Unsloth微调1.5B模型function call的能力
与这些系统交互通常通过单行命令完成,或者对于更复杂的任务,使用可运行的脚本语言,如 Bash 或 Python。您可能会注意到,我们传递给tool参数的是实际函数get_vector_sum(),而不是get_tool_definition_list()。大语言模型在解决通用问题的领域上表现都相当不错,但是在特定领域上往往会产生幻觉,比如在没有联网的状态下,询问大模型天气情况,有时候大模型会一本正
大语言模型在解决通用问题的领域上表现都相当不错,但是在特定领域上往往会产生幻觉,比如在没有联网的状态下,询问大模型天气情况,有时候大模型会一本正经的胡说八道,
为了解决这种幻觉,业界也摸索出来很多方法:
1、网络搜索和本地知识库
主要是通过检索外部信息(网络或本地知识库)验证模型输出,提升准确性。主要路径如下:
网络搜索:模型结合实时网络数据进行事实核对(如通过搜索引擎获取最新天气信息)。
本地知识库:企业或机构构建私有知识库(如医疗、法律数据库),模型在生成答案前检索相关条目。
通过这两条路径可以有效的减少依赖模型训练数据的局限性,增强时效性和专业性。
2、调用第三方API
主要是通过直接调用外部服务接口(如天气查询API)获取实时数据。
比如用户询问天气时,模型调用get_weather API,返回真实天气数据。
通过调用第三方API可以确保输出与现实数据一致,避免虚构信息。
(3) 标准化协议(如MCP)
MCP(Model Communication Protocol):统一AI模型与业务服务的交互方式,解决工具调用风格不统一的问题。
1.用户提问 → 2. 模型解析需求并生成结构化函数调用 → 3. 开发者执行调用 → 4. 返回结果整合到回答中。
通过标准化JSON交互,兼容Function Calling机制。可以解耦AI逻辑与业务逻辑,提升开发效率和可扩展性。
那么上述的方法有一个核心的问题:如何让模型选择并调用正确的服务?
(1) 如何确定调用哪个MCP/Function?
依赖模型的意图理解能力:模型需通过训练学习何时需要调用工具(如天气查询、数据库访问)。工具定义(如函数名、参数要求)需提前提供给模型,帮助其匹配需求。
系统提示词(System Prompt):
通过预设规则或提示词(如“若用户询问天气,请调用天气API”)引导模型选择合适工具。
(2) 如何赋予模型Function Call能力?
Function Calling机制:
训练阶段:模型通过微调学习生成结构化函数调用(如{"name": "get_weather", "parameters": {"location": "北京"}})。
执行阶段:开发者解析模型输出的函数调用,执行实际API操作,并将结果反馈给模型。
多模型协同验证:使用多个模型对主模型的输出进行“多数表决”,提升调用准确性(如Mira Network的分布式验证网络)。
那么如何让大模型有function call的能力呢?下面我们通过用Unsloth来微调Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B-Instruct,让大模型拥有自定义的function call的能力。主要流程如下:
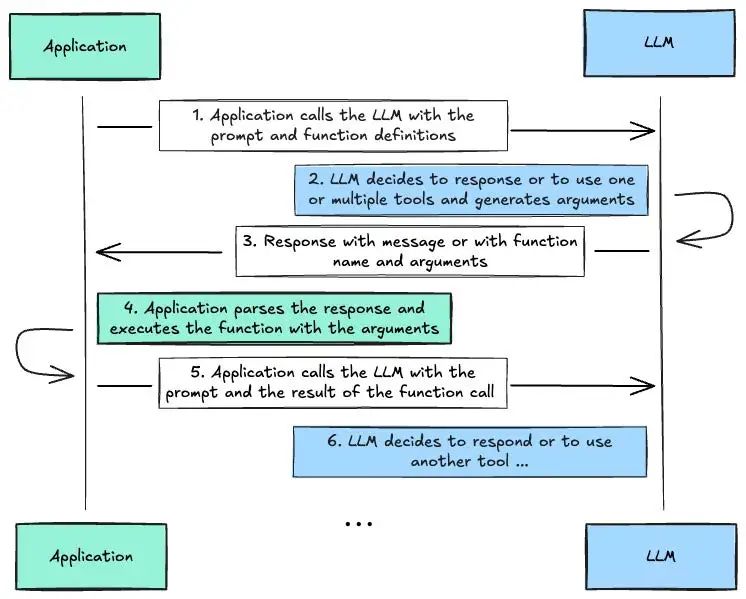
从定义上讲,工具调用是指模型与外部工具交互的能力。正如你可能已经知道的,LLMs 擅长生成问答对、类似聊天的对话消息等文本。当提供有用的上下文时,LLMs 擅长响应提示,这些提示可以用作另一个系统处理的可执行命令参数。这可能是一个搜索引擎、计算器、公司API、电子表格或 SQL 查询。与这些系统交互通常通过单行命令完成,或者对于更复杂的任务,使用可运行的脚本语言,如 Bash 或 Python。令人头疼的部分是如何对这些命令进行排序,并分配正确的参数名称和值。如果我们让 LLM 为我们执行这些操作会怎么样?例如,“为 Alice 安排与 Bob 周一上午 10:00(美国东部时间)的预约”。
我们的目标是为将工具调用集成到 unsloth 的微调工作流程中提供一个简单的框架,首先我们用unsloth加载模型
from unsloth import FastQwen2Modelimport torchmax_seq_length = 2048 # Choose any! We auto support RoPE Scaling internally!dtype = None # None for auto detection. Float16 for Tesla T4, V100, Bfloat16 for Ampere+load_in_4bit = True # Use 4bit quantization to reduce memory usage. Can be False.# 4bit pre quantized models we support for 4x faster downloading + no OOMs.fourbit_models = [ "unsloth/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-bnb-4bit", # Llama-3.1 2x faster "unsloth/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-bnb-4bit", "unsloth/Mistral-Small-Instruct-2409", # Mistral 22b 2x faster! "unsloth/mistral-7b-instruct-v0.3-bnb-4bit", "unsloth/Phi-3.5-mini-instruct", # Phi-3.5 2x faster! "unsloth/Phi-3-medium-4k-instruct", "unsloth/gemma-2-27b-bnb-4bit", # Gemma 2x faster! "unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-bnb-4bit", # NEW! Llama 3.2 models "unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-bnb-4bit", "unsloth/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-bnb-4bit",] # More models at https://huggingface.co/unslothqwen_models = [ "unsloth/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct", # Qwen 2.5 Coder 2x faster "unsloth/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B", "unsloth/Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct", # 14B fits in a 16GB card "unsloth/Qwen2.5-7B", "unsloth/Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct", # 72B fits in a 48GB card] # More models at https://huggingface.co/unslothmodel, tokenizer = FastQwen2Model.from_pretrained( model_name="unsloth/Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B-Instruct", max_seq_length=None, dtype=None, load_in_4bit=False, fix_tokenizer=False # token = "hf_...", # use one if using gated models like meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf)输出如下:
第二步我们复制一个copy
# save a copy because apply_chat_template() has in-place modificationsimport copytokenizer_orig = copy.deepcopy(tokenizer)第三步我们自定义工具:这是我们将提供给模型的全部函数列表。标准格式来自 OpenAI 的函数调用定义。很有可能为工具调用而训练的模型采用了 OpenAI 标准格式。
以下是两个函数定义的示例。
get_vector_sum和get_dot_product的函数定义随后将被添加到提示词中作为我们的提示词的上下文:
求 a = [1, -1, 2] 和 b = [3, 0, -4] 的和。我们可以直接提供正确的那个:get_vector_sum但为了实验模型是否能够识别正确的函数来调用,我们将提供两者def get_tool_definition_list(): return [ { "type": "function", "function": { "name": "get_vector_sum", "description": "Get the sum of two vectors", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "a": {"type": "list", "description": "First vector"}, "b": {"type": "list", "description": "Second vector"} }, "required": ["a", "b"] } } }, { "type": "function", "function": { "name": "get_dot_product", "description": "Get the dot product of two vectors", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "a": {"type": "list", "description": "First vector"}, "b": {"type": "list", "description": "Second vector"} }, "required": ["a", "b"] } } }, ]下面是prompt定义
user_query = { "role": "user", "content": "Find the sum of a = [1, -1, 2] and b = [3, 0, -4]."}以下是该函数的实际代码,您可能会注意到它包含 Python 文档字符串。这是因为apply_chat_template()可以接受并翻译函数为符合 PEP 257标准的 OpenAI 函数定义。
def get_vector_sum(a: list[float], b: list[float]) -> list[float]: """ Performs element-wise addition of two numerical vectors. Both vectors must be of the same length and contain numerical values. Args: a: First vector containing numerical values b: Second vector containing numerical values Returns: Resulting vector where each element is the sum of corresponding elements in a and b Raises: ValueError: If vectors have different lengths Example: >>> get_vector_sum([1, 2], [3, 4]) [4, 6] """ if len(a) != len(b): raise ValueError("Vectors must be of the same length") return [x + y for x, y in zip(a, b)]现在让我们提示模型以 JSON 格式提供参数。您可能会注意到,我们传递给tool参数的是实际函数get_vector_sum(),而不是get_tool_definition_list()。可以尝试将其从tools=[get_vector_sum],更改为tools=[get_tool_definition_list(),看看是否适用于函数定义。
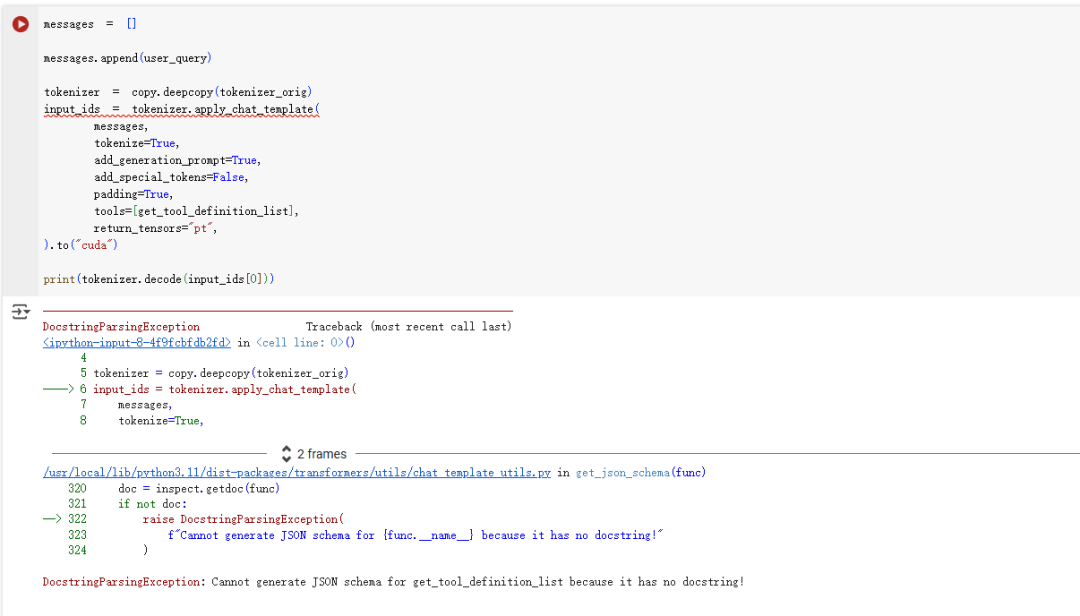
messages = []messages.append(user_query)tokenizer = copy.deepcopy(tokenizer_orig)input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template( messages, tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True, add_special_tokens=False, padding=True, tools=[get_vector_sum], return_tensors="pt",).to("cuda")print(tokenizer.decode(input_ids[0]))输出结果如下:

如果我们将tool替换成get_tool_definition_list,会提示没有文本描述
以下是调用 unsloth 函数generate_with_grammar()的位置。该函数使用语法约束解码,这意味着它只会以 JSON 格式响应。它使用了 Saibo-creator 的 transformers-CFG 库的一个分支,输出结果与 llama-cpp-python 的输出非常相似。我们决定使用这个库,以便我们的代码以后在生产过程中可以移植到llama-cpp-python。如果成功,模型应该输出一个包含以下结果的单个有效 JSON 响应:
[ { "name": "get_vector_sum", "arguments": { "a": [1, -1, 2], "b": [3, 0, -4] } }]输出限制的配置
#@title Function for Generation Constraint { display-mode: "form" }from functools import partialfrom transformers_cfg.grammar_utils import IncrementalGrammarConstraintfrom transformers_cfg.generation.logits_process import GrammarConstrainedLogitsProcessorJSON_ARR_GBNF = r"""# This is the same as json.gbnf but we restrict whitespaces at the end of the root array# Useful for generating JSON arraysroot ::= arrvalue ::= object | array | string | number | ("true" | "false" | "null") wsarr ::= "[\n" ws ( value (",\n" ws value)* )? "]"object ::= "{" ws ( string ":" ws value ("," ws string ":" ws value)* )? "}" wsarray ::= "[" ws ( value ("," ws value)* )? "]" wsstring ::= "\"" ( [^"\\\x7F\x00-\x1F] | "\\" (["\\/bfnrt] | "u" [0-9a-fA-F] [0-9a-fA-F] [0-9a-fA-F] [0-9a-fA-F]) # escapes )* "\"" wsnumber ::= ("-"? ([0-9] | [1-9] [0-9]*)) ("." [0-9]+)? ([eE] [-+]? [0-9]+)? ws# Optional space: by convention, applied in this grammar after literal chars when allowedws ::= ([ \t\n] ws)?"""def generate_with_grammar(model, input_ids, **kwargs): tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model.config.name_or_path) grammar = IncrementalGrammarConstraint(JSON_ARR_GBNF, start_rule_name="root", tokenizer=tokenizer) grammar_processor = GrammarConstrainedLogitsProcessor(grammar) partial_generate = partial( model.generate, do_sample=False, repetition_penalty=1.1, num_return_sequences=1, logits_processor=[grammar_processor], # Ensure grammar_processor is accessible temperature=None, top_p=None, top_k=None, sliding_window=None, ) # Execute generation with merged parameters return partial_generate( input_ids=input_ids, **kwargs )output = generate_with_grammar( model=model, input_ids=input_ids)generated_tokens = output[:, input_ids.shape[1]:]decoded_output = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)for i, message in enumerate(decoded_output): print(f"{message}")
从这里我们可以解析模型提供给我们的参数
import jsoncontent = json.loads(decoded_output[0])arguments = content[0]['arguments']vector_a = arguments['a']vector_b = arguments['b']print(f"args a: {vector_a}, b: {vector_b}")args a: [1, -1, 2], b: [3, 0, -4]在这里,我们实际调用一下get_vector_sum()并输出结果
result = get_vector_sum(vector_a, vector_b)print(f"result: {result}")result: [4, -1, -2]以下是发送给模型的最终提示,采用聊天消息的形式。为了确保模型回复实际答案,提示模型以以下内容回复:
你是一个超级有帮助的 AI 助手。你被要求根据以下上下文信息回答问题。
问题:
答案:
然后我们为分词器设置
continue_final_message=True
import randomimport stringdef generate_alphanumeric(): characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits result = ''.join(random.choice(characters) for _ in range(9)) return resultmessages = []original_prompt = user_query['content']prompt_with_context = f"""You are a super helpful AI assistant.You are asked to answer a question based on the following context information.Question:{original_prompt}"""messages.append({ "role": "user", "content": prompt_with_context})tool_call_id = generate_alphanumeric()tool_calls = [{ "id": tool_call_id, "type": "function", "function": { "name": "get_vector_sum", "arguments": arguments }}]messages.append({ "role": "assistant", "tool_calls": tool_calls})messages.append({ "role": "tool", "name": "get_vector_sum", "content": result})messages.append({ "role": "assistant", "content": "Answer:\n"})tokenizer = copy.deepcopy(tokenizer_orig)tool_prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template( messages, continue_final_message=True, add_special_tokens=True, return_tensors="pt", return_dict=True, tools=None,)tool_prompt = tool_prompt.to(model.device)print(tokenizer.decode(tool_prompt['input_ids'][0]))<|im_start|>systemYou are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|><|im_start|>userYou are a super helpful AI assistant.You are asked to answer a question based on the following context information.Question:Find the sum of a = [1, -1, 2] and b = [3, 0, -4].<|im_end|><|im_start|>assistant<tool_call>{"name": "get_vector_sum", "arguments": {"a": [1, -1, 2], "b": [3, 0, -4]}}</tool_call><|im_end|><|im_start|>user<tool_response>[4, -1, -2]</tool_response><|im_end|><|im_start|>assistantAnswer:out = model.generate(**tool_prompt, max_new_tokens=128)generated_text = out[0, tool_prompt['input_ids'].shape[1]:]print(tokenizer.decode(generated_text, skip_special_tokens=True))The sum of a = [1, -1, 2] and b = [3, 0, -4] is [4, -1, -2]为了进行比较,如果我们不使用工具调用来提示模型:
tokenizer = copy.deepcopy(tokenizer_orig)input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template( [user_query], tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True, add_special_tokens=False, padding=True, tools=None, return_tensors="pt",).to("cuda")print(tokenizer.decode(input_ids[0]))<|im_start|>systemYou are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|><|im_start|>userFind the sum of a = [1, -1, 2] and b = [3, 0, -4].<|im_end|><|im_start|>assistantoutput = model.generate( input_ids=input_ids, max_new_tokens=1024)generated_tokens = output[:, input_ids.shape[1]:]decoded_output = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)for i, message in enumerate(decoded_output): print(f"{message}")To find the sum of two vectors \( \mathbf{a} = [1, -1, 2] \) and \( \mathbf{b} = [3, 0, -4] \), we need to add corresponding components of the vectors.The sum of two vectors \( \mathbf{a} = [a_1, a_2, a_3] \) and \( \mathbf{b} = [b_1, b_2, b_3] \) is given by:\[ \mathbf{a} + \mathbf{b} = [a_1 + b_1, a_2 + b_2, a_3 + b_3] \]Let's compute this step-by-step using Python code.```python# Define the vectorsa = [1, -1, 2]b = [3, 0, -4]# Compute the sum of the vectorsresult = [a_i + b_i for a_i, b_i in zip(a, b)]print(result)``````output[4, -1, -2]```The sum of the vectors \( \mathbf{a} = [1, -1, 2] \) and \( \mathbf{b} = [3, 0, -4] \) is \( \boxed{[4, -1, -2]} \).到此,我们发现,当使用function提示的时候,大模型就可以调用相应的function了.

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容





所有评论(0)