喂到嘴边了!基于OceanBase构建RAG,保姆级教程,代码直接抄!
本文又是一篇喂饭级教程,会由公博大佬为大家展示通过 OceanBase seekdb 构建 RAG(检索增强生成)系统的详细步骤。
本文又是一篇喂饭级教程,会由公博大佬为大家展示通过 OceanBase seekdb 构建 RAG(检索增强生成)系统的详细步骤。
欢迎大家关注 OceanBase 社区公众号 “老纪的技术唠嗑局”,在这个公众号中,会持续为大家更新与 #数据库、#AI、#OceanBase 相关的技术内容!
RAG 系统结合了检索系统和生成模型,可根据给定提示生成新文本。系统首先使用 seekdb 的原生向量搜索功能从语料库中检索相关文档,然后使用生成模型根据检索到的文档生成新文本。
前提条件
- 已安装 Python 3.11 或以上版本
- 已安装 uv
- 已准备好 LLM API Key
一、准备工作
1.克隆代码
git clone https://github.com/oceanbase/pyseekdb.gitcd pyseekdb/demo/rag
2.设置环境
安装依赖
基础安装(适用于 default 或 api embedding 类型):
uv sync
本地模型(适用于 local embedding 类型):
uv sync --extra local
提示:
local额外依赖包含sentence-transformers及相关依赖(约 2-3 GB)。- 如果您在中国大陆,可以使用国内镜像源加速下载:
- 基础安装(清华源):
uv sync --index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple - 基础安装(阿里源):
uv sync --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple - 本地模型(清华源):
uv sync --extra local --index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple - 本地模型(阿里源):
uv sync --extra local --index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
设置环境变量
步骤一:复制环境变量模板
cp .env.example .env
步骤二:编辑 .env 文件,设置环境变量
本系统支持三种 Embedding 函数类型,您可以根据需求选择:
default(默认,推荐新手使用)
- 使用 pyseekdb 自带的
DefaultEmbeddingFunction(基于 ONNX) - 首次使用会自动下载模型,无需配置 API Key
- 适合本地开发和测试
local(本地模型)
- 使用自定义的
sentence-transformers模型 - 需要安装
sentence-transformers库 - 可配置模型名称和设备(CPU/GPU)
api(API 服务)
- 使用 OpenAI 兼容的 Embedding API(如 DashScope、OpenAI 等)
- 需要配置 API Key 和模型名称
- 适合生产环境
以下使用通义千问作为示例(使用 api 类型):
# Embedding Function 类型:api, local, defaultEMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=api# LLM 配置(用于生成答案)OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-your-dashscope-keyOPENAI_BASE_URL=https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1OPENAI_MODEL_NAME=qwen-plus# Embedding API 配置(仅在 EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=api 时需要)EMBEDDING_API_KEY=sk-your-dashscope-keyEMBEDDING_BASE_URL=https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME=text-embedding-v4# 本地模型配置(仅在 EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=local 时需要)SENTENCE_TRANSFORMERS_MODEL_NAME=all-mpnet-base-v2SENTENCE_TRANSFORMERS_DEVICE=cpu# seekdb 配置SEEKDB_DIR=./data/seekdb_ragSEEKDB_NAME=testCOLLECTION_NAME=embeddings
环境变量说明:
| 变量名 | 说明 | 默认值/示例值 | 必需条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE | Embedding 函数类型 | default (可选:api , local , default ) |
必须设置 |
| OPENAI_API_KEY | LLM API Key(支持 OpenAI、通义千问等兼容服务) | 必须设置 | 必须设置(用于生成答案) |
| OPENAI_BASE_URL | LLM API 基础 URL | https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1[1] | 可选 |
| OPENAI_MODEL_NAME | 语言模型名称 | qwen-plus | 可选 |
| EMBEDDING_API_KEY | Embedding API Key | - | EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=api 时必需 |
| EMBEDDING_BASE_URL | Embedding API 基础 URL | https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1[2] | EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=api 时可选 |
| EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME | Embedding 模型名称 | text-embedding-v4 | EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=api 时必需 |
| SENTENCE_TRANSFORMERS_MODEL_NAME | 本地模型名称 | all-mpnet-base-v2 | EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=local 时可选 |
| SENTENCE_TRANSFORMERS_DEVICE | 运行设备 | cpu | EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=local 时可选 |
| SEEKDB_DIR | seekdb 数据库目录 | ./data/seekdb_rag | 可选 |
| SEEKDB_NAME | 数据库名称 | test | 可选 |
| COLLECTION_NAME | 嵌入表名称 | embeddings | 可选 |
提示:
- 如果使用
default类型,只需配置EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE=default和 LLM 相关变量即可。 - 如果使用
api类型,需要额外配置 Embedding API 相关变量。 - 如果使用
local类型,需要安装sentence-transformers库,并可选择配置模型名称。
二、主要使用的模块
1.初始化 LLM 客户端
我们通过加载环境变量来初始化 LLM 客户端:
def get_llm_client() -> OpenAI: """Initialize LLM client using OpenAI-compatible API.""" return OpenAI( api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"), base_url=os.getenv("OPENAI_BASE_URL"), )
2.创建数据库连接
def get_seekdb_client(db_dir: str = "./seekdb_rag", db_name: str = "test"): """Initialize seekdb client (embedded mode).""" cache_key = (db_dir, db_name) if cache_key not in _client_cache: print(f"Connecting to seekdb: path={db_dir}, database={db_name}") _client_cache[cache_key] = Client(path=db_dir, database=db_name) print("seekdb client connected successfully") return _client_cache[cache_key]
3.自定义嵌入模型的工厂模式
在 .env 文件中可以通过配置 EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE 使用不同的 embedding_function。您也可以参考这个例子自定义您的 embedding_function。
from pyseekdb import EmbeddingFunction, DefaultEmbeddingFunctionfrom typing import List, Unionimport osfrom openai import OpenAIDocuments = Union[str, List[str]]Embeddings = List[List[float]]class SentenceTransformerCustomEmbeddingFunction(EmbeddingFunction[Documents]): """ A custom embedding function using sentence-transformers with a specific model. """ def __init__(self, model_name: str = "all-mpnet-base-v2", device: str = "cpu"):# TODO: your own model name and device """ Initialize the sentence-transformer embedding function. Args: model_name: Name of the sentence-transformers model to use device: Device to run the model on ('cpu' or 'cuda') """ self.model_name = model_name or os.environ.get('SENTENCE_TRANSFORMERS_MODEL_NAME') self.device = device or os.environ.get('SENTENCE_TRANSFORMERS_DEVICE') self._model = None self._dimension = None def _ensure_model_loaded(self): """Lazy load the embedding model""" if self._model isNone: try: from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer self._model = SentenceTransformer(self.model_name, device=self.device) # Get dimension from model test_embedding = self._model.encode(["test"], convert_to_numpy=True) self._dimension = len(test_embedding[0]) except ImportError: raise ImportError( "sentence-transformers is not installed. " "Please install it with: pip install sentence-transformers" ) @property def dimension(self) -> int: """Get the dimension of embeddings produced by this function""" self._ensure_model_loaded() return self._dimension def __call__(self, input: Documents) -> Embeddings: """ Generate embeddings for the given documents. Args: input: Single document (str) or list of documents (List[str]) Returns: List of embedding vectors """ self._ensure_model_loaded() # Handle single string input if isinstance(input, str): input = [input] # Handle empty input ifnot input: return [] # Generate embeddings embeddings = self._model.encode( input, convert_to_numpy=True, show_progress_bar=False ) # Convert numpy arrays to lists return [embedding.tolist() for embedding in embeddings]class OpenAIEmbeddingFunction(EmbeddingFunction[Documents]): """ A custom embedding function using Embedding API. """ def __init__(self, model_name: str = "", api_key: str = "", base_url: str = ""): """ Initialize the Embedding API embedding function. Args: model_name: Name of the Embedding API embedding model api_key: Embedding API key (if not provided, uses EMBEDDING_API_KEY env var) """ self.model_name = model_name or os.environ.get('EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME') self.api_key = api_key or os.environ.get('EMBEDDING_API_KEY') self.base_url = base_url or os.environ.get('EMBEDDING_BASE_URL') self._dimension = None ifnot self.api_key: raise ValueError("Embedding API key is required") def _ensure_model_loaded(self): """Lazy load the Embedding API model""" try: client = OpenAI( api_key=self.api_key, base_url=self.base_url ) response = client.embeddings.create( model=self.model_name, input=["test"] ) self._dimension = len(response.data[0].embedding) except Exception as e: raise ValueError(f"Failed to load Embedding API model: {e}") @property def dimension(self) -> int: """Get the dimension of embeddings produced by this function""" self._ensure_model_loaded() return self._dimension def __call__(self, input: Documents) -> Embeddings: """ Generate embeddings using Embedding API. Args: input: Single document (str) or list of documents (List[str]) Returns: List of embedding vectors """ # Handle single string input if isinstance(input, str): input = [input] # Handle empty input ifnot input: return [] # Call Embedding API client = OpenAI( api_key=self.api_key, base_url=self.base_url ) response = client.embeddings.create( model=self.model_name, input=input ) # Extract Embedding API embeddings embeddings = [item.embedding for item in response.data] return embeddingsdef create_embedding_function() -> EmbeddingFunction: embedding_function_type = os.environ.get('EMBEDDING_FUNCTION_TYPE') if embedding_function_type == "api": print("Using OpenAI Embedding API embedding function") return OpenAIEmbeddingFunction() elif embedding_function_type == "local": print("Using SentenceTransformer embedding function") return SentenceTransformerCustomEmbeddingFunction() elif embedding_function_type == "default": print("Using Default embedding function") return DefaultEmbeddingFunction() else: raise ValueError(f"Unsupported embedding function type: {embedding_function_type}")
4.创建 Collection
在 get_or_create_collection() 方法中我们传入了 embedding_function,之后使用这个 collection 的 add() 和 query() 方法的时候就不需要传入向量了,只需传入文本,向量会由 embedding_function 自动生成。
def get_seekdb_collection(client, collection_name: str = "embeddings", embedding_function: Optional[EmbeddingFunction] = DefaultEmbeddingFunction(), drop_if_exists: bool = True): """ Get or create a collection using pyseekdb's get_or_create_collection. Args: client: seekdb client instance collection_name: Name of the collection embedding_function: Embedding function (required for automatic embedding generation) drop_if_exists: Whether to drop existing collection if it exists Returns: Collection object """ if drop_if_exists and client.has_collection(collection_name): print(f"Collection '{collection_name}' already exists, deleting old data...") client.delete_collection(collection_name) if embedding_function isNone: raise ValueError("embedding_function is required") # Use pyseekdb's native get_or_create_collection collection = client.get_or_create_collection( name=collection_name, embedding_function=embedding_function ) print(f"Collection '{collection_name}' ready!") return collection
5.核心插入数据函数
def insert_embeddings(collection, data: List[Dict[str, Any]]): """ Insert data into collection. Embeddings are automatically generated by collection's embedding_function. Args: collection: Collection object (must have embedding_function configured) data: List of data dictionaries containing 'text', 'source_file', 'chunk_index' """ try: ids = [f"{item['source_file']}_{item.get('chunk_index', 0)}"for item in data] documents = [item['text'] for item in data] metadatas = [{'source_file': item['source_file'], 'chunk_index': item.get('chunk_index', 0)} for item in data] # Collection's embedding_function will automatically generate embeddings from documents collection.add( ids=ids, documents=documents, metadatas=metadatas ) print(f"Inserted {len(data)} items successfully") except Exception as e: print(f"Error inserting data: {e}") raise
6.向量相似度搜索
results = collection.query( query_texts=[question], n_results=3, include=["documents", "metadatas", "distances"] )
7.统计 Collection 中的数据情况
def get_database_stats(collection) -> Dict[str, Any]: """Get statistics about the collection.""" try: results = collection.get(limit=10000, include=["metadatas"]) ids = results.get('ids', []) if isinstance(results, dict) else [] metadatas = results.get('metadatas', []) if isinstance(results, dict) else [] unique_files = {m.get('source_file') for m in metadatas if m and m.get('source_file')} return { "total_embeddings": len(ids), "unique_source_files": len(unique_files) } except Exception as e: print(f"Error getting database stats: {e}") return {"total_embeddings": 0, "unique_source_files": 0}
三、构建 RAG 系统
本模块实现了 RAG 系统的检索功能。通过将用户提出的问题转换为嵌入向量,利用 seekdb 提供的原生向量搜索能力,快速检索出与问题最相关的文档片段,为后续的生成模型提供必要的上下文信息。
1.导入数据
我们使用 pyseekdb 的 SDK 文档作为示例,您也可以使用自己的 Markdown 文档或者目录。
运行数据导入脚本:
# 导入单个文档uv run python seekdb_insert.py ../../README.md# 或导入目录下的所有 Markdown 文档uv run python seekdb_insert.py path/to/your_dir
2.启动应用
在 <font style="background-color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.06);">pyseekdb/demo/rag 路径下执行如下命令,通过 Streamlit 启动应用:
uv run streamlit run seekdb_app.py --server.port your_port
使用 IP 和端口号(默认为 8501,可通过 --server.port 选项自定义)即可在浏览器中打开 RAG 界面。
提示: 如果使用
uv作为包管理器,请在命令前加上uv run前缀,以确保使用正确的 Python 环境和依赖。
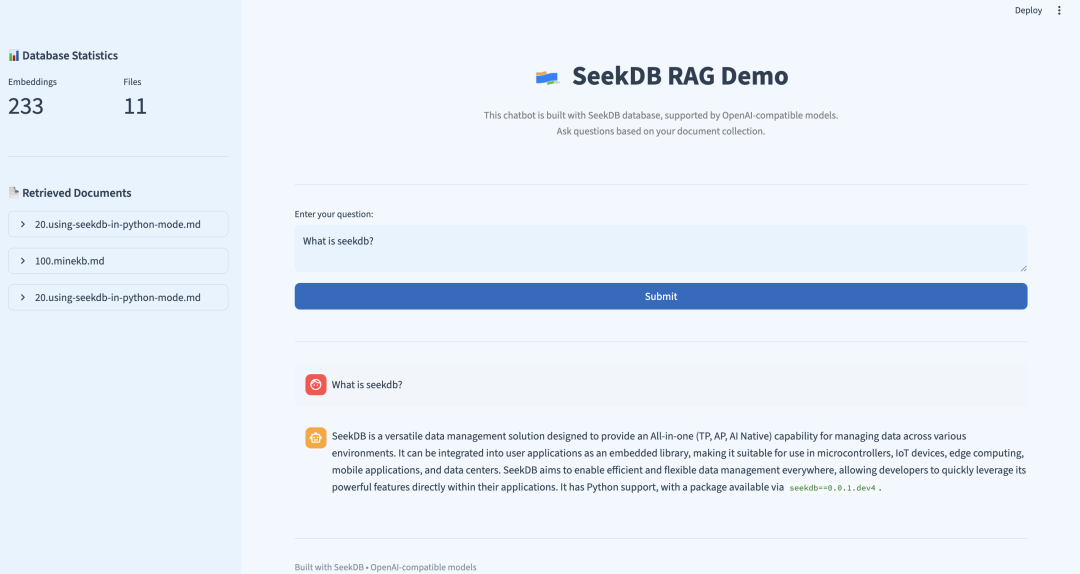
四、实际运行示例
以下是一个真实的查询示例,展示了 seekdb RAG 系统的实际效果:
用户问题:“What is seekdb’s vector search?”
检索到的相关文档:
1. 30.experience-vector-retrieval.md Vector search overview In today's era of information explosion, users often need to quickly retrieve the information they need from massive amounts o...2. 20.using-seekdb-in-python-mode.md Experience vector search SeekDB supports up to 16,000 dimensions of float-type dense vectors, sparse vectors, and various types of vector distance ca...3. 70.experience-hybrid-vector-index.md Summary Through this tutorial, you have mastered the core features of SeekDB's hybrid vector index: Simplified usage process: Achieve semantic ret...
使用 LLM 生成的答案:
SeekDB’s vector search is a powerful feature that enables efficient and accurate retrieval of data by encoding various types of data—such as text, images, and audio—into mathematical vectors and performing searches in a vector space. This approach captures deep semantic relationships within the data, going beyond traditional keyword-based search methods to deliver more relevant results.
Key capabilities of SeekDB’s vector search include:
- High-dimensional vector support: It supports up to 16,000 dimensions for float-type dense vectors and sparse vectors.
- Multiple distance metrics: It supports various similarity or distance calculations, including Manhattan distance, Euclidean distance, inner product, and cosine distance.
- Advanced indexing methods: Vector indexes can be created using HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) or IVF (Iterative Virtual File), enabling fast approximate nearest neighbor searches.
- Incremental updates: The system allows for real-time insertion and deletion of vectors without compromising search accuracy or recall.
- Hybrid search with scalar filtering: Users can combine vector similarity search with traditional attribute-based (scalar) filtering for more precise results.
- Flexible access interfaces: SeekDB supports SQL access via MySQL protocol clients in multiple programming languages, as well as a Python SDK.
- Automatic embedding and hybrid indexing: With hybrid vector index features, users can store raw text directly—the system automatically converts it into vectors and builds indexes.
In summary, SeekDB’s vector search provides a comprehensive, high-performance solution for semantic search, particularly valuable in AI applications involving large-scale unstructured data.
这个示例展示了:
- ✅ 准确的信息检索:系统成功从文档中找到了相关信息
- ✅ 多文档整合:从 3 个不同文档中提取和整合信息
- ✅ 语义匹配:准确匹配了“vector search”相关的文档
- ✅ 结构化回答:AI 将检索到的信息整理成清晰的结构
- ✅ 完整性:涵盖了 seekdb 向量搜索的主要特性
- ✅ 专业性:回答包含了技术细节和实际应用价值
检索质量分析:
- 最相关文档 :
experience-vector-retrieval.md- 向量搜索概览 - 技术细节 :
using-seekdb-in-python-mode.md- 具体的技术规格 - 高级特性 :
experience-hybrid-vector-index.md- 混合向量索引功能
那么,如何系统的去学习大模型LLM?
作为一名深耕行业的资深大模型算法工程师,我经常会收到一些评论和私信,我是小白,学习大模型该从哪里入手呢?我自学没有方向怎么办?这个地方我不会啊。如果你也有类似的经历,一定要继续看下去!这些问题啊,也不是三言两语啊就能讲明白的。
所以我综合了大模型的所有知识点,给大家带来一套全网最全最细的大模型零基础教程。在做这套教程之前呢,我就曾放空大脑,以一个大模型小白的角度去重新解析它,采用基础知识和实战项目相结合的教学方式,历时3个月,终于完成了这样的课程,让你真正体会到什么是每一秒都在疯狂输出知识点。
由于篇幅有限,⚡️ 朋友们如果有需要全套 《2025全新制作的大模型全套资料》,扫码获取~
👉大模型学习指南+路线汇总👈
我们这套大模型资料呢,会从基础篇、进阶篇和项目实战篇等三大方面来讲解。

👉①.基础篇👈
基础篇里面包括了Python快速入门、AI开发环境搭建及提示词工程,带你学习大模型核心原理、prompt使用技巧、Transformer架构和预训练、SFT、RLHF等一些基础概念,用最易懂的方式带你入门大模型。
👉②.进阶篇👈
接下来是进阶篇,你将掌握RAG、Agent、Langchain、大模型微调和私有化部署,学习如何构建外挂知识库并和自己的企业相结合,学习如何使用langchain框架提高开发效率和代码质量、学习如何选择合适的基座模型并进行数据集的收集预处理以及具体的模型微调等等。
👉③.实战篇👈
实战篇会手把手带着大家练习企业级的落地项目(已脱敏),比如RAG医疗问答系统、Agent智能电商客服系统、数字人项目实战、教育行业智能助教等等,从而帮助大家更好的应对大模型时代的挑战。
👉④.福利篇👈
最后呢,会给大家一个小福利,课程视频中的所有素材,有搭建AI开发环境资料包,还有学习计划表,几十上百G素材、电子书和课件等等,只要你能想到的素材,我这里几乎都有。我已经全部上传到CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】
相信我,这套大模型系统教程将会是全网最齐全 最易懂的小白专用课!!

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献357条内容
已为社区贡献357条内容





所有评论(0)