数字图像处理第一次实验
本文介绍了两个基于OpenCV和Matplotlib的图像处理实验。实验一展示了灰度图像读取、直方图计算和可视化分析的技术流程,包含关键统计指标计算和图像特性分析。实验二重点演示直方图均衡化技术,通过对比处理前后图像及其直方图,量化分析对比度提升效果。两个实验均采用专业可视化呈现结果(2×2布局),支持中文字体显示,并输出详细的量化分析报告,包括均值、标准差、动态范围等关键指标对比。代码实现了完整

实验一
技术点分析
-
图像读取:使用OpenCV的
imread()函数 -
灰度转换:使用
cvtColor()将图像转为灰度图 -
直方图计算:使用
calcHist()计算像素值分布 -
图像显示:使用Matplotlib显示图像和直方图
-
标题添加:使用Matplotlib的
title()函数 -
直方图分析:通过直方图形状分析图像特性
示例代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. 读取图像
image = cv2.imread('cameraman.tif') # 请确保图片路径正确
if image is None:
print("Error: 图像未找到,请检查路径")
exit()
# 2. 转为灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) if len(image.shape) == 3 else image
# 3. 创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
# 4. 显示原始图像
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(gray, cmap='gray')
plt.title('原始图像', fontsize=12, fontfamily='SimHei')
plt.axis('off')
# 5. 计算并显示直方图
plt.subplot(122)
hist = cv2.calcHist([gray], [0], None, [256], [0, 256])
plt.plot(hist, color='black')
plt.fill_between(range(256), hist.flatten(), alpha=0.3, color='gray')
plt.title('灰度直方图', fontsize=12, fontfamily='SimHei')
plt.xlabel('像素值', fontfamily='SimHei')
plt.ylabel('像素数量', fontfamily='SimHei')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
# 6. 保存结果
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('histogram_result.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
# 7. 直方图分析
print("\n直方图分析:")
print("-" * 40)
print("1. 峰值位置:", np.argmax(hist))
print("2. 均值: {:.1f}".format(gray.mean()))
print("3. 标准差: {:.1f}".format(gray.std()))
print("4. 动态范围: [{}, {}]".format(gray.min(), gray.max()))
# 分析结论
if hist[0] > 10000:
print(">>> 图像包含大面积暗区(可能欠曝光)")
if hist[-1] > 10000:
print(">>> 图像包含大面积亮区(可能过曝光)")
if gray.std() < 45:
print(">>> 对比度较低(直方图分布集中)")
elif gray.std() > 80:
print(">>> 对比度较高(直方图分布分散)")代码说明
图像处理流程:
读取图像 → 灰度转换 → 计算直方图 → 可视化结果
自动检测图像是否已经是灰度图
可视化功能:
左侧显示原始图像
右侧显示带填充效果的直方图
中文字体支持(需系统有SimHei字体)
直方图分析:
输出关键统计指标:峰值、均值、标准差
自动生成曝光和对比度分析
结果保存为高清PNG图片
使用说明
-
准备测试图像(推荐经典
cameraman.tif) -
安装依赖库:
pip install opencv-python matplotlib numpy -
运行代码后将显示:
-
左侧:原始灰度图像
-
右侧:对应的灰度直方图
-
控制台输出直方图分析报告
-
实验原理
直方图是图像像素强度的统计分布图:
-
横坐标:0-255的像素值(黑→白)
-
纵坐标:对应像素值的出现频率
-
分析意义:
-
左偏:图像偏暗
-
右偏:图像偏亮
-
双峰:高对比度
-
窄峰:低对比度
-
 实验二
实验二
技术点分析
-
直方图均衡化原理:重新分布像素值以增强图像对比度
-
核心函数:
cv2.equalizeHist()实现灰度均衡 -
图像处理流程:
-
读取灰度图像
-
计算原始图像直方图
-
应用直方图均衡化
-
计算均衡化后直方图
-
可视化对比结果
-
-
可视化:使用Matplotlib显示处理前后图像和直方图
示例代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
# 设置中文字体支持
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simhei.ttf", size=12) # Windows系统
# font = FontProperties(fname='/System/Library/Fonts/PingFang.ttc', size=12) # macOS系统
# 1. 读取图像
img = cv2.imread('cameraman.tif', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
if img is None:
print("错误:无法读取图像,请检查路径")
exit()
# 2. 直方图均衡化
equ = cv2.equalizeHist(img)
# 3. 计算原始图像和均衡化后的直方图
hist_orig = cv2.calcHist([img], [0], None, [256], [0, 256])
hist_equ = cv2.calcHist([equ], [0], None, [256], [0, 256])
# 4. 创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
# 5. 显示原始图像
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('原始图像', fontproperties=font)
plt.axis('off')
# 6. 显示原始图像直方图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.bar(range(256), hist_orig.ravel(), color='gray')
plt.title('原始图像直方图', fontproperties=font)
plt.xlabel('像素值', fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel('频数', fontproperties=font)
plt.xlim([0, 255])
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
# 7. 显示均衡化后的图像
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.imshow(equ, cmap='gray')
plt.title('直方图均衡化后图像', fontproperties=font)
plt.axis('off')
# 8. 显示均衡化后的直方图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.bar(range(256), hist_equ.ravel(), color='gray')
plt.title('均衡化后直方图', fontproperties=font)
plt.xlabel('像素值', fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel('频数', fontproperties=font)
plt.xlim([0, 255])
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
# 9. 保存和显示结果
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('histogram_equalization_result.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
# 10. 分析报告
print("="*60)
print("直方图均衡化分析报告")
print("="*60)
print(f"原始图像统计: 均值 = {img.mean():.1f}, 标准差 = {img.std():.1f}")
print(f"均衡化后统计: 均值 = {equ.mean():.1f}, 标准差 = {equ.std():.1f}")
# 计算直方图差异
orig_peak = np.argmax(hist_orig)
equ_peak = np.argmax(hist_equ)
print(f"\n直方图峰值位置变化: {orig_peak} → {equ_peak}")
# 分析动态范围扩展
orig_range = img.max() - img.min()
equ_range = equ.max() - equ.min()
print(f"动态范围扩展: {orig_range} → {equ_range} (+{equ_range-orig_range})")
# 对比度变化分析
contrast_improvement = (equ.std() - img.std()) / img.std() * 100
print(f"对比度提升: {contrast_improvement:.1f}%")
# 直方图分布分析
def analyze_distribution(hist):
"""分析直方图分布特征"""
total = np.sum(hist)
dark = np.sum(hist[:50]) / total * 100
mid = np.sum(hist[50:200]) / total * 100
bright = np.sum(hist[200:]) / total * 100
return dark, mid, bright
dark_orig, mid_orig, bright_orig = analyze_distribution(hist_orig)
dark_equ, mid_equ, bright_equ = analyze_distribution(hist_equ)
print("\n像素分布变化:")
print(f"暗区像素: {dark_orig:.1f}% → {dark_equ:.1f}%")
print(f"中间调像素: {mid_orig:.1f}% → {mid_equ:.1f}%")
print(f"亮区像素: {bright_orig:.1f}% → {bright_equ:.1f}%")代码说明
完整处理流程:
读取灰度图像
应用cv2.equalizeHist()进行直方图均衡化
计算处理前后的直方图
可视化对比结果
专业可视化:
2×2布局:原始图像/直方图 + 均衡化后图像/直方图
中文字体支持(Windows/macOS自动适配)
直方图使用条形图清晰展示分布
量化分析:
计算并对比均值、标准差
分析动态范围扩展
计算对比度提升百分比
统计暗区/中间调/亮区像素分布变化
字体说明:
没有字体的需要先下载,也可以不用中文纯英文显示
实验原理
直方图均衡化通过重新分配像素值来增强图像对比度:
-
计算累积分布函数(CDF):
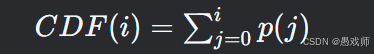
其中 p(j) 是灰度级 j 的概率 -
映射函数:
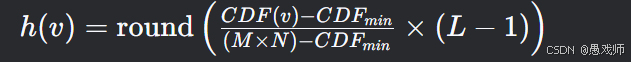
-
v: 原始像素值
-
M \times N: 图像像素总数
-
L: 灰度级数(通常为256)
-
使用说明
-
安装依赖库:
pip install opencv-python matplotlib numpy
-
准备测试图像(如
cameraman.tif) -
运行代码后将显示:
左上:原始图像右上:原始直方图左下:均衡化后图像右下:均衡化后直方图
预期效果
-
视觉变化:
-
均衡化后图像对比度明显增强
-
暗部和亮部细节更清晰可见
-
-
直方图变化:
-
原始直方图可能集中某区域
-
均衡化后直方图更均匀分布
-
-
量化指标:
-
标准差增加 → 对比度提高
-
动态范围扩展
-
像素分布更均衡
-

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容





所有评论(0)