WEBRTC 带你精通《平滑发送模块》上
这是一个回调函数,就像你点外卖后,外卖员到了会给你打电话一样。当视频编码器完成一帧视频的编码后,就会"打电话"给这个函数,说"EncodedImage 就像是一个装满编码后视频数据的"包裹"fec_controller_ 是"快递保险员",记录包裹大小和类型,准备在网络丢包时进行数据恢复就像快递员送包裹前要检查:🔒 确保同时只有一个人在处理包裹(线程安全)📦 确保有发送通道可用✅ 确保发送服务
整体架构图
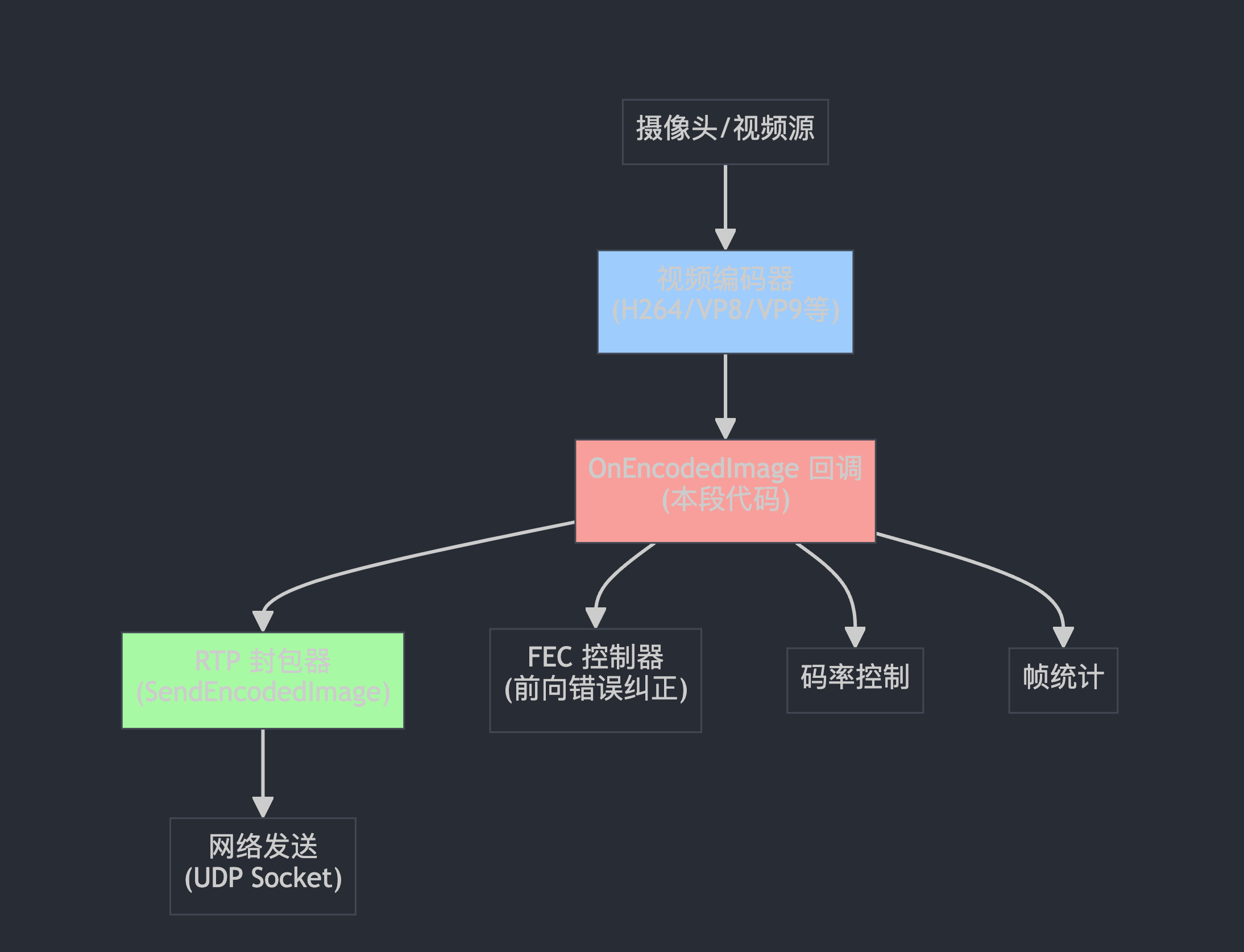
rtp_video_sender.cc
入口函数:
EncodedImageCallback::Result RtpVideoSender::OnEncodedImage(
const EncodedImage& encoded_image,
const CodecSpecificInfo* codec_specific_info)
这是一个回调函数,就像你点外卖后,外卖员到了会给你打电话一样。当视频编码器完成一帧视频的编码后,就会"打电话"给这个函数,说"编码完成了,这里有编码好的数据,你拿去发送吧"。
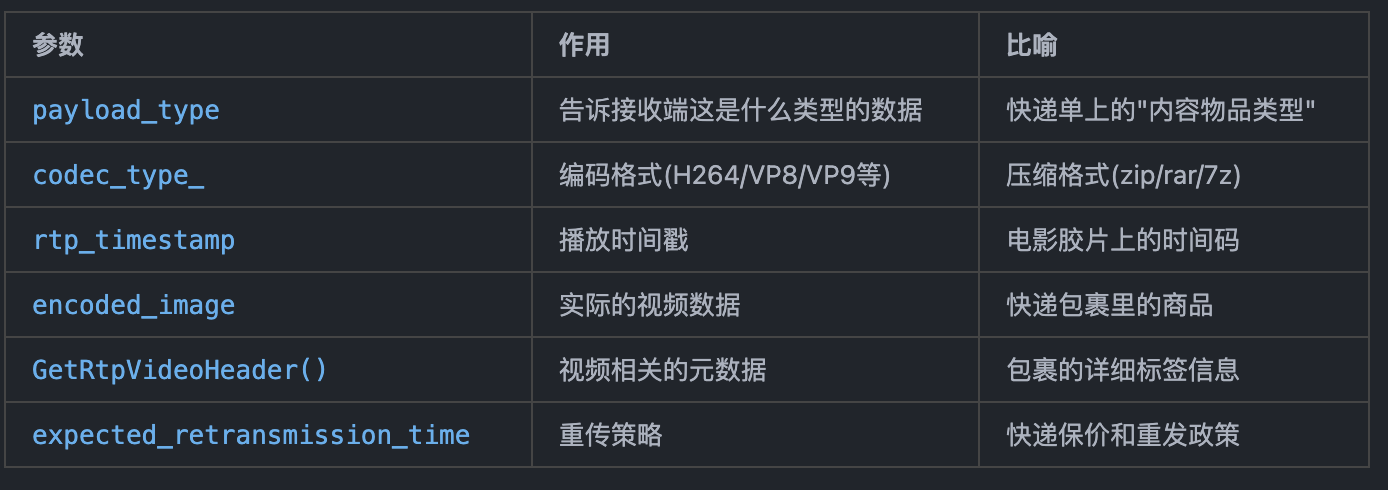
EncodedImage 就像是一个装满编码后视频数据的"包裹"
fec_controller_->UpdateWithEncodedData(encoded_image.size(),
encoded_image._frameType);
fec_controller_ 是"快递保险员",记录包裹大小和类型,准备在网络丢包时进行数据恢复
MutexLock lock(&mutex_); // 🔒 上锁,防止多线程冲突
RTC_DCHECK(!rtp_streams_.empty()); // 确保有发送通道
if (!active_) // 如果发送器没激活
return Result(Result::ERROR_SEND_FAILED); // 直接返回失败
就像快递员送包裹前要检查:
🔒 确保同时只有一个人在处理包裹(线程安全)
📦 确保有发送通道可用
✅ 确保发送服务是开启状态
shared_frame_id_++;
size_t simulcast_index = encoded_image.SimulcastIndex().value_or(0);
RTC_DCHECK_LT(simulcast_index, rtp_streams_.size());
shared_frame_id_++ 就像给每个包裹贴上递增的编号标签
simulcast_index 决定这个视频帧要走哪条"高速公路"(不同分辨率的流)
比如:0=高清路,1=标清路,2=低清路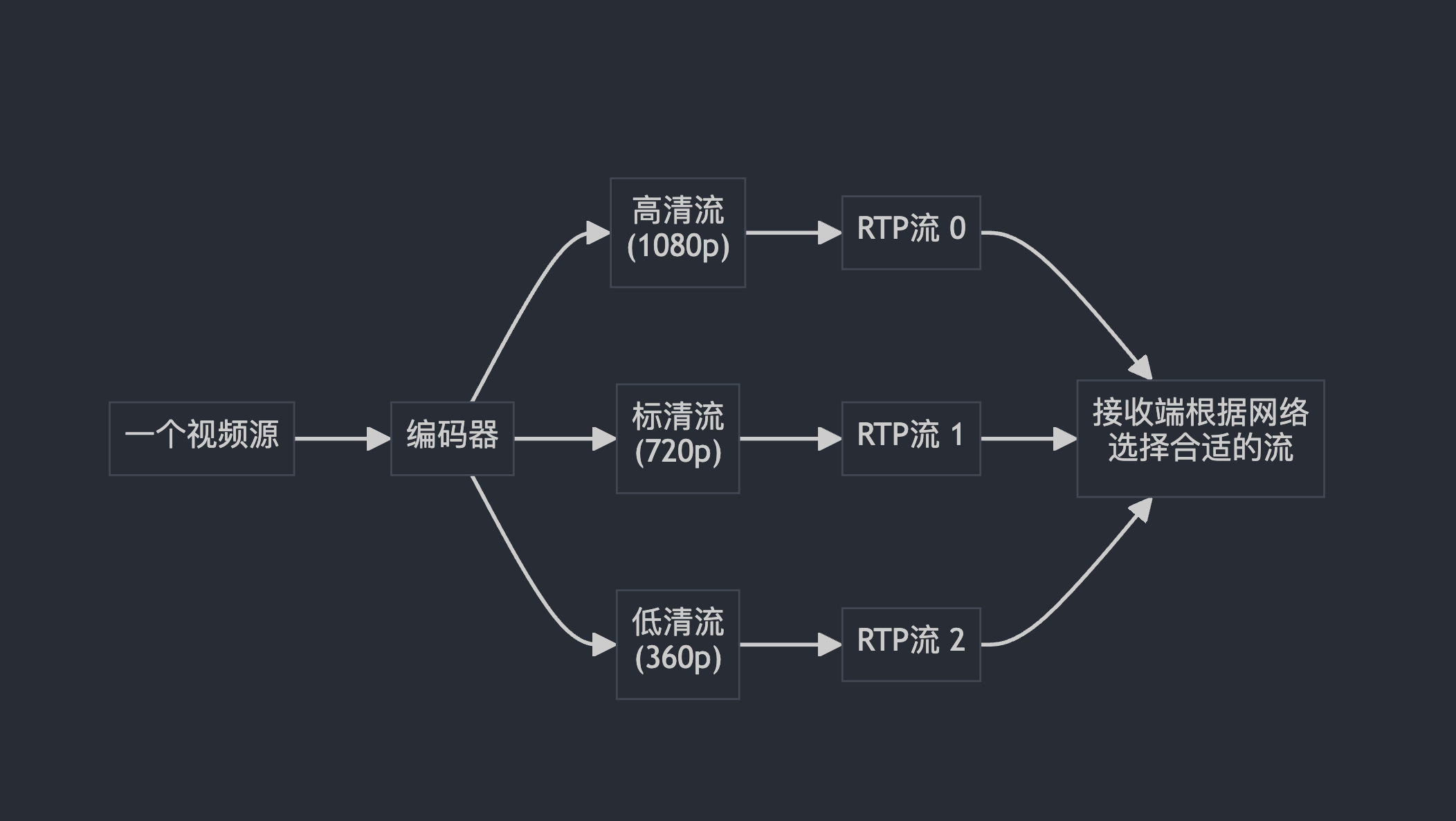
uint32_t rtp_timestamp =
encoded_image.RtpTimestamp() +
rtp_streams_[simulcast_index].rtp_rtcp->StartTimestamp();
就像寄快递要写发送时间一样,RTP需要精确的时间戳来:
让接收端知道这一帧什么时候该播放
保证音视频同步
StartTimestamp() 是这个会话的"起始时间",就像秒表的起点
if (!rtp_streams_[simulcast_index].rtp_rtcp->OnSendingRtpFrame(
encoded_image.RtpTimestamp(), encoded_image.capture_time_ms_,
rtp_config_.payload_type,
encoded_image._frameType == VideoFrameType::kVideoFrameKey)) {
return Result(Result::ERROR_SEND_FAILED);
}
这就像快递员发送前要向调度中心报告:
📝 “我要发送一个包裹了”
⏰ 包裹的时间戳信息
📋 包裹类型(关键帧还是普通帧)
如果调度中心说"不行,现在不能发",就返回失败
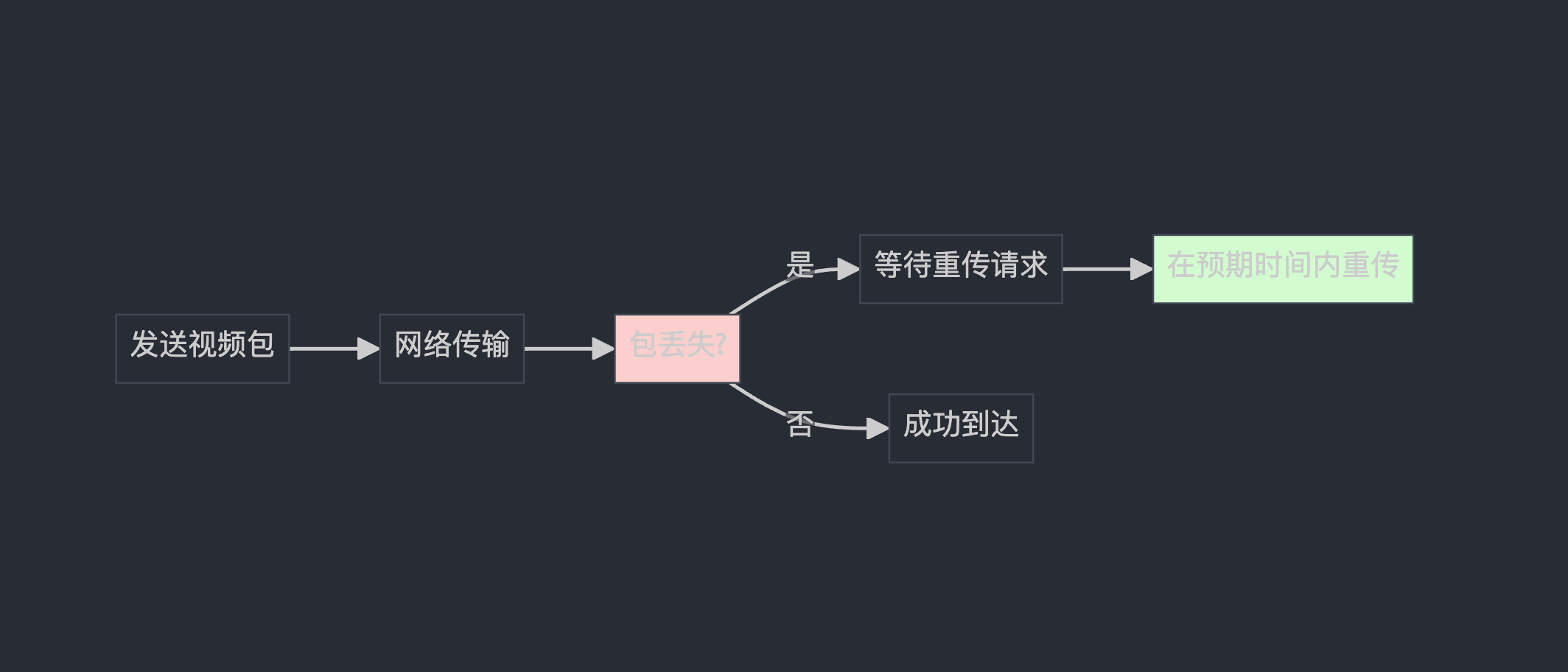
TimeDelta expected_retransmission_time = TimeDelta::PlusInfinity();
if (encoded_image.RetransmissionAllowed()) {
expected_retransmission_time =
rtp_streams_[simulcast_index].rtp_rtcp->ExpectedRetransmissionTime();
}
就像快递有"保价服务",某些重要的视频帧(如关键帧)允许重传
PlusInfinity() 表示"永远不重传"
ExpectedRetransmissionTime() 计算"如果丢包了,多久后应该重传"
if (IsFirstFrameOfACodedVideoSequence(encoded_image, codec_specific_info)) {
RTPSenderVideo& sender_video = *rtp_streams_[simulcast_index].sender_video;
if (codec_specific_info && codec_specific_info->template_structure) {
sender_video.SetVideoStructure(&*codec_specific_info->template_structure);
} else if (std::optional<FrameDependencyStructure> structure =
params_[simulcast_index].GenericStructure(codec_specific_info)) {
sender_video.SetVideoStructure(&*structure);
} else {
sender_video.SetVideoStructure(nullptr);
}
}
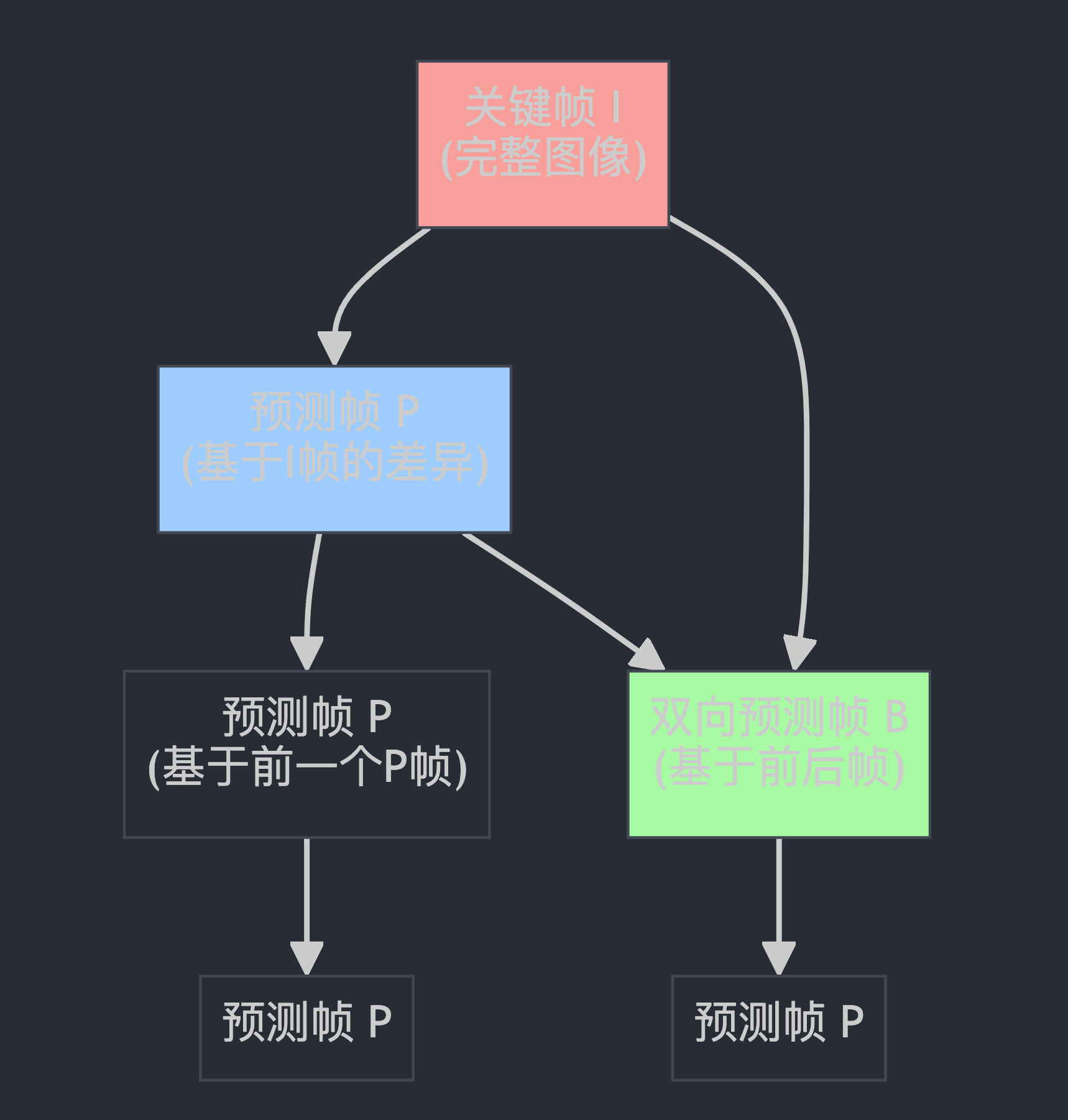
想象视频编码就像拍连环画:
I帧(关键帧):完整的一幅画,不依赖任何其他画
P帧(预测帧):只画与上一幅的差异部分
B帧(双向预测):参考前后两幅画来画差异
这段代码就是在告诉接收端:“这些画之间是怎么关联的”,这样接收端就知道:
📋 哪些帧可以独立解码
🔗 哪些帧需要依赖其他帧
🎯 丢包时优先保护哪些帧
std::optional<int64_t> frame_id;
if (!independent_frame_ids_) {
frame_id = shared_frame_id_;
}
frame_id 就像给每个视频帧发一个"身份证号码"
shared_frame_id_ 是全局共享的编号(多个流使用同一个编号系统)
independent_frame_ids_ 决定是否每个流都有独立的编号系统
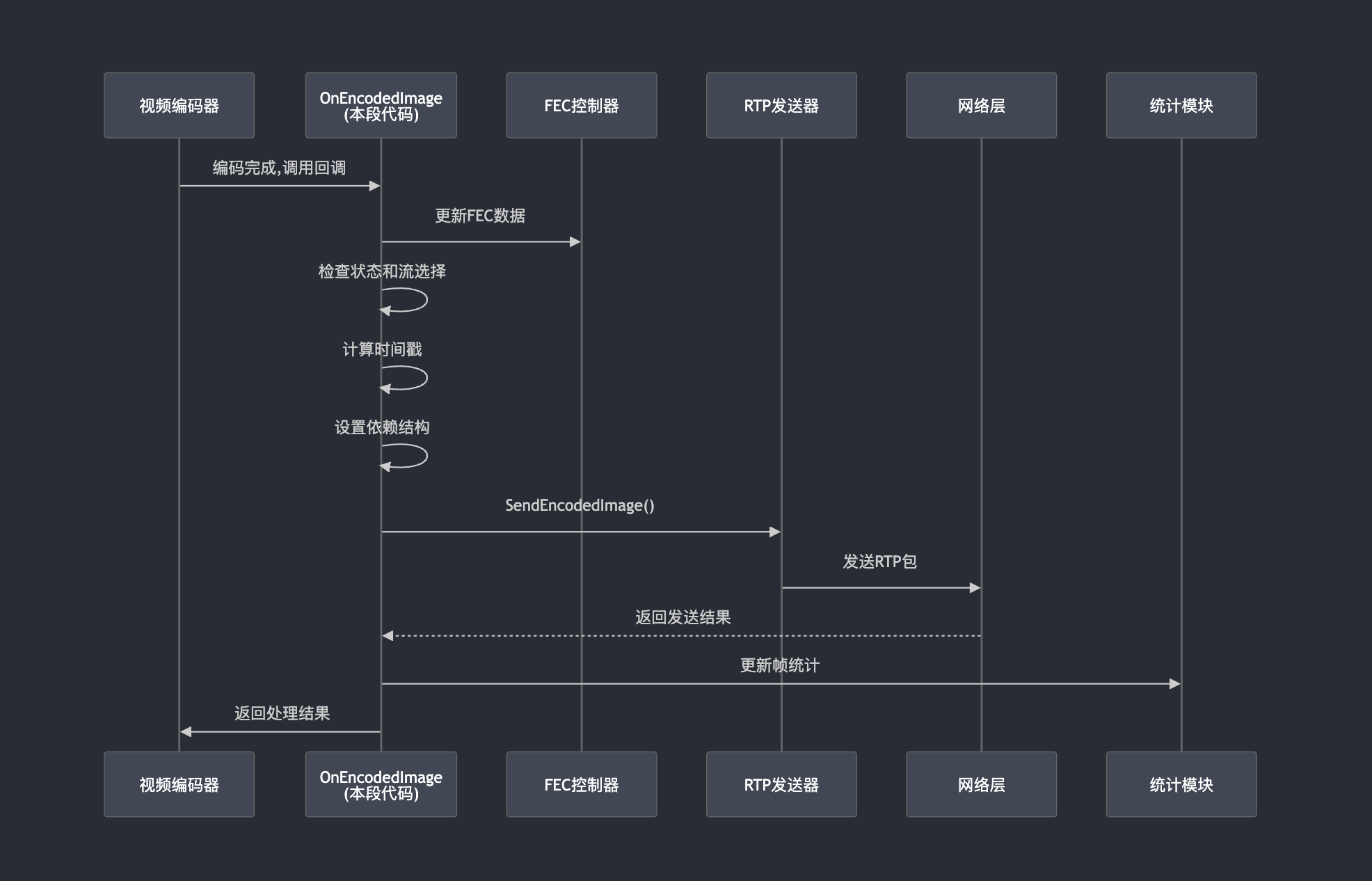
实际发送核心
bool send_result =
rtp_streams_[simulcast_index].sender_video->SendEncodedImage(
rtp_config_.payload_type, // 负载类型
codec_type_, // 编码类型
rtp_timestamp, // RTP时间戳
encoded_image, // 编码后的图像数据
params_[simulcast_index].GetRtpVideoHeader( // RTP视频头信息
encoded_image, codec_specific_info, frame_id),
expected_retransmission_time); // 预期重传时间
if (frame_count_observer_) {
FrameCounts& counts = frame_counts_[simulcast_index];
if (encoded_image._frameType == VideoFrameType::kVideoFrameKey) {
++counts.key_frames; // 关键帧计数+1
} else if (encoded_image._frameType == VideoFrameType::kVideoFrameDelta) {
++counts.delta_frames; // 差分帧计数+1
} else {
RTC_DCHECK(encoded_image._frameType == VideoFrameType::kEmptyFrame);
}
frame_count_observer_->FrameCountUpdated(counts, rtp_config_.ssrcs[simulcast_index]);
}
就像快递员要记录工作日志:
📊 今天发了多少个重要包裹(关键帧)
📈 发了多少个普通包裹(差分帧)
📋 向管理系统报告统计数据
if (!send_result)
return Result(Result::ERROR_SEND_FAILED);
return Result(Result::OK, rtp_timestamp);
- 如果发送失败:返回"❌ 发送失败"
- 如果发送成功:返回"✅ 发送成功 + 时间戳"
bool RTPSenderVideo::SendEncodedImage(int payload_type,
std::optional<VideoCodecType> codec_type,
uint32_t rtp_timestamp,
const EncodedImage& encoded_image,
RTPVideoHeader video_header,
TimeDelta expected_retransmission_time) {
if (frame_transformer_delegate_) {
// The frame will be sent async once transformed.
return frame_transformer_delegate_->TransformFrame(
payload_type, codec_type, rtp_timestamp, encoded_image, video_header,
expected_retransmission_time);
}
return SendVideo(payload_type, codec_type, rtp_timestamp,
encoded_image.CaptureTime(), encoded_image,
encoded_image.size(), video_header,
expected_retransmission_time, /*csrcs=*/{});
}
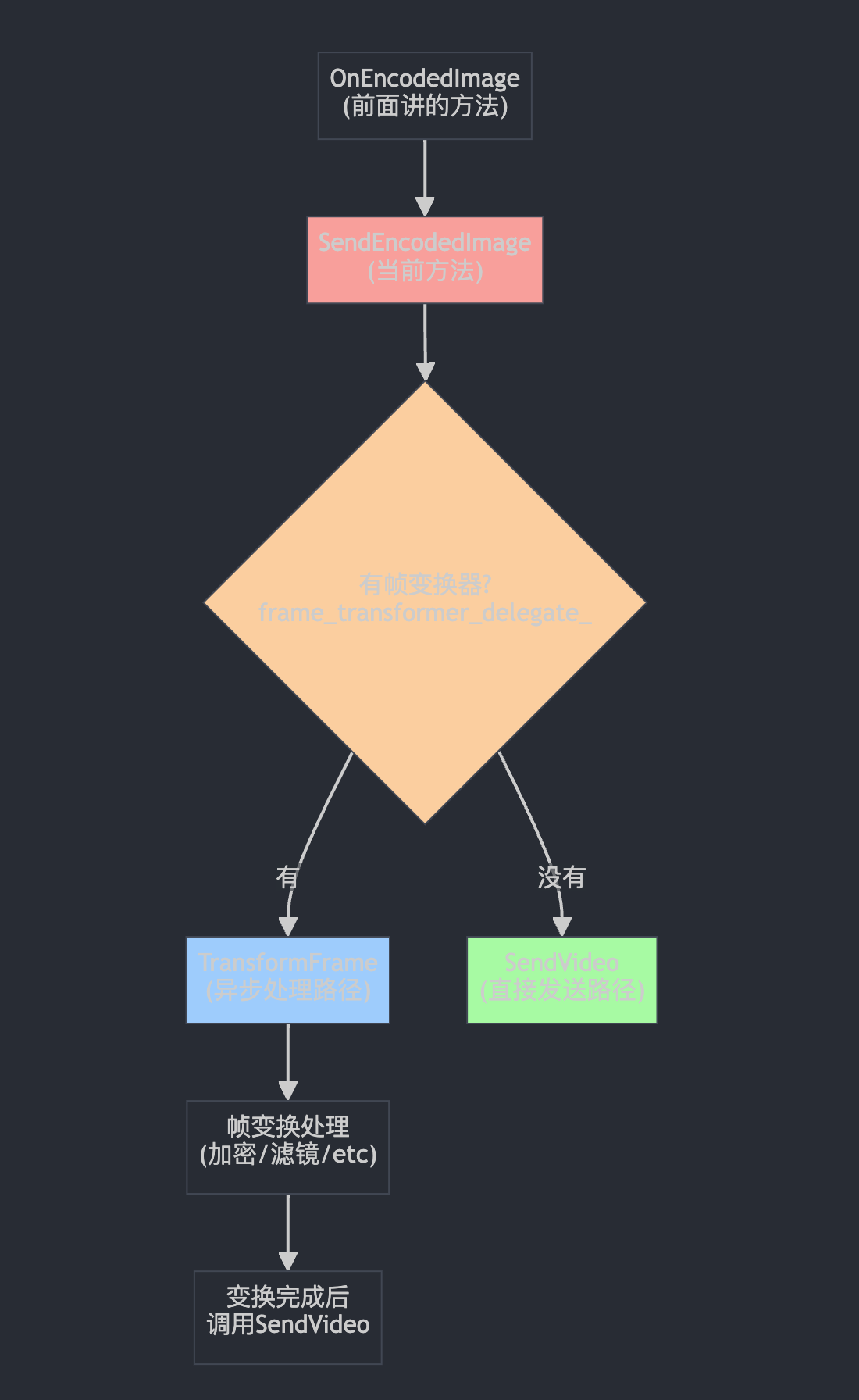
这个方法就像一个"快递分拣中心",接收编码好的视频帧,决定走哪条处理路线。
帧变换器的典型用例:
🔐 端到端加密:对视频内容进行加密
🎨 实时滤镜:美颜、背景虚化等
📝 水印叠加:添加公司logo或用户信息
🔄 格式转换:在不同编码格式间转换
🛡️ 内容审核:实时检测和过滤敏感内容
关键特点:
⚡ 异步处理:不阻塞主线程,变换完成后再发送
🔄 可插拔:可以动态添加或移除变换器
📤 最终还是调用SendVideo:变换完成后走相同的发送路径
核心发送方法
bool RTPSenderVideo::SendVideo(int payload_type,
std::optional<VideoCodecType> codec_type,
uint32_t rtp_timestamp,
Timestamp capture_time,
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload,
size_t encoder_output_size,
RTPVideoHeader video_header,
TimeDelta expected_retransmission_time,
std::vector<uint32_t> csrcs)
SendVideo 方法架构概览
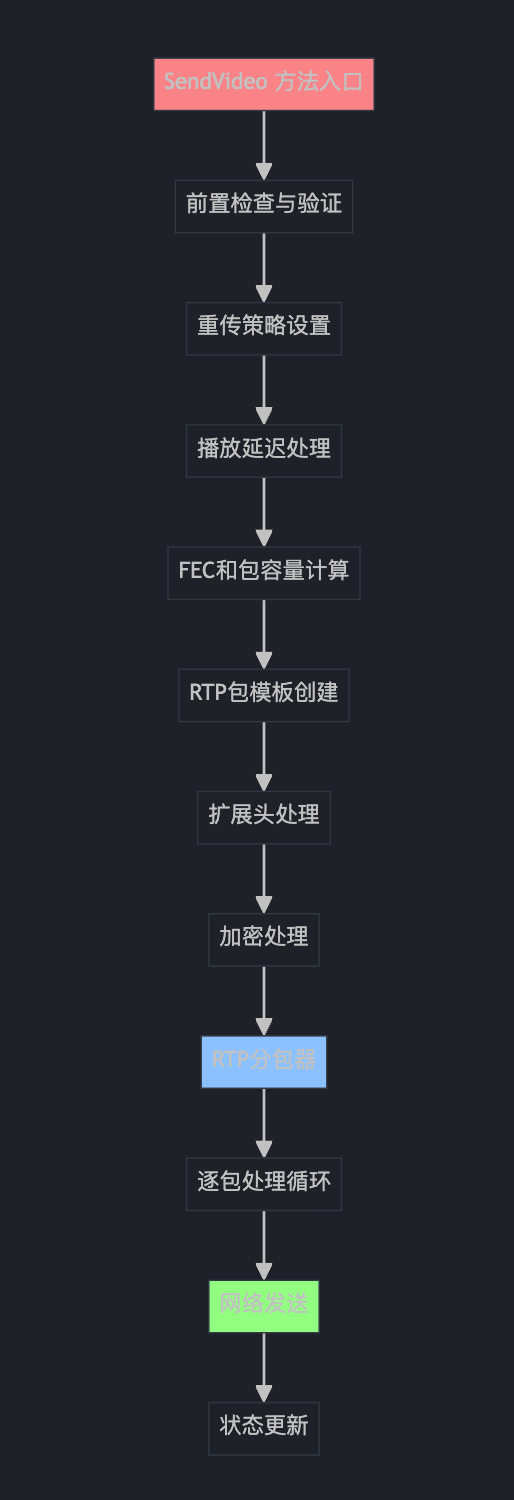
第一部分:前置检查与验证
bool RTPSenderVideo::SendVideo(int payload_type,
std::optional<VideoCodecType> codec_type,
uint32_t rtp_timestamp,
Timestamp capture_time,
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload,
size_t encoder_output_size,
RTPVideoHeader video_header,
TimeDelta expected_retransmission_time,
std::vector<uint32_t> csrcs) {
RTC_CHECK_RUNS_SERIALIZED(&send_checker_);
if (video_header.frame_type == VideoFrameType::kEmptyFrame)
return true;
if (payload.empty())
return false;
if (!rtp_sender_->SendingMedia()) {
return false;
}
这就像快递员发货前的检查清单: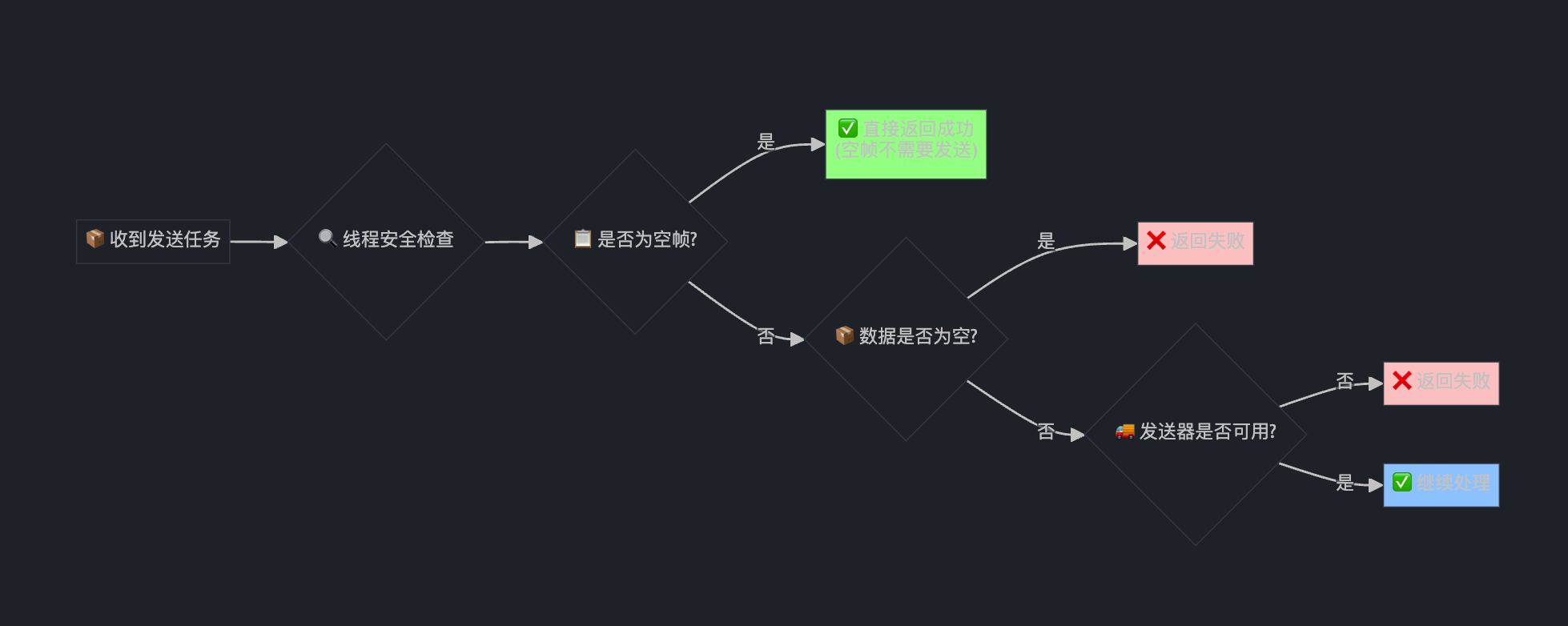
第二部分:重传策略设置
int32_t retransmission_settings = retransmission_settings_;
if (codec_type == VideoCodecType::kVideoCodecH264) {
// Backward compatibility for older receivers without temporal layer logic.
retransmission_settings = kRetransmitBaseLayer | kRetransmitHigherLayers;
}
const uint8_t temporal_id = GetTemporalId(video_header);
const bool allow_retransmission =
expected_retransmission_time.IsFinite() &&
AllowRetransmission(temporal_id, retransmission_settings,
expected_retransmission_time);
这就像为不同的快递包裹设置不同的"保价策略":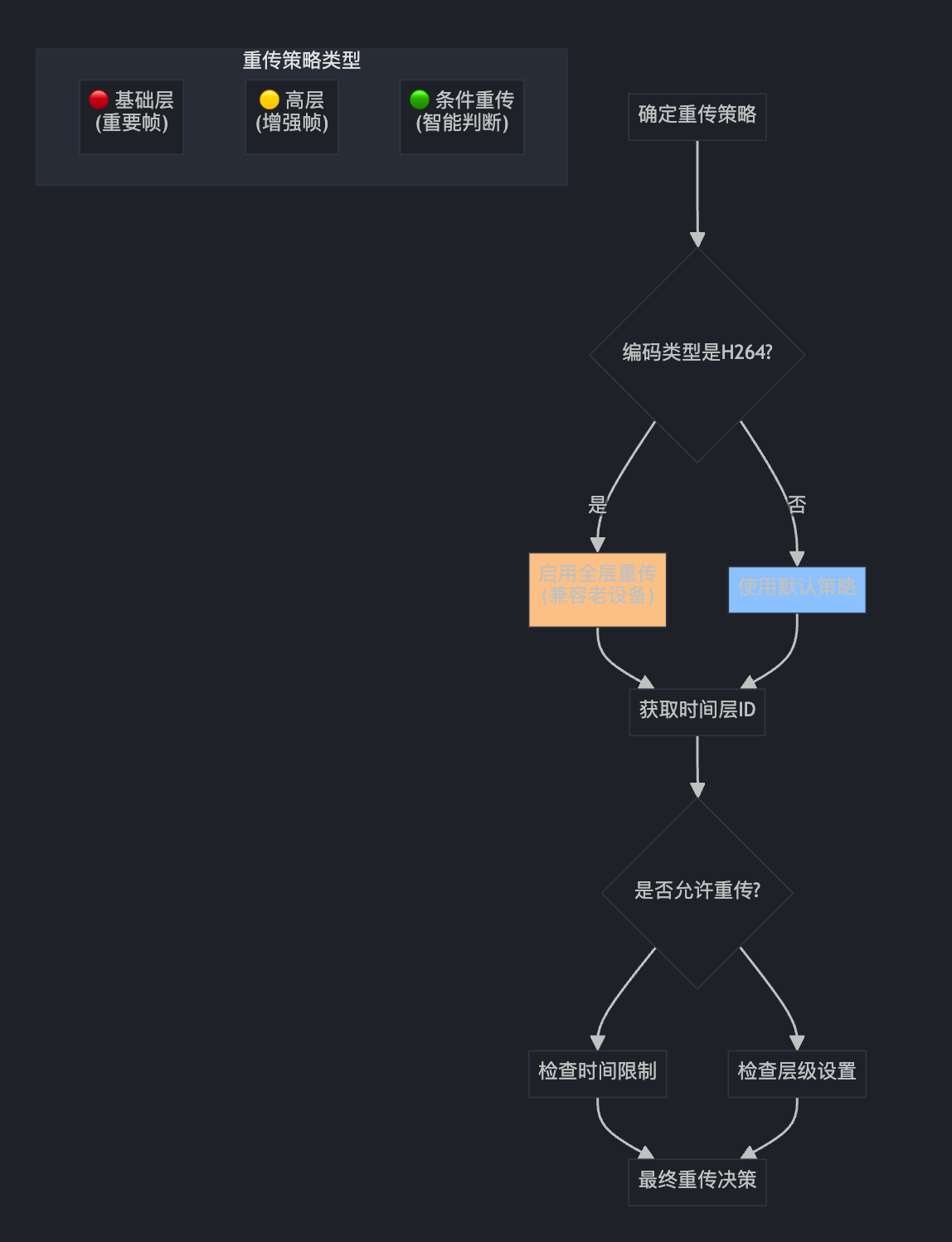
第三部分:播放延迟和码率分配
MaybeUpdateCurrentPlayoutDelay(video_header);
if (video_header.frame_type == VideoFrameType::kVideoFrameKey) {
if (current_playout_delay_.has_value()) {
// Force playout delay on key-frames, if set.
playout_delay_pending_ = true;
}
if (allocation_) {
// Send the bitrate allocation on every key frame.
send_allocation_ = SendVideoLayersAllocation::kSendWithResolution;
}
}
if (video_structure_ != nullptr && video_header.generic) {
active_decode_targets_tracker_.OnFrame(
video_structure_->decode_target_protected_by_chain,
video_header.generic->active_decode_targets,
video_header.frame_type == VideoFrameType::kVideoFrameKey,
video_header.generic->frame_id, video_header.generic->chain_diffs);
}
这就像电影院的"排片调度系统":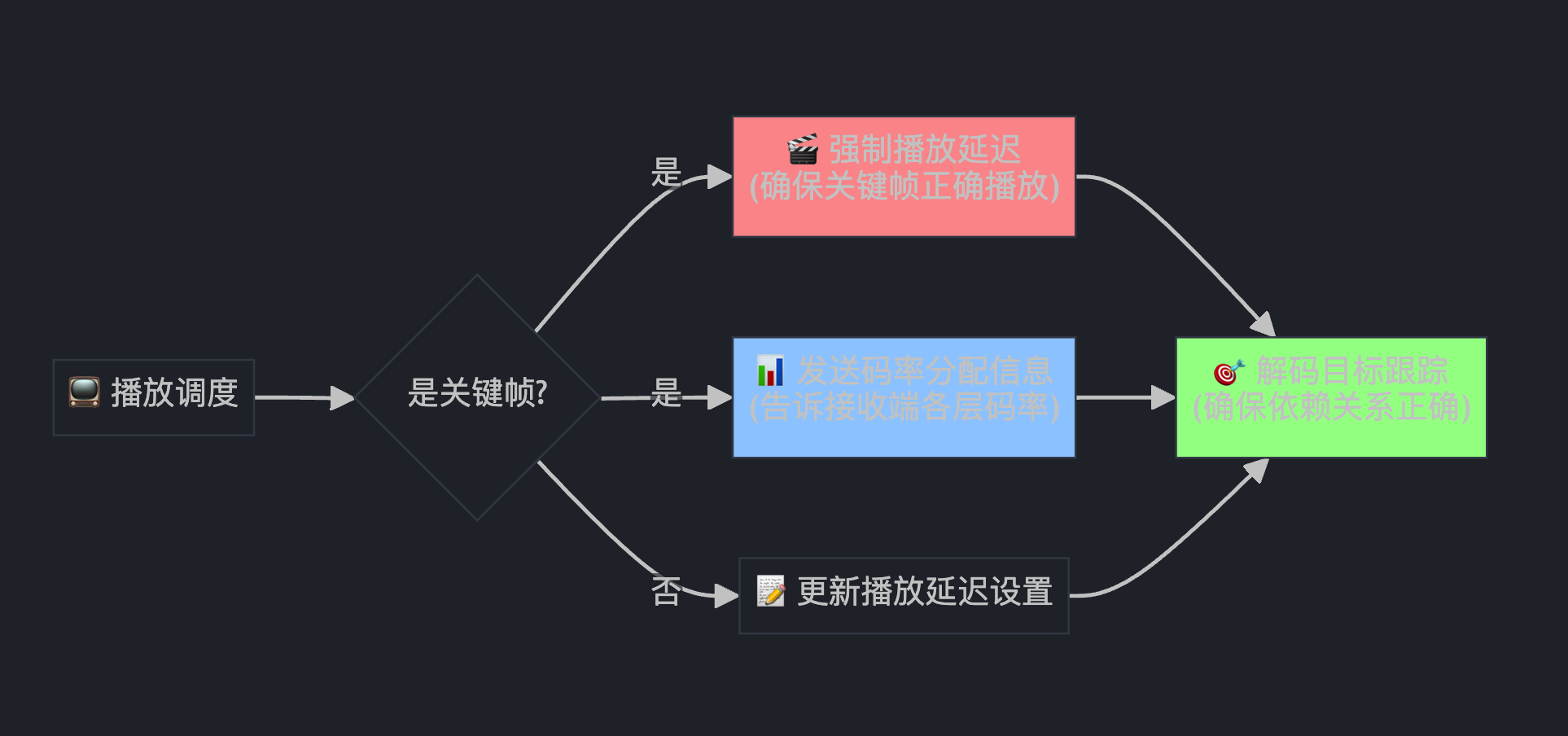
第四部分:FEC和包容量计算
// No FEC protection for upper temporal layers, if used.
const bool use_fec = fec_type_.has_value() &&
(temporal_id == 0 || temporal_id == kNoTemporalIdx);
// Maximum size of packet including rtp headers.
// Extra space left in case packet will be resent using fec or rtx.
int packet_capacity = rtp_sender_->MaxRtpPacketSize();
if (use_fec) {
packet_capacity -= FecPacketOverhead();
}
if (allow_retransmission) {
packet_capacity -= rtp_sender_->RtxPacketOverhead();
}
这就像计算快递箱的容量: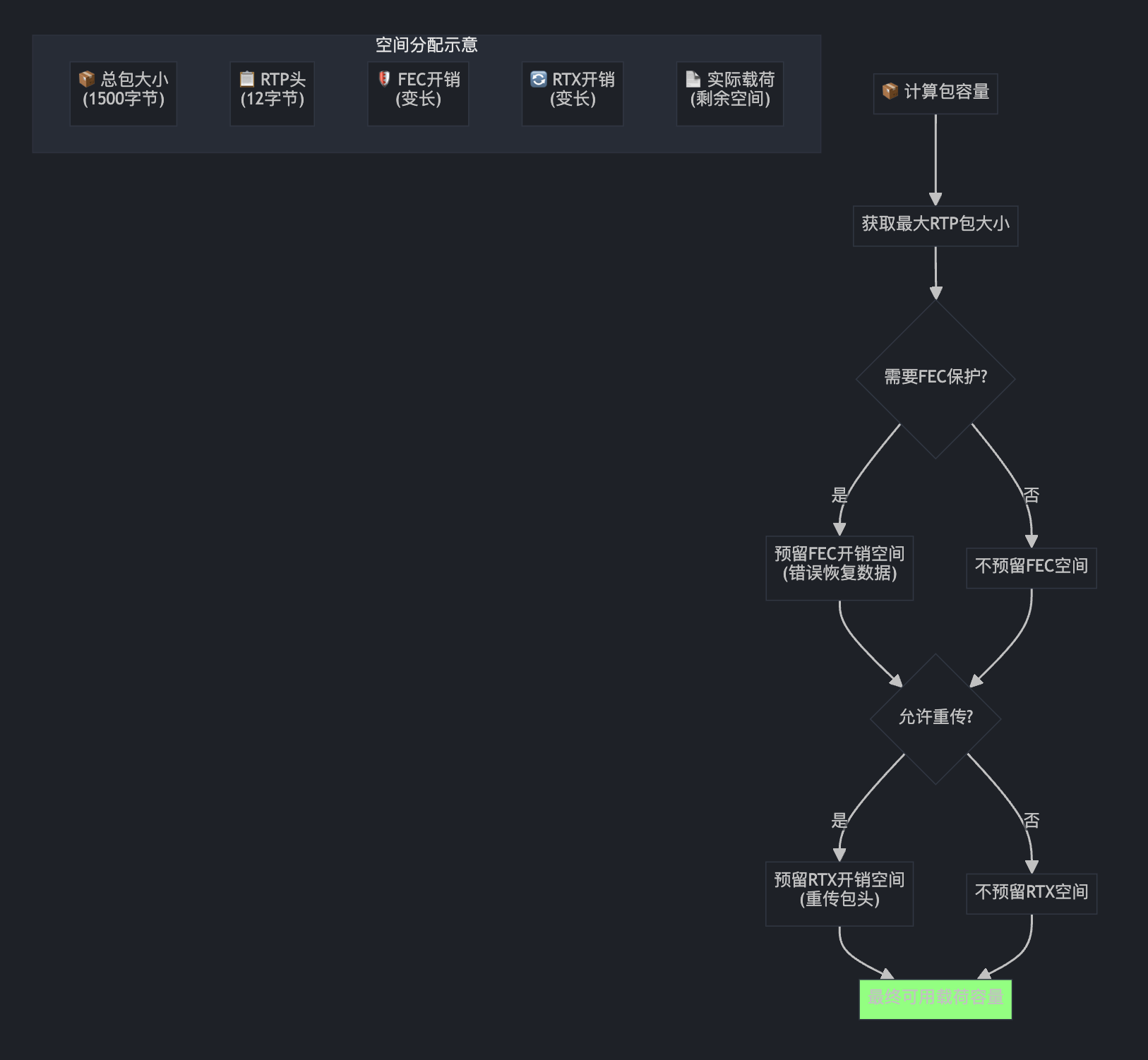
第五部分:RTP包模板创建与扩展头处理
std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend> single_packet =
rtp_sender_->AllocatePacket(csrcs);
// ... 设置基本属性 ...
auto first_packet = std::make_unique<RtpPacketToSend>(*single_packet);
auto middle_packet = std::make_unique<RtpPacketToSend>(*single_packet);
auto last_packet = std::make_unique<RtpPacketToSend>(*single_packet);
// 为不同类型的包添加扩展头
AddRtpHeaderExtensions(video_header, /*first_packet=*/true, /*last_packet=*/true, single_packet.get());
AddRtpHeaderExtensions(video_header, /*first_packet=*/true, /*last_packet=*/false, first_packet.get());
AddRtpHeaderExtensions(video_header, /*first_packet=*/false, /*last_packet=*/false, middle_packet.get());
AddRtpHeaderExtensions(video_header, /*first_packet=*/false, /*last_packet=*/true, last_packet.get());
这就像快递公司为不同类型的包裹预制标签模板: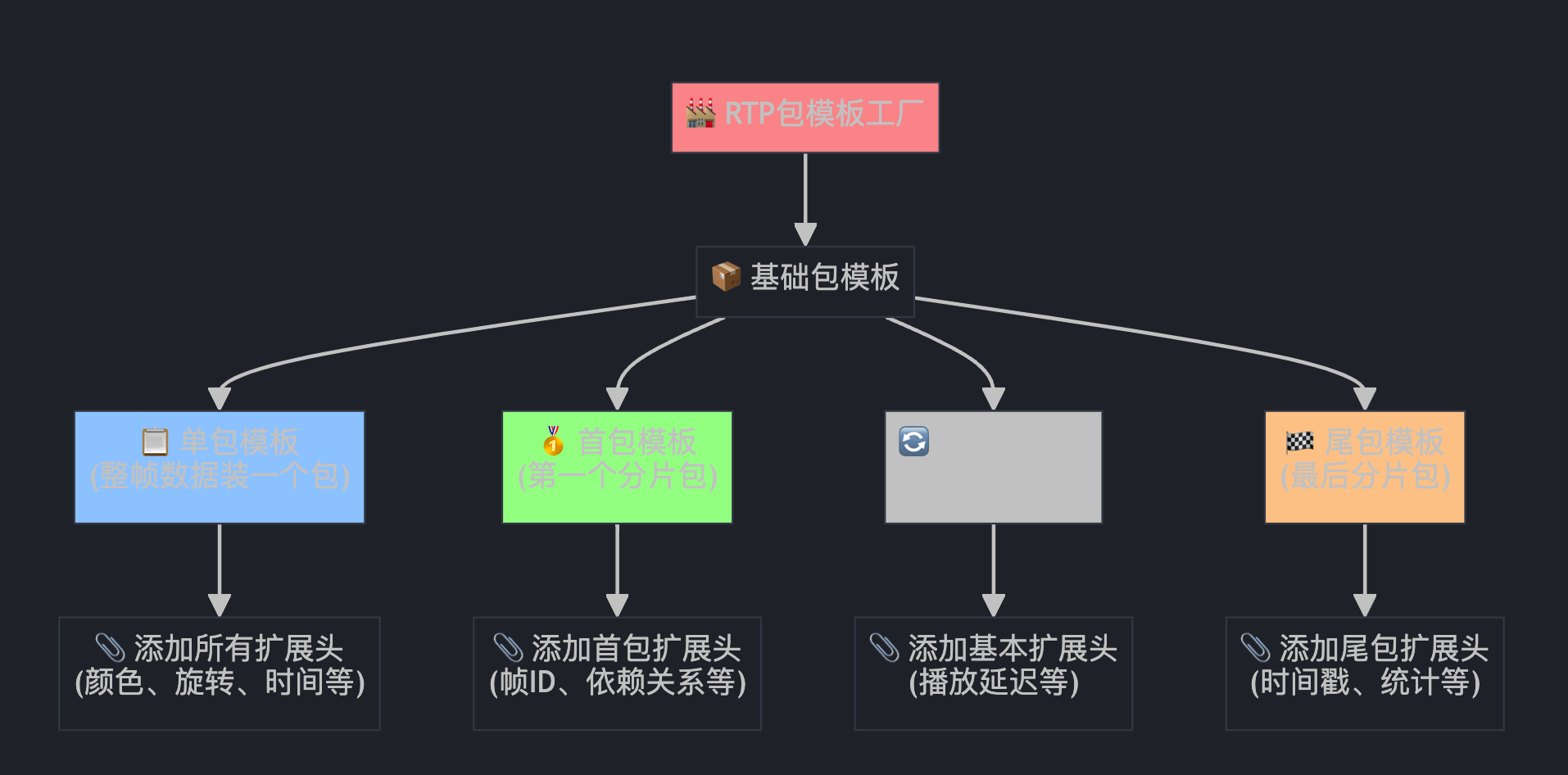
为什么需要不同的包模板?
想象一个大视频帧就像一本厚书要邮寄: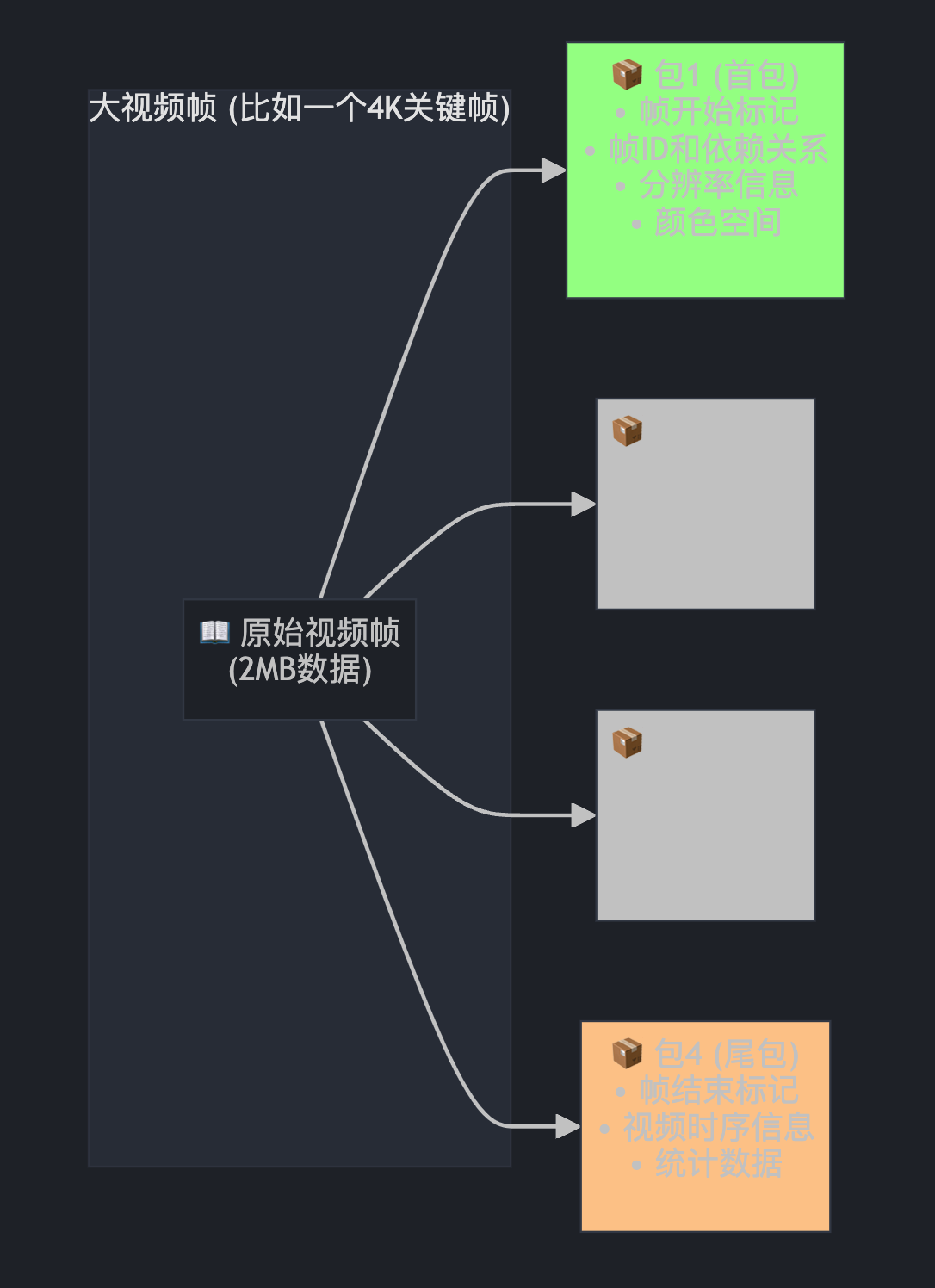
第六部分:载荷大小限制计算
RtpPacketizer::PayloadSizeLimits limits;
limits.max_payload_len = packet_capacity - middle_packet->headers_size();
limits.single_packet_reduction_len =
single_packet->headers_size() - middle_packet->headers_size();
limits.first_packet_reduction_len =
first_packet->headers_size() - middle_packet->headers_size();
limits.last_packet_reduction_len =
last_packet->headers_size() - middle_packet->headers_size();
这就像计算不同规格快递盒的实际装货空间: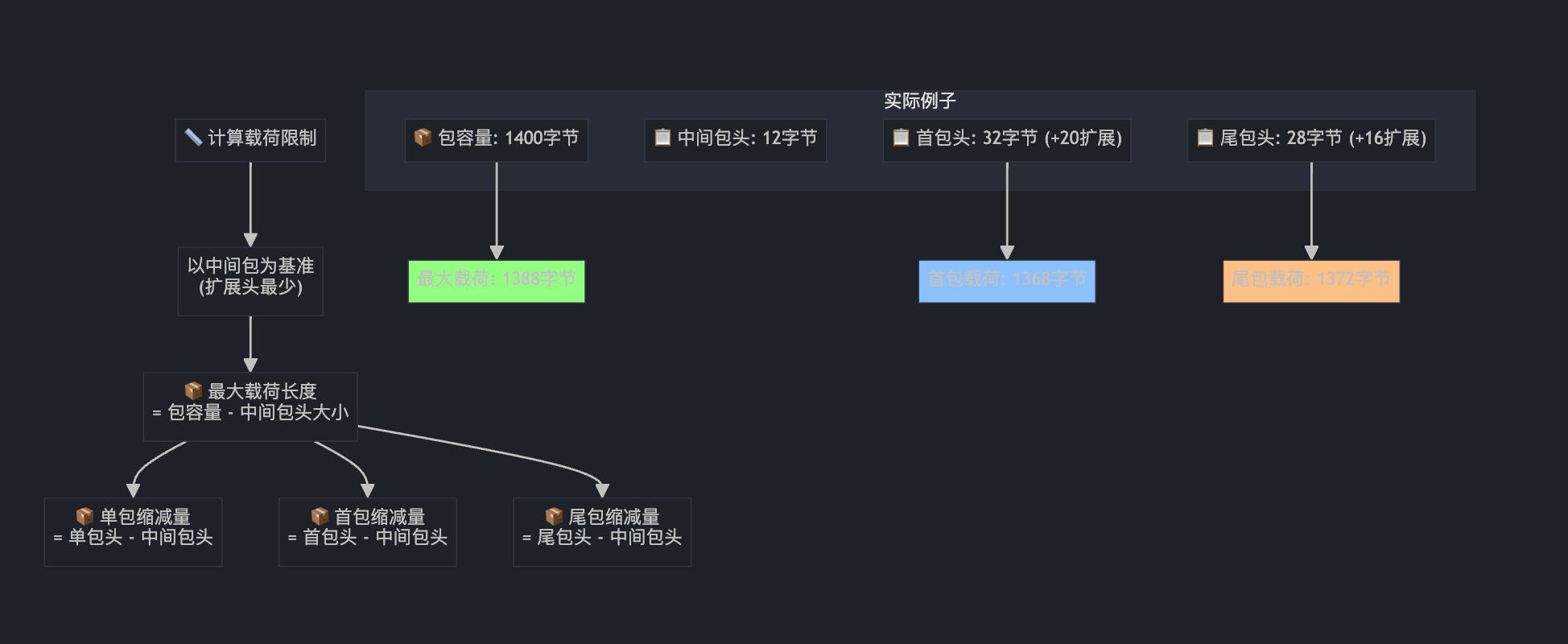
第七部分:加密处理
rtc::Buffer encrypted_video_payload;
if (frame_encryptor_ != nullptr) {
const size_t max_ciphertext_size =
frame_encryptor_->GetMaxCiphertextByteSize(cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO,
payload.size());
encrypted_video_payload.SetSize(max_ciphertext_size);
size_t bytes_written = 0;
// Enable header authentication if the field trial isn't disabled.
std::vector<uint8_t> additional_data;
if (generic_descriptor_auth_experiment_) {
additional_data = RtpDescriptorAuthentication(video_header);
}
if (frame_encryptor_->Encrypt(
cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, first_packet->Ssrc(), additional_data,
payload, encrypted_video_payload, &bytes_written) != 0) {
return false;
}
encrypted_video_payload.SetSize(bytes_written);
payload = encrypted_video_payload;
} else if (require_frame_encryption_) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING) << "No FrameEncryptor is attached...";
}
这就像给重要文件加密封存: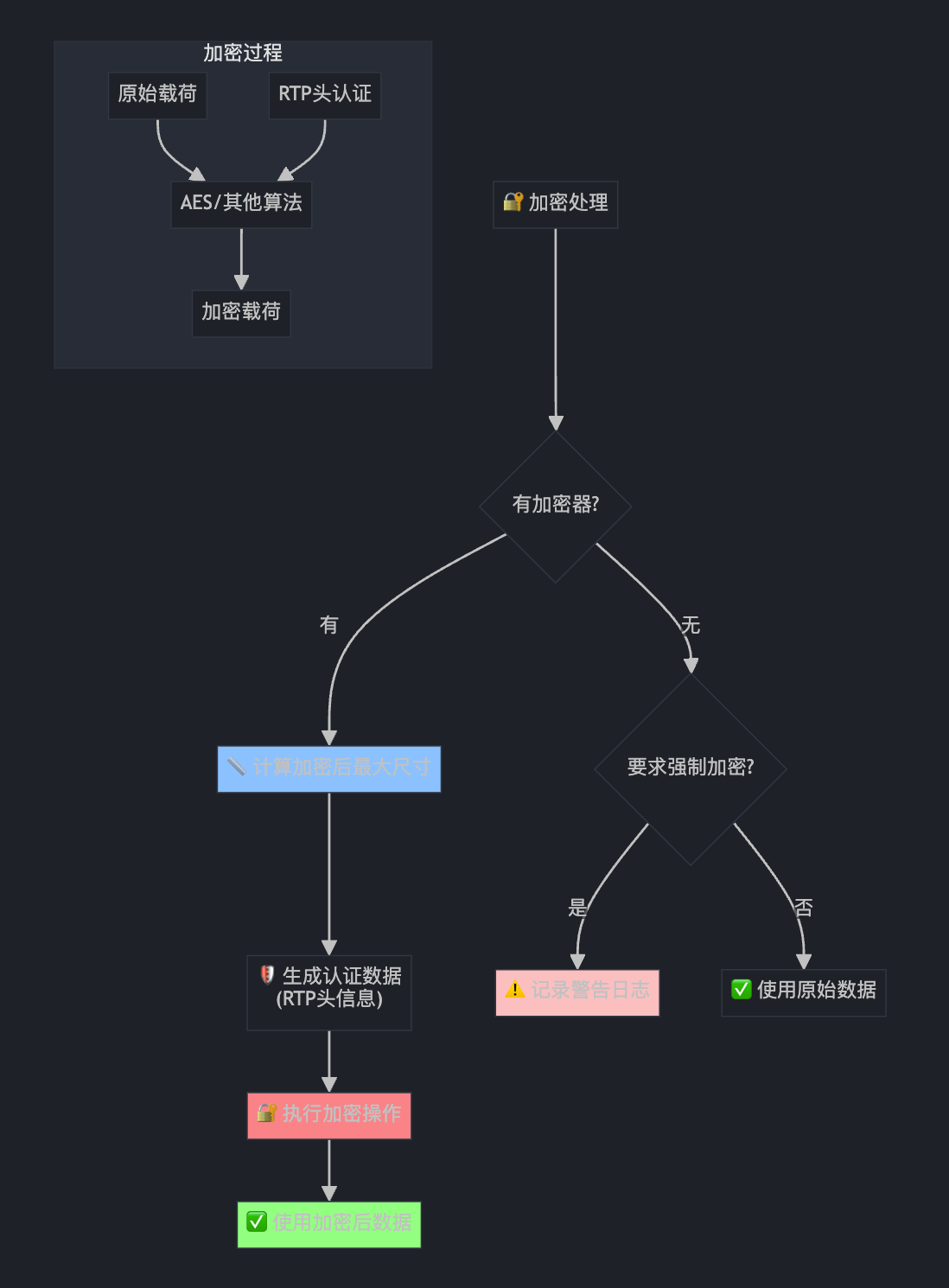
第八部分:RTP分包器(核心!)
std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketizer> packetizer = RtpPacketizer::Create(
codec_type, payload, limits, video_header, enable_av1_even_split_);
const size_t num_packets = packetizer->NumPackets();
if (num_packets == 0)
return false;
这就像智能切菜机,根据不同食材选择不同的切法:
第九部分:分包循环处理(超级重要!)
bool first_frame = first_frame_sent_();
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend>> rtp_packets;
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_packets; ++i) {
std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend> packet;
int expected_payload_capacity;
// Choose right packet template:
if (num_packets == 1) {
packet = std::move(single_packet);
expected_payload_capacity = limits.max_payload_len - limits.single_packet_reduction_len;
} else if (i == 0) {
packet = std::move(first_packet);
expected_payload_capacity = limits.max_payload_len - limits.first_packet_reduction_len;
} else if (i == num_packets - 1) {
packet = std::move(last_packet);
expected_payload_capacity = limits.max_payload_len - limits.last_packet_reduction_len;
} else {
packet = std::make_unique<RtpPacketToSend>(*middle_packet);
expected_payload_capacity = limits.max_payload_len;
}
packet->set_first_packet_of_frame(i == 0);
if (!packetizer->NextPacket(packet.get()))
return false;
// 设置包属性...
packet->set_allow_retransmission(allow_retransmission);
packet->set_is_key_frame(video_header.frame_type == VideoFrameType::kVideoFrameKey);
packet->set_fec_protect_packet(use_fec);
这就像流水线装配包裹: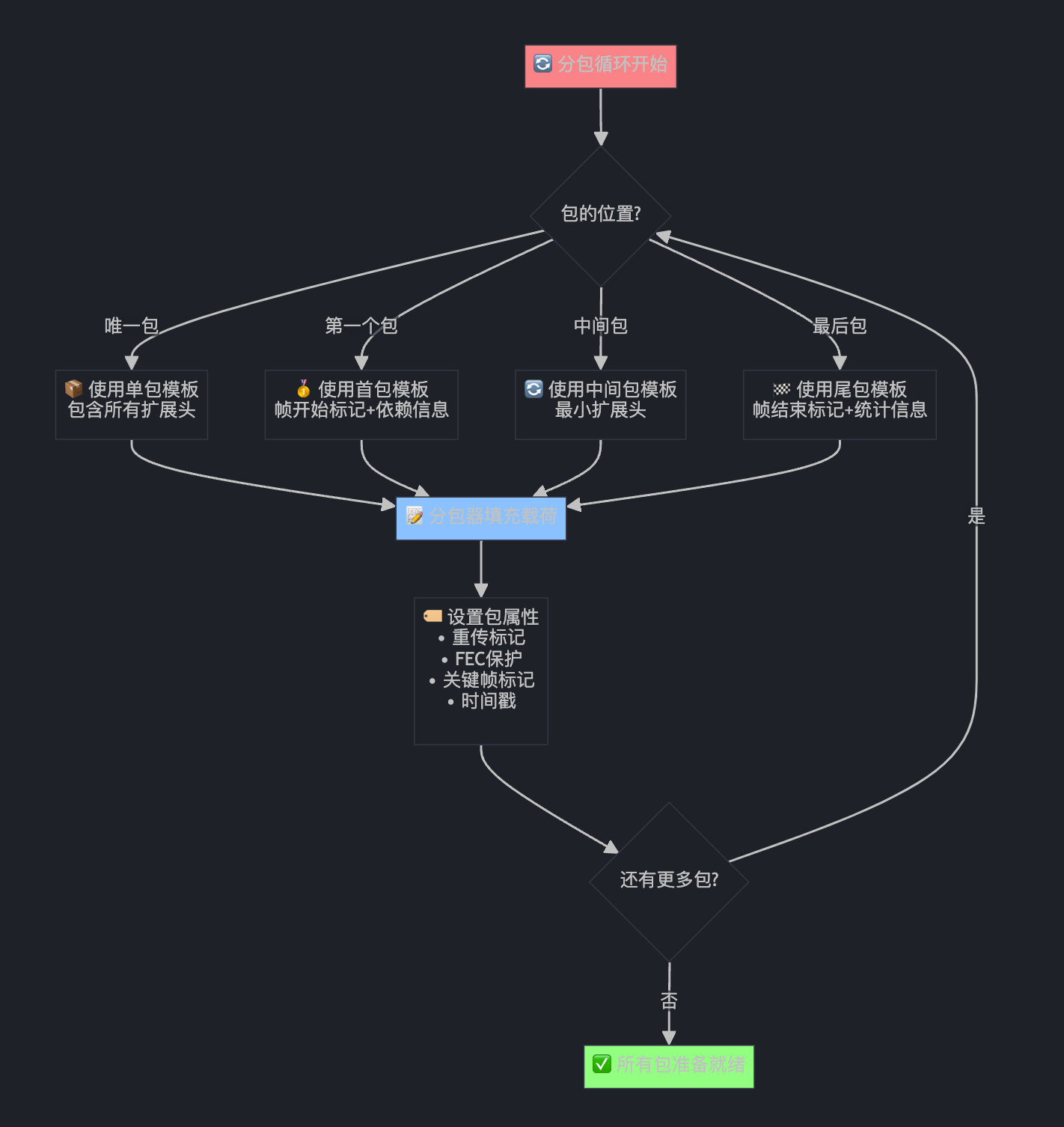
第十部分:RED冗余编码与最终发送
if (red_enabled()) {
// TODO(sprang): Consider packetizing directly into packets with the RED
// header already in place, to avoid this copy.
std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend> red_packet(new RtpPacketToSend(*packet));
BuildRedPayload(*packet, red_packet.get());
red_packet->SetPayloadType(*red_payload_type_);
red_packet->set_is_red(true);
// Append `red_packet` instead of `packet` to output.
red_packet->set_packet_type(RtpPacketMediaType::kVideo);
red_packet->set_allow_retransmission(packet->allow_retransmission());
rtp_packets.emplace_back(std::move(red_packet));
} else {
packet->set_packet_type(RtpPacketMediaType::kVideo);
rtp_packets.emplace_back(std::move(packet));
}
// 首帧日志记录...
if (first_frame) {
if (i == 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Sent first RTP packet of the first video frame (pre-pacer)";
}
if (i == num_packets - 1) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Sent last RTP packet of the first video frame (pre-pacer)";
}
}
// 实际发送
LogAndSendToNetwork(std::move(rtp_packets), encoder_output_size);
这就像给重要包裹加"双保险":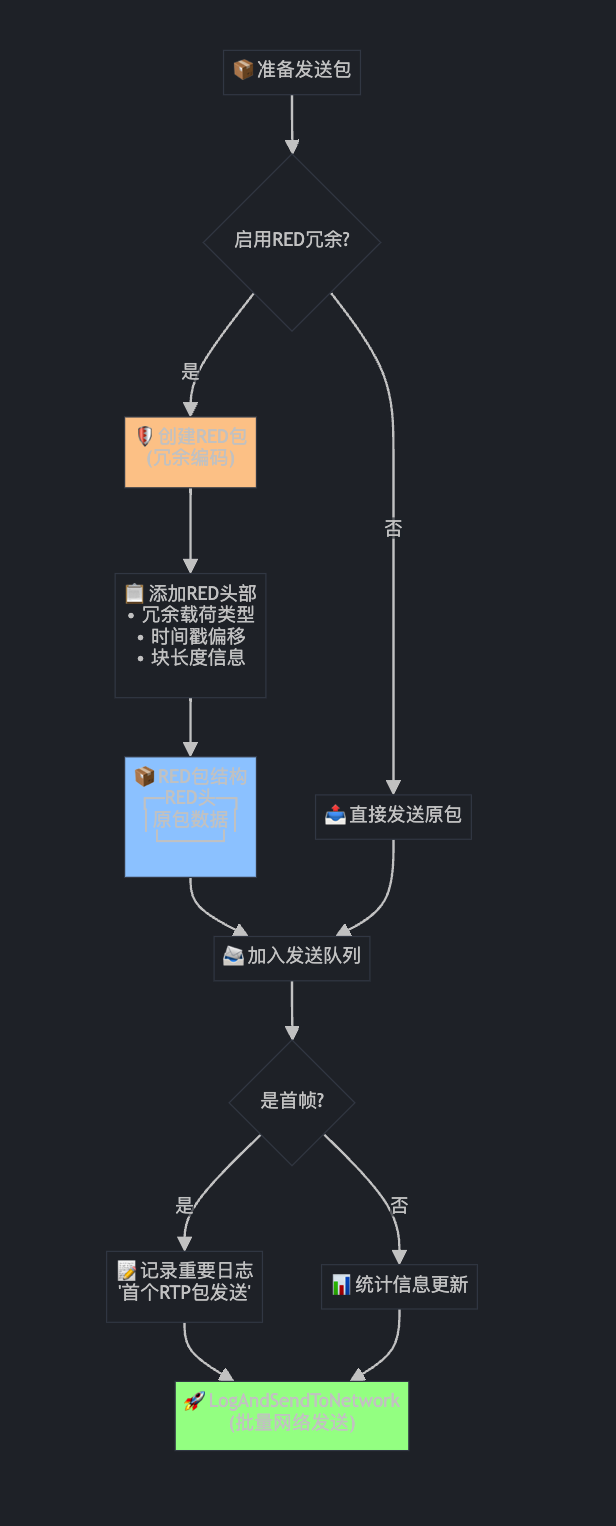
第十一部分:状态更新与收尾
// Update details about the last sent frame.
last_rotation_ = video_header.rotation;
if (video_header.color_space != last_color_space_) {
last_color_space_ = video_header.color_space;
transmit_color_space_next_frame_ = !IsBaseLayer(video_header);
} else {
transmit_color_space_next_frame_ =
transmit_color_space_next_frame_ ? !IsBaseLayer(video_header) : false;
}
if (video_header.frame_type == VideoFrameType::kVideoFrameKey ||
PacketWillLikelyBeRequestedForRestransmissionIfLost(video_header)) {
// This frame will likely be delivered, no need to populate playout
// delay extensions until it changes again.
playout_delay_pending_ = false;
if (send_allocation_ == SendVideoLayersAllocation::kSendWithResolution) {
last_full_sent_allocation_ = allocation_;
}
send_allocation_ = SendVideoLayersAllocation::kDontSend;
}
return true;
这就像快递发送后的"记录备案"工作: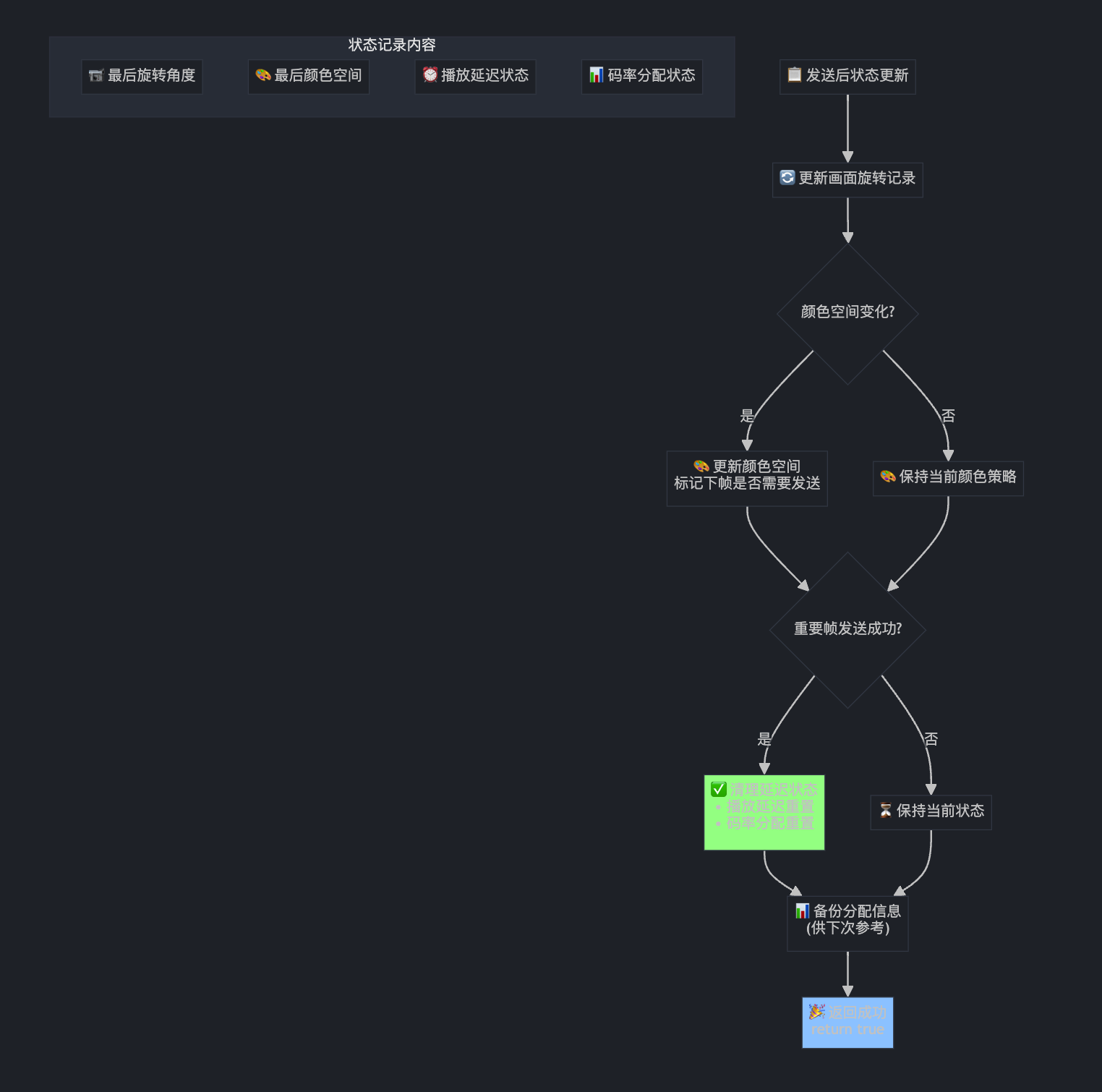
SendVideo 方法完整流程总结
现在让我们把整个 SendVideo 方法的处理流程串联起来: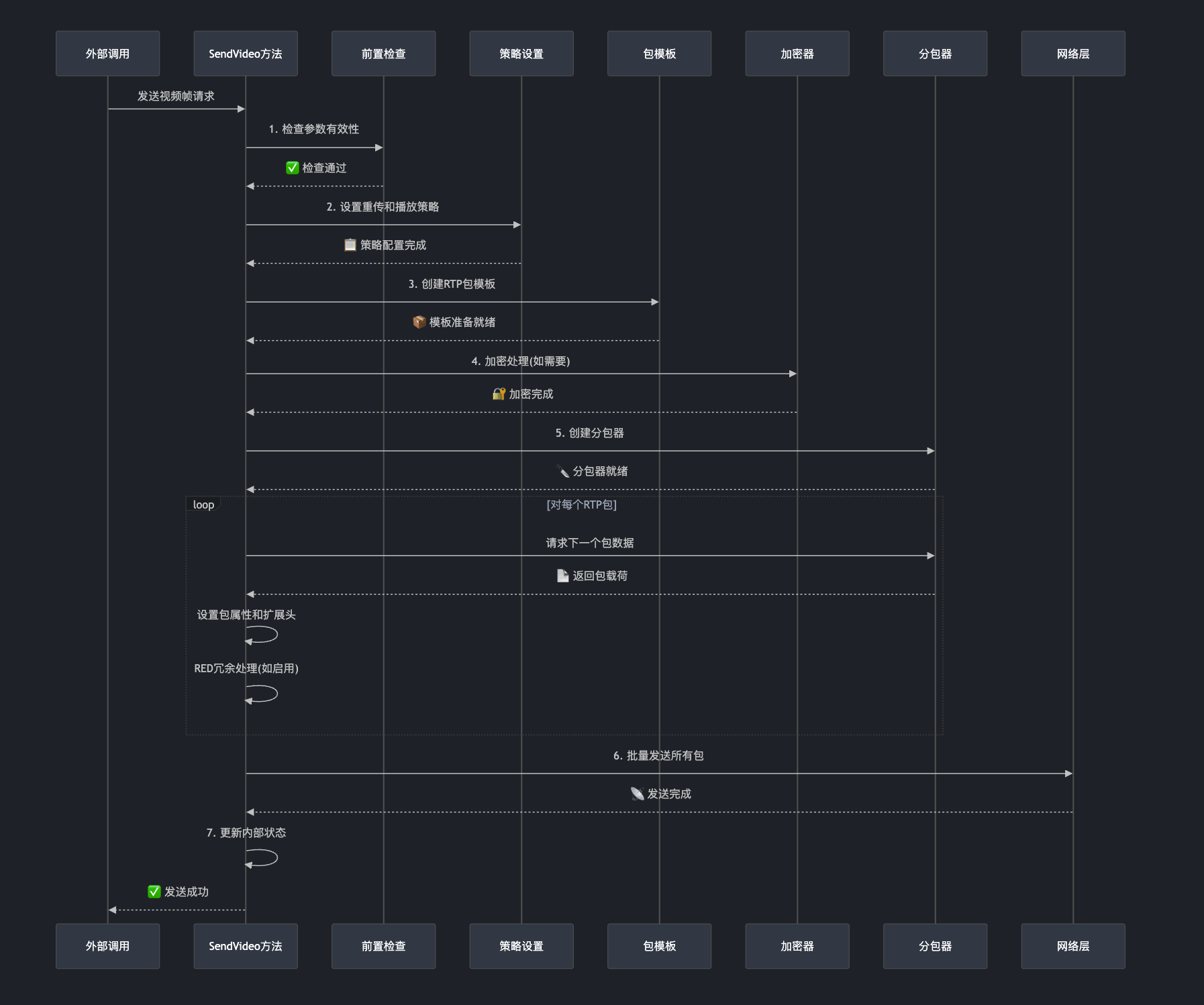
SendVideo 方法虽然代码很长,但它就像一个经验丰富的快递调度员:
📋 接单时仔细检查包裹信息
🎯 打包时选择最合适的策略
🔐 封装时确保安全和完整性
🚀 发送时优化网络传输效率
📊 送达后及时更新状态记录
这就是为什么 WebRTC 能在复杂的网络环境中稳定传输高质量视频的关键所在!

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献14条内容
已为社区贡献14条内容





所有评论(0)