBufferDelay
int NetEqImpl::ExtractPackets(size_t required_samples,
PacketList* packet_list) {
bool first_packet = true;
bool next_packet_available = false;
const Packet* next_packet = packet_buffer_->PeekNextPacket();
RTC_DCHECK(next_packet);
if (!next_packet) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "Packet buffer unexpectedly empty.";
return -1;
}
uint32_t first_timestamp = next_packet->timestamp;
size_t extracted_samples = 0;
// Packet extraction loop.
do {
/*timestamp_记录下一个音频报文的时间戳*/
timestamp_ = next_packet->timestamp;
absl::optional<Packet> packet = packet_buffer_->GetNextPacket();
// `next_packet` may be invalid after the `packet_buffer_` operation.
next_packet = nullptr;
if (!packet) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "Should always be able to extract a packet here";
RTC_DCHECK_NOTREACHED(); // Should always be able to extract a packet
// here.
return -1;
}
const uint64_t waiting_time_ms = packet->waiting_time->ElapsedMs();
stats_->StoreWaitingTime(waiting_time_ms);
RTC_DCHECK(!packet->empty());
if (first_packet) {
first_packet = false;
if (nack_enabled_) {
RTC_DCHECK(nack_);
// TODO(henrik.lundin): Should we update this for all decoded packets?
nack_->UpdateLastDecodedPacket(packet->sequence_number,
packet->timestamp);
}
}
const bool has_cng_packet =
decoder_database_->IsComfortNoise(packet->payload_type);
// Store number of extracted samples.
size_t packet_duration = 0;
if (packet->frame) {
packet_duration = packet->frame->Duration();
// TODO(ossu): Is this the correct way to track Opus FEC packets?
if (packet->priority.codec_level > 0) {
stats_->SecondaryDecodedSamples(
rtc::dchecked_cast<int>(packet_duration));
}
} else if (!has_cng_packet) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Unknown payload type "
<< static_cast<int>(packet->payload_type);
RTC_DCHECK_NOTREACHED();
}
if (packet_duration == 0) {
// Decoder did not return a packet duration. Assume that the packet
// contains the same number of samples as the previous one.
packet_duration = decoder_frame_length_/*一个采样周期内的采样点个数*/;
}
/*计算当前报文之后的下一个报文的起始时戳:
* 当前报文相对本地操作读取的第一个报文的时戳偏移+一个采样周期内的采样点个数
*/
extracted_samples = packet->timestamp - first_timestamp + packet_duration;
RTC_DCHECK(controller_);
stats_->JitterBufferDelay(packet_duration, waiting_time_ms,
controller_->TargetLevelMs(),
controller_->UnlimitedTargetLevelMs());
// Check what packet is available next.
/*判断是否还存在需要读取的音频报文:
*1)缓存中还存在要读取的报文; 2)要读取的报文类型和之前一致,例如都为Opus;
*3)要读取的报文的时间戳和当前取出的报文只相差一个编码的采集周期(例如20ms);
*4)没有CNG(舒适背景噪音)报文
*/
next_packet = packet_buffer_->PeekNextPacket();
next_packet_available =
next_packet && next_packet->payload_type == packet->payload_type &&
next_packet->timestamp == packet->timestamp + packet_duration &&
!has_cng_packet;
packet_list->push_back(std::move(*packet)); // Store packet in list.
packet = absl::nullopt; // Ensure it's never used after the move.
/*如果还有报文可取且需要的累计采样点个数不够,则继续读取报文*/
} while (extracted_samples < required_samples && next_packet_available);
/*若从缓存中真实地取出了音频报文,
*则尝试将所有过期的音频报文全部清除
*/
if (extracted_samples > 0) {
// Delete old packets only when we are going to decode something. Otherwise,
// we could end up in the situation where we never decode anything, since
// all incoming packets are considered too old but the buffer will also
// never be flooded and flushed.
/*将缓存中所有时戳小于timestamp_的报文全部删掉
*(timestamp_记录了下一个要取的音频报文的时间戳)
*/
packet_buffer_->DiscardAllOldPackets(timestamp_, stats_.get());
}
return rtc::dchecked_cast<int>(extracted_samples);
}3.4.3. NetEqImpl::Decode
音频解码模块从NetEqImpl::packet_buffer_中取出报文,调用解码器对其解码,解码后的数据存入NetEqImpl::decode_buffer_中。
NetEq负责音频解码的函数为NetEqImpl::Decode(),该函数根据operation的不同,对packet_list的音频报文做不同的处理(packet_list就是NetEqImpl::ExtractPackets()从Packet Buffer中取出的音频报文):
- Operation::kMerge:执行编码器对应的DecodePlc()。这个行为只在iLBC编码器下会出现,其他编码器都不会执行。对于Opus而言,会在在WebRtcOpus_Decode()内部执行PLC解码;
- Operation::kCodecInternalCng:舒适噪音相关,执行DecodeCng();
- Else: 执行DecodeLoop(),根据编码器类型选择不同的解码调用。
NetEqImpl的初始化函数申请了一块内存(由decoded_buffer_指向该内存块首地址),长度为5760*sizeof(int16_t),可存放48K采样率/单声道120ms的PCM数据,这块内存用于音频解码后的数据存放并循环利用。注意,如果是双声道,在同样的采样率和采样周期下,PCM数据的大小是单声道的2倍。
NetEqImpl::NetEqImpl(const NetEq::Config& config,
Dependencies&& deps,
bool create_components)
: ...
decoded_buffer_length_(kMaxFrameSize/*5760,120 ms @ 48 kHz*/),
decoded_buffer_(new int16_t[decoded_buffer_length_])...{
...
}int NetEqImpl::Decode(PacketList* packet_list,
Operation* operation,
int* decoded_length,
AudioDecoder::SpeechType* speech_type) {
*speech_type = AudioDecoder::kSpeech;
// When packet_list is empty, we may be in kCodecInternalCng mode, and for
// that we use current active decoder.
AudioDecoder* decoder = decoder_database_->GetActiveDecoder();
...
*decoded_length = 0;
// Update codec-internal PLC state.
/*decoder->HasDecodePlc()在iLBC编码时Return True,其他编码器都Return False*/
if ((*operation == Operation::kMerge) && decoder && decoder->HasDecodePlc()) {
/*对于iLBC而言,Call AudioDecoderIlbcImpl::DecodePlc()
*对于Opus而言,在WebRtcOpus_Decode()里面执行PLC
*/
decoder->DecodePlc(1, &decoded_buffer_[*decoded_length]);
}
int return_value;
if (*operation == Operation::kCodecInternalCng) {
RTC_DCHECK(packet_list->empty());
return_value = DecodeCng(decoder, decoded_length, speech_type);
} else {
return_value = DecodeLoop(packet_list, *operation, decoder, decoded_length,
speech_type);
}
...
return return_value;
}对音频数据调用解码器执行解码任务的具体函数是NetEqImpl::DecodeLoop(),顾名思义,这个函数实现了对音频报文的批处理。在函数第12行代码根据编码类型选择不同的解码器执行Decode任务,具体实现为packet_list中的每个EncodedAudioFrame都有实际的继承类,如OpusFrame,继承类实现了EncodedAudioFrame::Decode()这个虚函数。
int NetEqImpl::DecodeLoop(PacketList* packet_list,
const Operation& operation,
AudioDecoder* decoder,
int* decoded_length,
AudioDecoder::SpeechType* speech_type) {
// Do decoding.
while (!packet_list->empty() && !decoder_database_->IsComfortNoise(
packet_list->front().payload_type)) {
/*std::unique_ptr<AudioDecoder::EncodedAudioFrame> frame;
*根据音频格式的不同,对应不同的继承类,例如OpusFrame
*/
auto opt_result = packet_list->front().frame->Decode(
rtc::ArrayView<int16_t>(&decoded_buffer_[*decoded_length],
decoded_buffer_length_ - *decoded_length));
if (packet_list->front().packet_info) {
last_decoded_packet_infos_.push_back(*packet_list->front().packet_info);
}
packet_list->pop_front();
if (opt_result) {/*音频解码成功*/
const auto& result = *opt_result;
*speech_type = result.speech_type;
if (result.num_decoded_samples > 0) {
/*result.num_decoded_samples存放的是当前已解码的音频报文的*/
*decoded_length += rtc::dchecked_cast<int>(result.num_decoded_samples);
// Update `decoder_frame_length_` with number of samples per channel.
decoder_frame_length_ =
result.num_decoded_samples / decoder->Channels();
}
} else {
// Error.
// TODO(ossu): What to put here?
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Decode error";
*decoded_length = -1;
last_decoded_packet_infos_.clear();
packet_list->clear();
break;
}
if (*decoded_length > rtc::dchecked_cast<int>(decoded_buffer_length_)) {
// Guard against overflow.
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Decoded too much.";
packet_list->clear();
return kDecodedTooMuch;
}
} // End of decode loop.
return 0;
}OpusFrame实现了Decode()函数,由于Opus支持带内FEC,所以本函数要先判断当前Frame是原始报文,还是FEC,并做不同的处理。
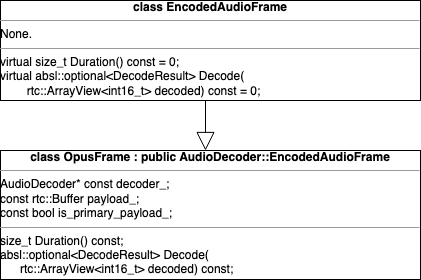
class OpusFrame : public AudioDecoder::EncodedAudioFrame {
public:
...
absl::optional<DecodeResult> Decode(
rtc::ArrayView<int16_t> decoded) const override {
AudioDecoder::SpeechType speech_type = AudioDecoder::kSpeech;
int ret;
if (is_primary_payload_) {
ret = decoder_->Decode(
payload_.data(), payload_.size(), decoder_->SampleRateHz(),
decoded.size() * sizeof(int16_t), decoded.data(), &speech_type);
} else {
ret = decoder_->DecodeRedundant(
payload_.data(), payload_.size(), decoder_->SampleRateHz(),
decoded.size() * sizeof(int16_t), decoded.data(), &speech_type);
}
if (ret < 0){
return absl::nullopt;
}
return DecodeResult{static_cast<size_t>(ret), speech_type};
}
...
}如果是原始报文的解码,则先计算该Frame的采样周期(例如20ms一帧音频数据),采样周期(Packet Duration)*采样率(Sample Rate)*通道数(Channels)*一个采样点占用的字节数(sizeof(int16_t))=解码后PCM数据的占用空间,如果该字节数大于解码缓存的剩余空间则直接返回错误,否则调用WebRtcOpus_Decode()完成Opus解码工作。
对In-Band FEC报文的解码思路同上。这部分的细节放在“Opus带内FEC”部分详细讲解。

int AudioDecoder::Decode(const uint8_t* encoded,
size_t encoded_len,
int sample_rate_hz,
size_t max_decoded_bytes,
int16_t* decoded,
SpeechType* speech_type) {
rtc::MsanCheckInitialized(rtc::MakeArrayView(encoded, encoded_len));
int duration = PacketDuration(encoded, encoded_len);
if (duration >= 0 &&
duration * Channels() * sizeof(int16_t) > max_decoded_bytes) {
return -1;
}
return DecodeInternal(encoded, encoded_len, sample_rate_hz, decoded,
speech_type);
}int AudioDecoderOpusImpl::DecodeInternal(const uint8_t* encoded,
size_t encoded_len,
int sample_rate_hz,
int16_t* decoded,
SpeechType* speech_type) {
int16_t temp_type = 1; // Default is speech.
int ret =
WebRtcOpus_Decode(dec_state_, encoded, encoded_len, decoded, &temp_type);
if (ret > 0)
ret *= static_cast<int>(channels_); // Return total number of samples.
*speech_type = ConvertSpeechType(temp_type);
return ret;
}WebRtcOpus_Decode()同时处理PLC和音频帧解码的工作(待解码的数据为NULL则自动执行PLC)。
int WebRtcOpus_Decode(OpusDecInst* inst,
const uint8_t* encoded,
size_t encoded_bytes,
int16_t* decoded,
int16_t* audio_type) {
int decoded_samples;
if (encoded_bytes == 0) {
*audio_type = DetermineAudioType(inst, encoded_bytes);
decoded_samples = DecodePlc(inst, decoded);
} else {
decoded_samples = DecodeNative(inst, encoded, encoded_bytes,
MaxFrameSizePerChannel(inst->sample_rate_hz),
decoded, audio_type, 0);
}
if (decoded_samples < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (inst->plc_use_prev_decoded_samples) {
/* Update decoded sample memory, to be used by the PLC in case of losses. */
inst->prev_decoded_samples = decoded_samples;
}
return decoded_samples;
}DecodePlc()旨在调用Opus的库函数opus_decode()生成PLC模拟采样点,此时传入opus_decode()的buffer和length分别为NULL和0,Opus根据这两个参数确定是执行PLC操作,而不是解码音频帧。
static int DecodePlc(OpusDecInst* inst, int16_t* decoded) {
int16_t audio_type = 0;
int decoded_samples;
/*计算10ms采样周期下单声道产生的采样点个数*/
int plc_samples =
FrameSizePerChannel(kWebRtcOpusPlcFrameSizeMs/*10*/, inst->sample_rate_hz);
if (inst->plc_use_prev_decoded_samples) {
/* The number of samples we ask for is `number_of_lost_frames` times
* `prev_decoded_samples_`. Limit the number of samples to maximum
* `MaxFrameSizePerChannel()`. */
plc_samples = inst->prev_decoded_samples;
/*计算120ms采样周期下单声道产生的采样点个数*/
const int max_samples_per_channel =
MaxFrameSizePerChannel(inst->sample_rate_hz);
/*取上次plc采样点的个数和最大采样点个数的较小值*/
plc_samples = plc_samples <= max_samples_per_channel
? plc_samples
: max_samples_per_channel;
}
/*执行opus_decode(),插入plc模拟采样点*/
decoded_samples =
DecodeNative(inst, NULL, 0, plc_samples, decoded, &audio_type, 0);
if (decoded_samples < 0) {
return -1;
}
/*返回采样点个数*/
return decoded_samples;
}DecodeNative()调用Opus库函数opus_decode(),对音频帧做解码,入参frame_size是根据采样周期和采样率得出的单个声道的采样点的个数,decoded指向的内存块的大小不小于frame_size(该帧音频在单个声道下的采样点个数) * sizeof(int16_t)*声道数,否则会出现解码失败。该函数的返回值是解码后的采样点的总个数(如果是双声道,则包含两个声道的采样点)。
/* `frame_size` is set to maximum Opus frame size in the normal case, and
* is set to the number of samples needed for PLC in case of losses.
* It is up to the caller to make sure the value is correct.
*/
static int DecodeNative(OpusDecInst* inst,
const uint8_t* encoded,
size_t encoded_bytes,
int frame_size,
int16_t* decoded,
int16_t* audio_type,
int decode_fec) {
int res = -1;
if (inst->decoder) {
/*Decode an Opus frame.
*Returns Number of decoded samples or Error codes
*/
res = opus_decode(
inst->decoder, encoded, static_cast<opus_int32>(encoded_bytes),
reinterpret_cast<opus_int16*>(decoded), frame_size, decode_fec);
} else {
res = opus_multistream_decode(inst->multistream_decoder, encoded,
static_cast<opus_int32>(encoded_bytes),
reinterpret_cast<opus_int16*>(decoded),
frame_size, decode_fec);
}
if (res <= 0){
return -1;
}
*audio_type = DetermineAudioType(inst, encoded_bytes);
return res;
}The End.

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容





所有评论(0)