WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第三部分-接收端
音频模块是WebRTC非常重要的部分,音频模块中的NetEq是WebRTC的三大核心技术(NetEq/GCC/音频3A)之一,我们分五部分介绍该模块,本文是第三部分(接收端)。WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第一部分-整体介绍WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第二部分-发送端WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第三部分-接收端WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第四部分-NetEqWebRTC音频模块详细介绍第五部分-体验
1. 前言
音频模块是WebRTC非常重要的部分,音频模块中的NetEq是WebRTC的三大核心技术(NetEq/GCC/音频3A)之一,我们分七部分介绍该模块,本文是第三部分(接收端)。这个专题包括:
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第一部分-整体介绍
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第二部分-发送端
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第三部分-接收端
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第四部分-NetEq核心原理
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第五部分-NetEq音频决策
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第六部分-NetEq数字信号处理
- WebRTC音频模块详细介绍第七部分-体验保障
2. 音频报文的网络接收
2.1. 调用堆栈
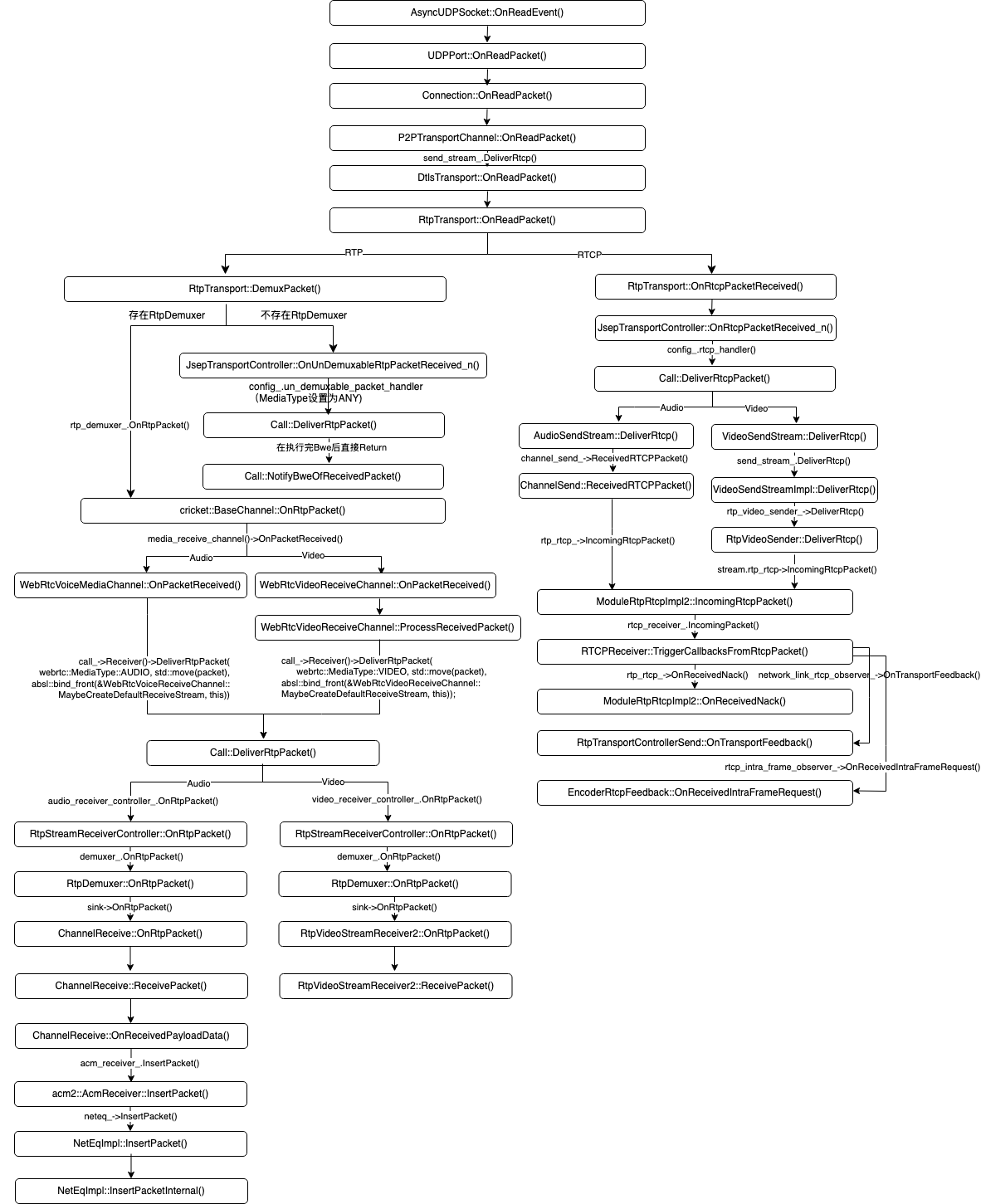
2.2. 流程详解
WebRTC在收到音频的RTP报文之后,会先做反序列化的工作,然后将网络中收到的音频数据(如Opus编码后的数据)送入NetEq,在NetEq完成抖动消除(Jitter Buffer)、丢包隐藏(PLC)和解码工作。
ChannelReceive::OnReceivedPayloadData()最重要的事情是将反序列化后的RTP报文存入NetEq的Packet Buffer中,音频播放线程会从该Packet中取出报文做播放。此外,该函数在将报文存入NetEq的Packet Buffer之前,先做了NACK和RED的处理,这部分请参阅音频NACK和RED的相关章节。
void ChannelReceive::OnReceivedPayloadData(
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload,
const RTPHeader& rtpHeader) {
...
// Push the incoming payload (parsed and ready for decoding) into the ACM
/*Call acm2::AcmReceiver::InsertPacket()*/
if (acm_receiver_.InsertPacket(rtpHeader, payload) != 0) {
RTC_DLOG(LS_ERROR) << "ChannelReceive::OnReceivedPayloadData() unable to "
"push data to the ACM";
return;
}
TimeDelta round_trip_time = rtp_rtcp_->LastRtt().value_or(TimeDelta::Zero());
std::vector<uint16_t> nack_list =
acm_receiver_.GetNackList(round_trip_time.ms());
if (!nack_list.empty()) {
// Can't use nack_list.data() since it's not supported by all
// compilers.
ResendPackets(&(nack_list[0]), static_cast<int>(nack_list.size()));
}
}int AcmReceiver::InsertPacket(const RTPHeader& rtp_header,
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> incoming_payload) {
...
/*Call NetEqImpl::InsertPacket()*/
if (NetEq_->InsertPacket(rtp_header, incoming_payload) < 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "AcmReceiver::InsertPacket "
<< static_cast<int>(rtp_header.payloadType)
<< " Failed to insert packet";
return -1;
}
return 0;
}int NetEqImpl::InsertPacket(const RTPHeader& rtp_header,
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload) {
rtc::MsanCheckInitialized(payload);
MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
if (InsertPacketInternal(rtp_header, payload) != 0) {
return kFail;
}
return kOK;
}
NetEqImpl::InsertPacketInternal()将RTP Header反序列化后得到的字段以及封装成EncodedAudioFrame格式的Payload做一次整体封装(由Packet类管理)后,放入packet_buffer_中,音频播放线程会从该buffer中取走数据。注意:这个函数还处理Nack和RED,这部分我们在相关章节有详细分析。
int NetEqImpl::InsertPacketInternal(const RTPHeader& rtp_header,
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload) {
if (payload.empty()) {
RTC_LOG_F(LS_ERROR) << "payload is empty";
return kInvalidPointer;
}
Timestamp receive_time = clock_->CurrentTime();
stats_->ReceivedPacket();
PacketList packet_list;
// Insert packet in a packet list.
packet_list.push_back([&rtp_header, &payload] {
// Convert to Packet.
Packet packet;
packet.payload_type = rtp_header.payloadType;
packet.sequence_number = rtp_header.sequenceNumber;
packet.timestamp = rtp_header.timestamp;
packet.payload.SetData(payload.data(), payload.size());
return packet;
}());
...
// Store these for later use, since the first packet may very well disappear
// before we need these values.
uint32_t main_timestamp = packet_list.front().timestamp;
uint8_t main_payload_type = packet_list.front().payload_type;
uint16_t main_sequence_number = packet_list.front().sequence_number;
...
/*处理Nack和RED*/
if (nack_enabled_) {
if (update_sample_rate_and_channels) {
nack_->Reset();
}
nack_->UpdateLastReceivedPacket(main_sequence_number, main_timestamp);
}
// Check for RED payload type, and separate payloads into several packets.
if (decoder_database_->IsRed(rtp_header.payloadType)) {
if (!red_payload_splitter_->SplitRed(&packet_list)) {
return kRedundancySplitError;
}
// Only accept a few RED payloads of the same type as the main data,
// DTMF events and CNG.
red_payload_splitter_->CheckRedPayloads(&packet_list, *decoder_database_);
if (packet_list.empty()) {
return kRedundancySplitError;
}
}
...
/*将收到的RTP报文封装成EncodedAudioFrame*/
PacketList parsed_packet_list;
bool is_dtx = false;
while (!packet_list.empty()) {
Packet& packet = packet_list.front();
const DecoderDatabase::DecoderInfo* info =
decoder_database_->GetDecoderInfo(packet.payload_type);
if (!info) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "SplitAudio unknown payload type";
return kUnknownRtpPayloadType;
}
if (info->IsComfortNoise()) {
// Carry comfort noise packets along.
parsed_packet_list.splice(parsed_packet_list.end(), packet_list,
packet_list.begin());
} else {
const uint16_t sequence_number = packet.sequence_number;
const uint8_t payload_type = packet.payload_type;
const Packet::Priority original_priority = packet.priority;
/*将RTP Header反序列化后得到的字段以及封装成EncodedAudioFrame格式的Payload
*整体赋值给Packet实例
*/
auto packet_from_result = [&](AudioDecoder::ParseResult& result) {
Packet new_packet;
new_packet.sequence_number = sequence_number;
new_packet.payload_type = payload_type;
new_packet.timestamp = result.timestamp;
new_packet.priority.codec_level = result.priority;
new_packet.priority.red_level = original_priority.red_level;
// Only associate the header information with the primary packet.
if (new_packet.timestamp == rtp_header.timestamp) {
new_packet.packet_info = RtpPacketInfo(rtp_header, receive_time);
}
new_packet.frame = std::move(result.frame);
return new_packet;
};
/*根据Decoder的不同调用不同的实现函数,
*将RTP Payload封装在EncodedAudioFrame的继承类中,
*在AudioDecoderOpusImpl::ParsePayload()的实现中,
*将RTP Payload封装在OpusFrame中
*Call AudioDecoderIlbcImpl::ParsePayload() or
*AudioDecoderG722Impl::ParsePayload() or
*AudioDecoderOpusImpl::ParsePayload()
*/
std::vector<AudioDecoder::ParseResult> results =
info->GetDecoder()->ParsePayload(std::move(packet.payload),
packet.timestamp);
if (results.empty()) {
packet_list.pop_front();
} else {
bool first = true;
for (auto& result : results) {
is_dtx = is_dtx || result.frame->IsDtxPacket();
if (first) {
// Re-use the node and move it to parsed_packet_list.
packet_list.front() = packet_from_result(result);
parsed_packet_list.splice(parsed_packet_list.end(), packet_list,
packet_list.begin());
first = false;
} else {
parsed_packet_list.push_back(packet_from_result(result));
}
}
}
}
}
...
// Insert packets in buffer.
/*将EncodedAudioFrame格式的报文存入packet_buffer_中
*音频播放线程会从packet_buffer_中取走Audio Frame
*/
const int target_level_ms = controller_->TargetLevelMs();
const int ret = packet_buffer_->InsertPacketList(
&parsed_packet_list, *decoder_database_, ¤t_rtp_payload_type_,
¤t_cng_rtp_payload_type_, stats_.get(), decoder_frame_length_,
last_output_sample_rate_hz_, target_level_ms);
...
return 0;
}AudioDecoder::ParsePayload()由继承类实现,不同音频格式的编码器都实现了该函数,包括AudioDecoderIlbcImpl::ParsePayload()/AudioDecoderG722Impl::ParsePayload()/AudioDecoderOpusImpl::ParsePayload()。这里给出了Opus的实现。
由于Opus支持in-band FEC,所以要先判断RTP Payload是否含有FEC,若含有FEC则拷贝一份payload,构造出一个新的OpusFrame,然后为原始报文构造一个OpusFrame,两个OpusFrame都存入ParseResult中。OpusFrame有三个私有数据:
AudioDecoder* const decoder_;
const rtc::Buffer payload_;
const bool is_primary_payload_;
其中is_primary_payload_为True表示这是Opus的带内FEC,否则为正常的音频数据。
payload存放要解码的数据,而decoder则指向AudioDecoderOpusImpl结构体。理解这一点对我们理解带内FEC解码至关重要。
std::vector<AudioDecoder::ParseResult> AudioDecoderOpusImpl::ParsePayload(
rtc::Buffer&& payload,
uint32_t timestamp) {
std::vector<ParseResult> results;
if (PacketHasFec(payload.data(), payload.size())) {
/*根据音频帧数据和采样率,计算在一个声道上一帧数据的采样点的总个数*/
const int duration =
PacketDurationRedundant(payload.data(), payload.size());
rtc::Buffer payload_copy(payload.data(), payload.size());
std::unique_ptr<EncodedAudioFrame> fec_frame(
new OpusFrame(this, std::move(payload_copy), false));
/*timestamp用单个声道的采样点个数表示,此处要将FEC报文的采样点个数给去掉
*优先级低于原始报文
*/
results.emplace_back(timestamp - duration, 1, std::move(fec_frame));
}
std::unique_ptr<EncodedAudioFrame> frame(
new OpusFrame(this, std::move(payload), true));
/*优先级为0,表示优先级高于FEC报文*/
results.emplace_back(timestamp, 0, std::move(frame));
return results;
}2.3. 音频报文重传
WebRTC在收到音频RTP报文之后,会更新Nack模块并处理RED解码(通过前向冗余对抗网络丢包),再将原始报文或通过RED恢复得到的报文存入NetEq的Packet Buffer,NetEq的播放线程从该Buffer中取帧播放。下表展示了Nack/RED模块和NetEq之间的调用关系,这里先讨论Nack模块,下一章节再讨论RED解码。
|
函数调用关系 |
函数调用语句 |
函数作用 |
|
ChannelReceive::OnReceivedPayloadData() |
将收到的RTP Payload送入NetEq模块 |
|
|
->acm2::AcmReceiver::InsertPacket() |
acm_receiver_.InsertPacket() |
向NetEq的Packet Buffer中插入RTP Payload,此时RTP报文已被解析(反序列化)但并未解码。NetEq的播放线程(ACM模块)从该Buffer中读取RTP Payload,并选择合适的解码器解码,得到PCM数据。 |
|
-->NetEqImpl::InsertPacket() |
NetEq_->InsertPacket() |
|
|
--->NetEqImpl::InsertPacketInternal() |
||
|
---->NackTracker::UpdateLastReceivedPacket() |
nack_->UpdateLastReceivedPacket() |
更新Nack模块维护的丢包序号列表 |
|
---->RedPayloadSplitter::SplitRed() |
red_payload_splitter_->SplitRed() |
解析RED报文,通过冗余数据恢复丢失的原始数据 |
|
->AcmReceiver::GetNackList() |
acm_receiver_.GetNackList() |
获取Nack模块维护的丢包序号列表 |
|
-->NetEqImpl::GetNackList() |
NetEq_->GetNackList() |
|
|
--->NackTracker::GetNackList() |
nack_->GetNackList() |
|
|
->ChannelReceive::ResendPackets() |
通过网络发送Nack请求到媒体发送端,发送端重发在网络中丢失的报文 |
|
|
-->ModuleRtpRtcpImpl2::SendNACK() |
rtp_rtcp_->SendNACK() |
|
|
--->RTCPSender::SendRTCP() |
rtcp_sender_.SendRTCP() |
2.3.1. Nack模块更新
NetEqImpl::InsertPacketInternal()调用NackTracker::UpdateLastReceivedPacket()更新Nack模块,主要的操作包括:
- 更新丢包率统计。Nack模式使用指数加权平滑算法更新丢包率。
- 更新丢包序号列表,将当前报文序号和之前收到的最大报文序号LastSeqNum之间的序号空洞全部记录到该列表中。
假设之前收到的最大报文序号为5,丢包序号列表为{1,3},根据当前报文序号SeqNum的不同,我们分情况讨论:
- 若SeqNum=5,则当前报文为重传报文,直接Return;
- 若SeqNum=3,则将丢包序号列表更新为{1},然后Return;
- 若SeqNum=6,则当前报文和上次收到的最大序号的报文是紧挨着的,此时不产生序号空洞,直接Return;
- 若SeqNum=8,则SeqNum和LastSeqNum之间产生了序号空洞{6,7},此时更新丢包序号列表为{1,6,7}。
对第四种情况,考虑到SeqNum是一个uint16_t类型的整数,存在序号回环现象,所以序号空洞不一定是连续的。例如LastSeqNum=0xFFFE,SeqNum=2,此时的序号空洞为{0xFFFF,0,1}。
int NetEqImpl::InsertPacketInternal(const RTPHeader& rtp_header,
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload) {
...
/*处理Nack和RED*/
if (nack_enabled_) {
if (update_sample_rate_and_channels) {
nack_->Reset();
}
nack_->UpdateLastReceivedPacket(main_sequence_number, main_timestamp);
}
// Check for RED payload type, and separate payloads into several packets.
if (decoder_database_->IsRed(rtp_header.payloadType)) {
if (!red_payload_splitter_->SplitRed(&packet_list)) {
return kRedundancySplitError;
}
// Only accept a few RED payloads of the same type as the main data,
// DTMF events and CNG.
red_payload_splitter_->CheckRedPayloads(&packet_list, *decoder_database_);
if (packet_list.empty()) {
return kRedundancySplitError;
}
}
...
}void NackTracker::UpdateLastReceivedPacket(uint16_t sequence_number,
uint32_t timestamp) {
// Just record the value of sequence number and timestamp if this is the
// first packet.
if (!any_rtp_received_) {
sequence_num_last_received_rtp_ = sequence_number;
timestamp_last_received_rtp_ = timestamp;
any_rtp_received_ = true;
// If no packet is decoded, to have a reasonable estimate of time-to-play
// use the given values.
if (!any_rtp_decoded_) {
sequence_num_last_decoded_rtp_ = sequence_number;
timestamp_last_decoded_rtp_ = timestamp;
}
return;
}
if (sequence_number == sequence_num_last_received_rtp_){/*重传报文,直接丢弃*/
return;
}
// Received RTP should not be in the list.
nack_list_.erase(sequence_number);/*已收到该报文,从丢包序号列表中删除该SeqNum*/
// If this is an old sequence number, no more action is required, return.
if (IsNewerSequenceNumber(sequence_num_last_received_rtp_, sequence_number)){
/*如果当前报文比之前收到的报文要旧(先发后至),此时不会产生新的丢包空洞,
*所以除了在丢包序号列表中删除该报文序号之外,不需要做其他事情
*/
return;
}
/*之前收到的最新的报文序号和当前报文序号之间产生了丢包空洞
*此时需要做两件事:1)更新丢包率统计;2)更新丢包序号列表
*/
UpdatePacketLossRate(sequence_number - sequence_num_last_received_rtp_ - 1);
UpdateList(sequence_number, timestamp);
sequence_num_last_received_rtp_ = sequence_number;
timestamp_last_received_rtp_ = timestamp;
LimitNackListSize();
}/*将之前收到的最大报文序号和当前报文序号之间的序号空洞都存入丢包序列列表中*/
void NackTracker::UpdateList(uint16_t sequence_number_current_received_rtp,
uint32_t timestamp_current_received_rtp) {
/*如果新到报文的序号紧挨着之前收到的报文最大序号,
*那就说明没有产生丢包空洞,直接return即可
*/
if (!IsNewerSequenceNumber(sequence_number_current_received_rtp,
sequence_num_last_received_rtp_ + 1)) {
return;
}
absl::optional<int> samples_per_packet = GetSamplesPerPacket(
sequence_number_current_received_rtp, timestamp_current_received_rtp);
if (!samples_per_packet) {
return;
}
/*将之前收到的最大报文序号和新到的报文序列之间的序号空洞都存入nack_list_中
*由于序号用16比特无符号整数表示,存在序号回环的问题,
*所以序号空洞中的序号有可能是先增大到0xFFFF,再从0开始增长
*/
for (uint16_t n = sequence_num_last_received_rtp_ + 1;
IsNewerSequenceNumber(sequence_number_current_received_rtp, n); ++n) {
uint32_t timestamp = EstimateTimestamp(n, *samples_per_packet);
NackElement nack_element(TimeToPlay(timestamp), timestamp);
nack_list_.insert(nack_list_.end(), std::make_pair(n, nack_element));
}
}2.3.2. 发起Nack请求
根据上述表格描述的调用关系,结合ChannelReceive::OnReceivedPayloadData()的代码,我们发现音频Nack请求相关的代码简单、清晰:
- 调用Nack模块拿到丢包序号列表;
- 根据RTCP协议规范创建并序列化Nack报文并通过网络发送出去。序列化Nack报文的函数是RTCPSender::BuildNACK()。
void ChannelReceive::OnReceivedPayloadData(
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload,
const RTPHeader& rtpHeader) {
...
// Push the incoming payload (parsed and ready for decoding) into the ACM
if (acm_receiver_.InsertPacket(rtpHeader, payload) != 0) {
RTC_DLOG(LS_ERROR) << "ChannelReceive::OnReceivedPayloadData() unable to "
"push data to the ACM";
return;
}
TimeDelta round_trip_time = rtp_rtcp_->LastRtt().value_or(TimeDelta::Zero());
std::vector<uint16_t> nack_list =
acm_receiver_.GetNackList(round_trip_time.ms());
if (!nack_list.empty()) {
// Can't use nack_list.data() since it's not supported by all
// compilers.
ResendPackets(&(nack_list[0]), static_cast<int>(nack_list.size()));
}
}2.4. RED解码
RED解码相关的函数有两处:
- RedPayloadSplitter::SplitRed:针对每个RED报文,取出所有的冗余数据做反序列化,为每个RED Block创建Packet并设置Payload Type、Sequence Number、Timestamp、Payload Data,将其作为普通报文插入到入参packet_list中,再将原先的RED报文直接删除。
- RedPayloadSplitter::CheckRedPayloads:调用此函数之前,已经通过调用SplitRed()将RED报文中的冗余数据提取出来并封装成正常报文,同时将RED报文本身删除了,所以函数的入参packet_list中包含的报文可以视为正常报文。函数针对每个报文的payload type做了一次检查,发现payload type依然为RED、或者和第一个报文的payload type不一致的报文,都会直接删除掉。
结合前面关于RED编码部分的说明,我们再解释下payload字段的赋值。在下面的SDP协商给出的RED报文的payload type为121,此时RED报文的RTP Header中的PT字段要明确赋值为121,然后在RED Header的block PT要写成音频编码对应的payloat type,例如这里的0(对应PCM原始音频格式)、5(对应DVI原始音频格式)。
m=audio 12345 RTP/AVP 121 0 5
a=rtpmap:121 red/8000/1
a=fmtp:121 0/5bool RedPayloadSplitter::SplitRed(PacketList* packet_list) {
// Too many RED blocks indicates that something is wrong. Clamp it at some
// reasonable value.
const size_t kMaxRedBlocks = 32;
bool ret = true;
PacketList::iterator it = packet_list->begin();
while (it != packet_list->end()) {
Packet& red_packet = *it;
const uint8_t* payload_ptr = red_packet.payload.data();
size_t payload_length = red_packet.payload.size();
// Read RED headers (according to RFC 2198):
//
// 0 1 2 3
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
// +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
// |F| block PT | timestamp offset | block length |
// +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
// Last RED header:
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
// |0| Block PT |
// +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
struct RedHeader {
uint8_t payload_type;
uint32_t timestamp;
size_t payload_length;
};
std::vector<RedHeader> new_headers;
bool last_block = false;
size_t sum_length = 0;
while (!last_block) {
if (payload_length == 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "SplitRed header too short";
return false;
}
/*将每个RED Block的信息单独提取出来,存入new_headers中*/
RedHeader new_header;
// Check the F bit. If F == 0, this was the last block.
last_block = ((*payload_ptr & 0x80) == 0);
// Bits 1 through 7 are payload type.
new_header.payload_type = payload_ptr[0] & 0x7F;
if (last_block) {
// No more header data to read.
sum_length += kRedLastHeaderLength/*1*/; // Account for RED header size.
new_header.timestamp = red_packet.timestamp;
/*sum_length记录了之前所有RED Block的Header+Data的总长度,
*外加最后一个RED Block的Header Length,
*所以这里用RED Payload Length - sum_length就算出了最后一个RED Block的Data Length
*/
new_header.payload_length = red_packet.payload.size() - sum_length;
payload_ptr += kRedLastHeaderLength; // Advance to first payload byte.
payload_length -= kRedLastHeaderLength;
} else {
if (payload_length < kRedHeaderLength) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "SplitRed header too short";
return false;
}
// Bits 8 through 21 are timestamp offset.
int timestamp_offset =
(payload_ptr[1] << 6) + ((payload_ptr[2] & 0xFC) >> 2);
new_header.timestamp = red_packet.timestamp - timestamp_offset;
// Bits 22 through 31 are payload length.
new_header.payload_length =
((payload_ptr[2] & 0x03) << 8) + payload_ptr[3];
sum_length += new_header.payload_length;
sum_length += kRedHeaderLength; // Account for RED header size.
payload_ptr += kRedHeaderLength; // Advance to next RED header.
payload_length -= kRedHeaderLength;
}
// Store in new list of packets.
if (new_header.payload_length > 0) {
new_headers.push_back(new_header);
}
}
/*根据new_headers中存放的每个RED Block的信息创建Packet,
*并存入packet_list中
*/
if (new_headers.size() <= kMaxRedBlocks/*32*/) {
// Populate the new packets with payload data.
// `payload_ptr` now points at the first payload byte.
PacketList new_packets; // An empty list to store the split packets in.
for (size_t i = 0; i != new_headers.size(); ++i) {
const auto& new_header = new_headers[i];
size_t payload_length = new_header.payload_length;
if (payload_ptr + payload_length >
red_packet.payload.data() + red_packet.payload.size()) {
// The block lengths in the RED headers do not match the overall
// packet length. Something is corrupt. Discard this and the remaining
// payloads from this packet.
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "SplitRed length mismatch";
ret = false;
break;
}
Packet new_packet;
new_packet.timestamp = new_header.timestamp;
new_packet.payload_type = new_header.payload_type;
new_packet.sequence_number = red_packet.sequence_number;
new_packet.priority.red_level =
rtc::dchecked_cast<int>((new_headers.size() - 1) - i);
new_packet.payload.SetData(payload_ptr, payload_length);
new_packets.push_front(std::move(new_packet));
payload_ptr += payload_length;
}
// Insert new packets into original list, before the element pointed to by
// iterator `it`.
packet_list->splice(it, std::move(new_packets));
} else {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "SplitRed too many blocks: " << new_headers.size();
ret = false;
}
// Remove `it` from the packet list. This operation effectively moves the
// iterator `it` to the next packet in the list. Thus, we do not have to
// increment it manually.
it = packet_list->erase(it);
}/*end of while (it != packet_list->end())*/
/*此时packet_list中存放的都是以RED Block创建的报文,原先的RED报文已被删除*/
return ret;
}/*检查从RED报文中读取到的冗余数据,
*这些冗余数据的payload type必须是真实编码时产生的payload type,
*并且这些payload type要保持一致,
*否则哪些不合法的冗余数据就会被直接删除
*/
void RedPayloadSplitter::CheckRedPayloads(
PacketList* packet_list,
const DecoderDatabase& decoder_database) {
int main_payload_type = -1;
for (auto it = packet_list->begin(); it != packet_list->end(); /* */) {
uint8_t this_payload_type = it->payload_type;
if (decoder_database.IsRed(this_payload_type)) {
it = packet_list->erase(it);
continue;
}
if (!decoder_database.IsDtmf(this_payload_type) &&
!decoder_database.IsComfortNoise(this_payload_type)) {
if (main_payload_type == -1) {
// This is the first packet in the list which is non-DTMF non-CNG.
main_payload_type = this_payload_type;
} else {
if (this_payload_type != main_payload_type) {
// We do not allow redundant payloads of a different type.
// Remove `it` from the packet list. This operation effectively
// moves the iterator `it` to the next packet in the list. Thus, we
// do not have to increment it manually.
it = packet_list->erase(it);
continue;
}
}
}
++it;
}
}The End.

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容





所有评论(0)