RAG的21种技术测评(二)
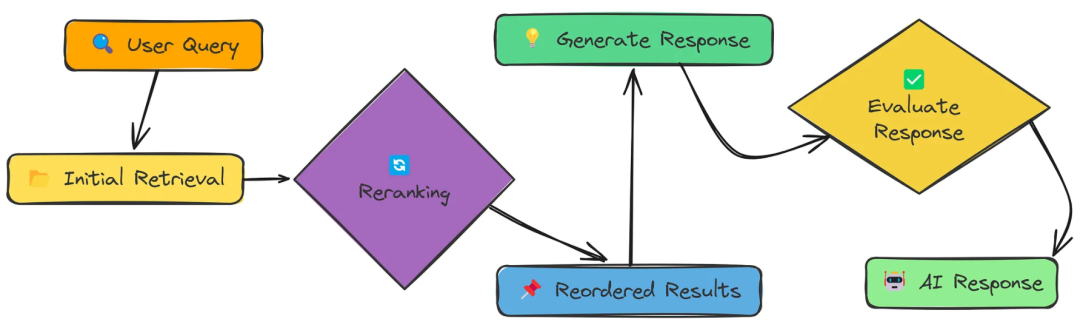
重新排序技术,是以提高RAG系统的检索质量。,以确保将最相关的内容用于生成响应。
RAG的21种技术测评(二)
八、ReRanker(重排序)
重新排序技术,是以提高RAG系统的检索质量。重新排序是初始检索之后的第二个过滤步骤,以确保将最相关的内容用于生成响应。
核心代码
基于llm的重新排序功能。
依次遍历第一次检索后的数据,然后让模型对用户查询以及每一个结果文档进行打分,0~10分,越接近分越高。
def rerank_with_llm(query, results, top_n=3, model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"):
"""
使用LLM相关性评分对搜索结果重新排序。
query: 查询的问题
results: 第一次检索后的结果
"""
print(f"Reranking {len(results)} documents...") # Print the number of documents to be reranked
scored_results = [] # Initialize an empty list to store scored results
# Define the system prompt for the LLM
"""
你是评估搜索查询文档相关性的专家。
您的任务是根据文档对给定查询的回答程度,对文档进行从0到10的评分。
指南:
- 得分0-2:文件完全无关紧要
- 3-5分:文档有一些相关信息,但没有直接回答问题
— 6-8分:文档内容相关,部分回答了问题
— 9-10分:文档高度相关,直接回答了问题
你只能回答一个0到10之间的整数分。不要包括任何其他文本。
"""
system_prompt = """You are an expert at evaluating document relevance for search queries.
Your task is to rate documents on a scale from 0 to 10 based on how well they answer the given query.
Guidelines:
- Score 0-2: Document is completely irrelevant
- Score 3-5: Document has some relevant information but doesn't directly answer the query
- Score 6-8: Document is relevant and partially answers the query
- Score 9-10: Document is highly relevant and directly answers the query
You MUST respond with ONLY a single integer score between 0 and 10. Do not include ANY other text."""
# Iterate through each result
for i, result in enumerate(results):
# 每5个文件显示进度
if i % 5 == 0:
print(f"Scoring document {i+1}/{len(results)}...")
# Define the user prompt for the LLM
# 将此文档与查询问题的相关性从0到10进行评分:
user_prompt = f"""Query: {query}
Document:
{result['text']}
Rate this document's relevance to the query on a scale from 0 to 10:
"""
# Get the LLM response
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
temperature=0,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt}
]
)
# Extract the score from the LLM response
score_text = response.choices[0].message.content.strip()
# 使用正则表达式提取数值分数
score_match = re.search(r'\b(10|[0-9])\b', score_text)
if score_match:
score = float(score_match.group(1))
else:
# 如果分数提取失败,则使用相似分数作为回退
print(f"Warning: Could not extract score from response: '{score_text}', using similarity score instead")
score = result["similarity"] * 10
# 将得分结果追加到列表中
scored_results.append({
"text": result["text"],
"metadata": result["metadata"],
"similarity": result["similarity"],
"relevance_score": score
})
# 按相关性评分降序排序结果
reranked_results = sorted(scored_results, key=lambda x: x["relevance_score"], reverse=True)
# Return the top_n results
return reranked_results[:top_n]
基于关键字的重新排名
1、首先对查询进行分词
2、然后遍历分好的词
3、依次匹配第一次检索中的结果,如果检索结果包含关键字,则给该结果增加分数
def rerank_with_keywords(query, results, top_n=3):
"""
基于关键字的重新排名
Args:
query: 用户的查询
results: 第一次检索的结果
"""
# 从查询中提取重要的关键字
keywords = [word.lower() for word in query.split() if len(word) > 3]
scored_results = [] # Initialize a list to store scored results
for result in results:
document_text = result["text"].lower() # 将文档文本转换为小写
# 基础分数从向量相似度开始
base_score = result["similarity"] * 0.5
# Initialize keyword score
keyword_score = 0
for keyword in keywords:
if keyword in document_text:
# 为找到的每个关键字添加点
keyword_score += 0.1
# 如果关键字出现在开头,添加更多的点
first_position = document_text.find(keyword)
if first_position < len(document_text) / 4: # In the first quarter of the text
keyword_score += 0.1
# 添加关键字频率点
frequency = document_text.count(keyword)
keyword_score += min(0.05 * frequency, 0.2) # Cap at 0.2
# 结合基础分数和关键字分数计算最终分数
final_score = base_score + keyword_score
# Append the scored result to the list
scored_results.append({
"text": result["text"],
"metadata": result["metadata"],
"similarity": result["similarity"],
"relevance_score": final_score
})
# 按最终相关性评分降序排序结果
reranked_results = sorted(scored_results, key=lambda x: x["relevance_score"], reverse=True)
# Return the top_n results
return reranked_results[:top_n]
评测
重排序带来了显著的改进。通过使用LLM排序以及关键字排序,对每个检索到的文档和查询的相关性进行评分排序,能够优先获取到最佳信息。这是一项强大的技术,可以显著提高RAG系统的质量。
优点: 提高了最终传递给生成模型的信息质量,减少了低相关度文档的干扰。
缺点: 增加了系统的计算开销,需要设计高效的排序算法以保证响应速度。
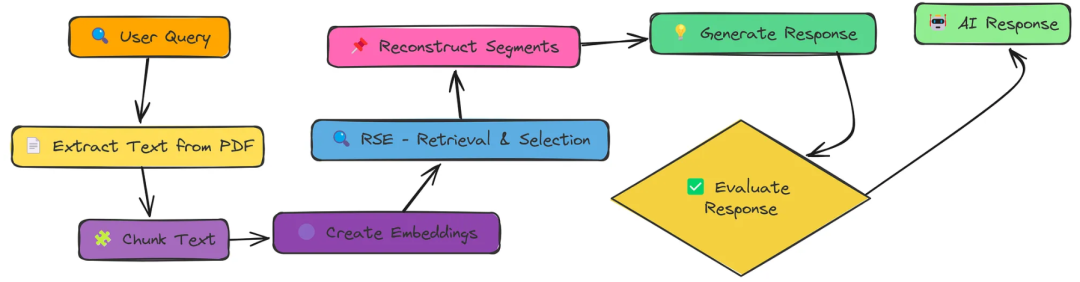
九、RSE(基于检索的语义增强 Retrieval-based Semantic Enhancement)
增强型RAG的相关段提取(RSE)
RSE技术以提高我们的RAG系统中的上下文质量。我们不是简单地检索孤立块的集合,而是识别和重建连续的文本片段,为我们的语言模型提供更好的上下文。
相关的组块倾向于在文档中聚集在一起。通过识别这些集群并保持它们的连续性,我们为LLM提供了更一致的工作环境。
核心代码
RSE核心算法:计算块值和寻找最佳分段
def calculate_chunk_values(query, chunks, vector_store, irrelevant_chunk_penalty=0.2):
"""
结合相关性和位置计算块值。
"""
# Create query embedding
query_embedding = create_embeddings([query])[0]
# 获得所有具有相似分数的块
num_chunks = len(chunks)
results = vector_store.search(query_embedding, top_k=num_chunks)
# 创建chunk_index到关联分数的映射
relevance_scores = {result["metadata"]["chunk_index"]: result["score"] for result in results}
# 计算块值(相关性分数减去惩罚)
chunk_values = []
for i in range(num_chunks):
# 获得相关性评分,如果结果中没有,则默认为0
score = relevance_scores.get(i, 0.0)
# 在不相关的块具有负值时,应用惩罚来转换为值
value = score - irrelevant_chunk_penalty
chunk_values.append(value)
return chunk_values
评测
测试评分为0.8。
优点: 能够提升检索结果的语义一致性,可以适用于检索信息更复杂或语义更模糊的问题。
缺点: 实现过程中对语义提取的依赖较高,需确保语义模型的准确性。
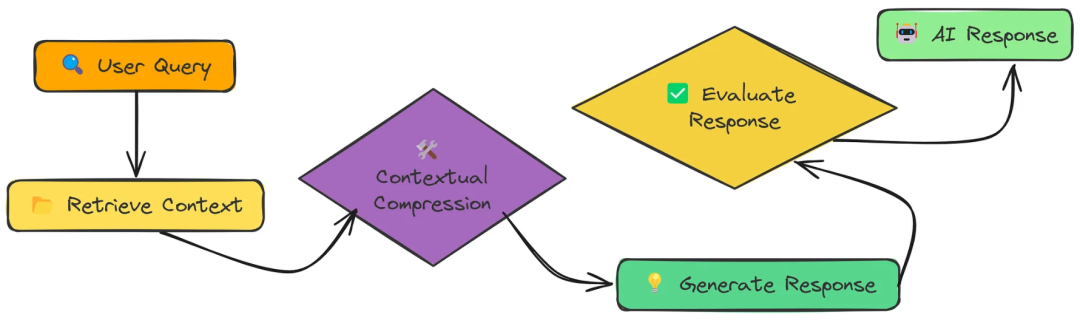
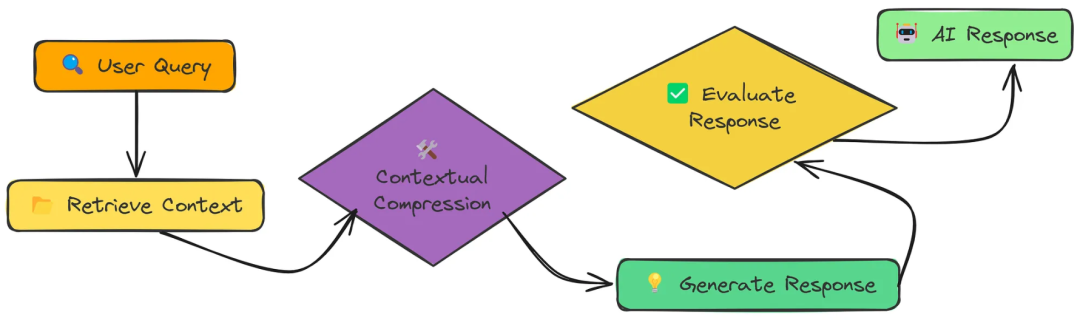
十、Contextual Compression(上下文压缩)
上下文压缩,将过滤和压缩检索到的文本块,只保留最相关的部分,减少噪音,提高响应质量。
在为RAG检索文档时,我们经常得到包含相关和不相关信息的块。上下文压缩帮助我们:
- 删除不相关的句子和段落
- 只关注与查询相关的信息
- 最大化上下文窗口中的有用信号
核心代码
# 这是我们方法的核心——我们将使用LLM来过滤和压缩检索到的内容
def compress_chunk(chunk, query, compression_type="selective", model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"):
"""
通过只保留与查询相关的部分来压缩检索到的块。
"""
# 为不同的压缩方法定义系统提示
if compression_type == "selective":
"""
你是信息过滤的专家。
你的任务是分析一个文档块,并只提取直接相关的句子或段落
与用户查询相关。删除所有无关的内容。
您的输出应该:
1. 只包含有助于回答查询的文本
2. 保留相关句子的准确措辞(不要转述)
3. 保持原文的顺序
4. 包括所有相关的内容,即使它看起来多余
5. 排除任何与查询无关的文本
将您的回复格式为纯文本,不带任何额外的注释。
"""
system_prompt = """You are an expert at information filtering.
Your task is to analyze a document chunk and extract ONLY the sentences or paragraphs that are directly
relevant to the user's query. Remove all irrelevant content.
Your output should:
1. ONLY include text that helps answer the query
2. Preserve the exact wording of relevant sentences (do not paraphrase)
3. Maintain the original order of the text
4. Include ALL relevant content, even if it seems redundant
5. EXCLUDE any text that isn't relevant to the query
Format your response as plain text with no additional comments."""
elif compression_type == "summary":
"""
你是总结的专家。
您的任务是创建提供块的简明摘要,该块仅关注于
与用户查询相关的信息。
您的输出应该:
1. 与查询相关的信息要简短但全面
2. 只关注与查询相关的信息
3. 省略无关的细节
4. 用中立的、实事求是的语气写作
将您的回复格式为纯文本,不带任何额外的注释
"""
system_prompt = """You are an expert at summarization.
Your task is to create a concise summary of the provided chunk that focuses ONLY on
information relevant to the user's query.
Your output should:
1. Be brief but comprehensive regarding query-relevant information
2. Focus exclusively on information related to the query
3. Omit irrelevant details
4. Be written in a neutral, factual tone
Format your response as plain text with no additional comments."""
else: # extraction
"""
你是信息提取的专家。
您的任务是从文档块中提取包含相关信息的准确句子
回答用户的查询。
您的输出应该:
1. 只直接引用原文中的相关句子
2. 保留原文(不修改文本)
3. 只包含与查询直接相关的句子
4. 用换行符分隔提取的句子
5. 不要添加任何评论或附加文本
将您的回复格式为纯文本,不带任何额外的注释。
"""
system_prompt = """You are an expert at information extraction.
Your task is to extract ONLY the exact sentences from the document chunk that contain information relevant
to answering the user's query.
Your output should:
1. Include ONLY direct quotes of relevant sentences from the original text
2. Preserve the original wording (do not modify the text)
3. Include ONLY sentences that directly relate to the query
4. Separate extracted sentences with newlines
5. Do not add any commentary or additional text
Format your response as plain text with no additional comments."""
# Define the user prompt with the query and document chunk
user_prompt = f"""
Query: {query}
Document Chunk:
{chunk}
Extract only the content relevant to answering this query.
"""
# Generate a response using the OpenAI API
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt}
],
temperature=0
)
# 从响应中提取压缩块
compressed_chunk = response.choices[0].message.content.strip()
# 计算压缩比
original_length = len(chunk)
compressed_length = len(compressed_chunk)
compression_ratio = (original_length - compressed_length) / original_length * 100
return compressed_chunk, compression_ratio
def batch_compress_chunks(chunks, query, compression_type="selective", model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"):
"""
单独压缩多个块。
"""
print(f"Compressing {len(chunks)} chunks...") # Print the number of chunks to be compressed
results = [] # Initialize an empty list to store the results
total_original_length = 0 # 初始化一个变量来存储块的总原始长度
total_compressed_length = 0 # 初始化一个变量来存储块的总压缩长度
# Iterate over each chunk
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Compressing chunk {i+1}/{len(chunks)}...") # Print the progress of compression
# 压缩数据块,得到压缩后的数据块和压缩比
# compress_chunk 通过只保留与查询相关的部分来压缩检索到的块。
compressed_chunk, compression_ratio = compress_chunk(chunk, query, compression_type, model)
results.append((compressed_chunk, compression_ratio)) # 将结果追加到结果列表
total_original_length += len(chunk) # 将原始块的长度与原始总长度相加
#将压缩块的长度与压缩的总长度相加
total_compressed_length += len(compressed_chunk)
# 计算整体压缩比
overall_ratio = (total_original_length - total_compressed_length) / total_original_length * 100
print(f"Overall compression ratio: {overall_ratio:.2f}%") # Print the overall compression ratio
return results # Return the list of compressed chunks with compression ratios
评测
| Technique | Avg Ratio | Context Length | Original Length | des |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| selective | 39.93% | 6025 | 10018 | 只保留直接相关的句子 |
| summary | 63.87% | 3631 | 10018 | 创建针对查询的简短摘要 |
| extraction | 54.41% | 4577 | 10018 | 仅提取包含答案的句子 |
上下文压缩是一项强大的技术,因为它平衡了广度(初始检索获得广泛的信息)和焦点(压缩消除噪音)。
通过向 LLM 提供最相关的信息,通常可以获得更简洁、更准确的答案。
优点: 降低输入信息的冗余度,加快生成模型的处理速度,同时保持必要的语义信息。
缺点: 摘要质量直接影响最终答案的准确性,压缩过程需要精细调控以防信息丢失。
十一、Feedback Loop(反馈循环)
反馈循环机制的RAG系统,该机制会随着时间的推移不断改进。通过收集和整合用户反馈,系统学会了在每次交互中提供更相关、更高质量的响应。
传统的RAG系统是静态的——它们仅仅基于嵌入的相似性来检索信息。通过反馈循环,我们创建了一个动态系统:
- 记得什么管用(什么没用)
- 随时间调整文档相关性评分
- 将成功的问答对整合到知识库中
- 通过每个用户交互变得更智能
核心代码
这个函数编排了整个检索增强生成过程:
- 1、负载历史反馈数据
- 2、处理和分块文档
- 3、可选择微调矢量索引与先前的反馈
- 4、根据反馈调整的相关性评分执行检索和生成
- 5、收集新用户反馈,以便将来改进
- 6、存储反馈以使系统能够随时间学习
def full_rag_workflow(pdf_path, query, feedback_data=None, feedback_file="feedback_data.json", fine_tune=False):
"""
执行完整的RAG工作流程,并集成反馈以进行持续改进。
Args:
pdf_path (str): 要处理的PDF文档的路径
query (str): 用户的自然语言查询
feedback_data (List[Dict], optional): 预加载反馈数据,如果无则从文件加载
feedback_file (str): 存储反馈历史的JSON文件的路径
fine_tune (bool): 是否以过往成功的Q&A配对提升指数
Returns:
Dict: Results containing the response and retrieval metadata
"""
# Step 1: 如果没有明确提供,则加载相关调整的历史反馈
if feedback_data is None:
feedback_data = load_feedback_data(feedback_file)
print(f"Loaded {len(feedback_data)} feedback entries from {feedback_file}")
# Step 2: 通过抽取、分块和嵌入管道对文档进行处理
chunks, vector_store = process_document(pdf_path)
# Step 3: 通过整合高质量的过去互动来微调矢量指数
# 这将从成功的问答对中创建增强的可检索内容
if fine_tune and feedback_data:
vector_store = fine_tune_index(vector_store, chunks, feedback_data)
# Step 4: 执行带有反馈感知检索的核心RAG
# Note: 这取决于rag_with_feedback_loop函数,该函数应该在其他地方定义以上翻译结果来自有道神经网络翻译(YNMT)· 通用场景
result = rag_with_feedback_loop(query, vector_store, feedback_data)
# Step 5: 收集用户反馈以改进未来的性能
print("\n=== Would you like to provide feedback on this response? ===")
print("Rate relevance (1-5, with 5 being most relevant):")
relevance = input()
print("Rate quality (1-5, with 5 being highest quality):")
quality = input()
print("Any comments? (optional, press Enter to skip)")
comments = input()
# Step 6: 将反馈格式化为结构化数据
feedback = get_user_feedback(
query=query,
response=result["response"],
relevance=int(relevance),
quality=int(quality),
comments=comments
)
# Step 7: 持续反馈以实现持续的系统学习
store_feedback(feedback, feedback_file)
print("Feedback recorded. Thank you!")
return result
评测
测试评分为0.7。
反馈回路通过以下方式显著提高了响应质量:
*提供神经网络如何运作的清晰简明的解释
*提供更具体的应用示例
*解决标准RAG回应的局限性(例如,缺乏清晰度和简洁性)
*对神经网络的组成部分提供更准确的解释
反馈循环有助于确定缺乏标准RAG响应的领域,并对该主题提供了更全面和详细的解释。这是一个反馈循环如何提高响应质量的清晰例子。
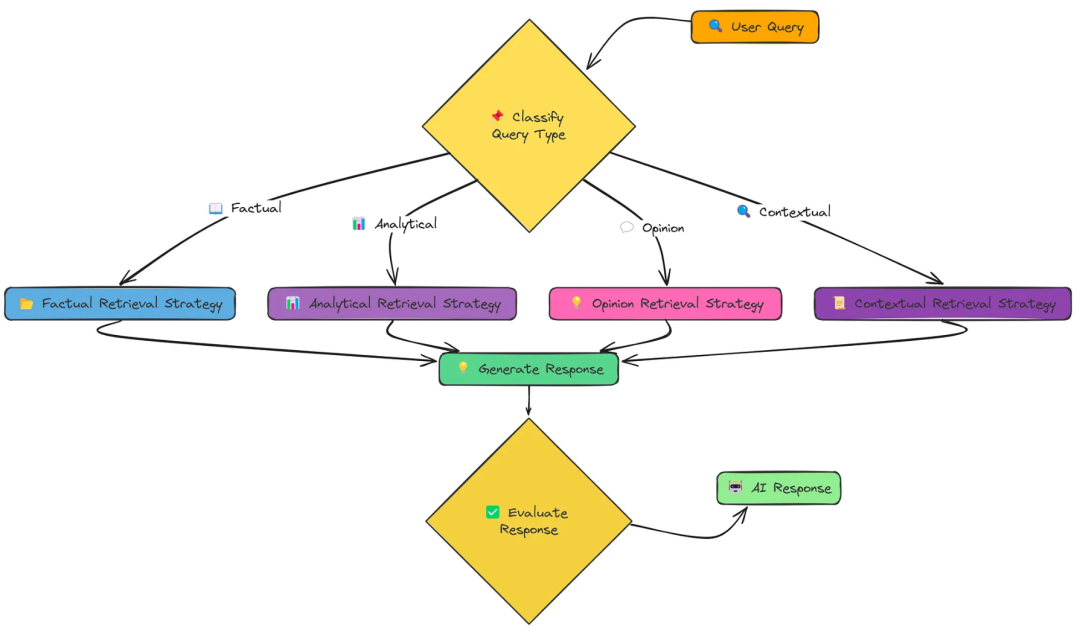
十二、Adaptive RAG(自适应RAG)
个Adaptive Retrieval系统,它可以根据查询的类型动态地选择最合适的检索策略。这种方法大大提高了我们的RAG系统在各种问题上提供准确和相关响应的能力。
不同的问题需要不同的检索策略:
-
1、策略类型(事实、分析、意见或上下文)
事实策略:注重检索精确的事实和数据。 分析策略:旨在全面涵盖某个主题,探索不同的方面。 意见策略:试图收集有关主观问题的不同观点。 上下文策略:结合用户特定的上下文来定制检索。 -
2、选择适当的检索策略
-
3、执行专门的检索技术
-
4、生成定制的响应
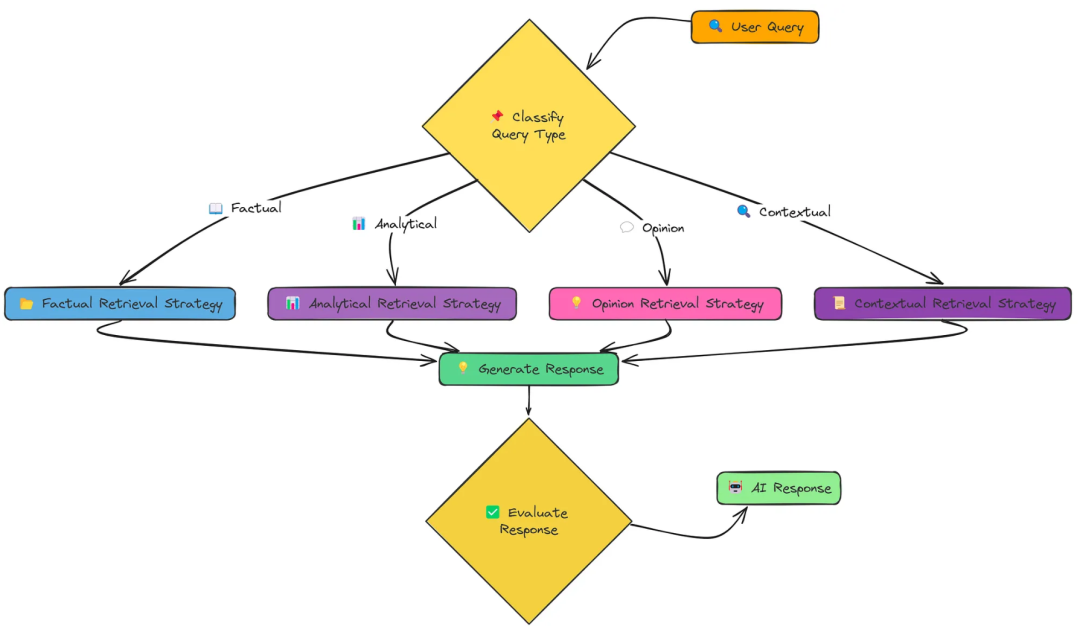
核心代码
def adaptive_retrieval(query, vector_store, k=4, user_context=None):
"""
通过选择和执行适当的策略来执行自适应检索。
"""
# 对查询进行分类以确定其类型
query_type = classify_query(query)
print(f"Query classified as: {query_type}")
# S根据查询类型选择并执行适当的检索策略
if query_type == "Factual": # 事实策略
# 使用事实检索策略来获取精确的信息
results = factual_retrieval_strategy(query, vector_store, k)
elif query_type == "Analytical": # 分析策略
# 使用分析检索策略进行全面的覆盖
results = analytical_retrieval_strategy(query, vector_store, k)
elif query_type == "Opinion": # 意见策略
# 对不同的观点使用意见检索策略
results = opinion_retrieval_strategy(query, vector_store, k)
elif query_type == "Contextual": # 上下文策略
# 使用上下文检索策略,结合用户上下文
results = contextual_retrieval_strategy(query, vector_store, k, user_context)
else:
# Default to factual retrieval strategy if classification fails
results = factual_retrieval_strategy(query, vector_store, k)
return results # Return the retrieved documents
def rag_with_adaptive_retrieval(pdf_path, query, k=4, user_context=None):
"""
完整的RAG管道与自适应检索。
"""
print("\n=== RAG WITH ADAPTIVE RETRIEVAL ===")
print(f"Query: {query}")
# 处理文档以提取文本、分块并创建嵌入
chunks, vector_store = process_document(pdf_path)
# 对查询进行分类以确定其类型
query_type = classify_query(query)
print(f"Query classified as: {query_type}")
# 使用基于查询类型的自适应检索策略检索文档
retrieved_docs = adaptive_retrieval(query, vector_store, k, user_context)
# 根据查询、检索的文档和查询类型生成响应
response = generate_response(query, retrieved_docs, query_type)
# 将结果汇编成字典
result = {
"query": query,
"query_type": query_type,
"retrieved_documents": retrieved_docs,
"response": response
}
print("\n=== RESPONSE ===")
print(response)
return result
测评
测试评分为0.86
Adaptive RAG的优势
1、动态适应性:能够根据查询复杂度自动调整策略,避免不必要的计算开销
2、高效性:在处理简单查询时使用最简单的非检索方法,处理复杂查询时采用多步检索,确保答案的准确性
2、全面性:结合了多种检索增强方法,适用于不同类型的查询场景
十三、Self RAG(自我 RAG)
Self-RAG,这是一个先进的RAG系统,可以动态地决定何时以及如何使用检索到的信息。与传统的RAG方法不同,Self-RAG在整个检索和生成过程中引入了反射点,从而产生更高质量和更可靠的响应。
核心代码
def determine_if_retrieval_needed(query):
"""
确定给定查询是否需要检索。
"""
# 系统提示指示AI如何确定是否需要检索
"""
您是一名人工智能助理,负责确定是否需要检索来回答查询。
对于事实问题、特定信息请求或有关事件、人员或概念的问题,请回答“是”。
对于观点、假设场景或具有常识的简单疑问,请回答“否”。
仅回答“是”或“否”。
"""
system_prompt = """You are an AI assistant that determines if retrieval is necessary to answer a query.
For factual questions, specific information requests, or questions about events, people, or concepts, answer "Yes".
For opinions, hypothetical scenarios, or simple queries with common knowledge, answer "No".
Answer with ONLY "Yes" or "No"."""
# User prompt containing the query
user_prompt = f"Query: {query}\n\nIs retrieval necessary to answer this query accurately?"
# Generate response from the model
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt}
],
temperature=0
)
# Extract the answer from the model's response and convert to lowercase
answer = response.choices[0].message.content.strip().lower()
# Return True if the answer contains "yes", otherwise return False
return "yes" in answer
测评价
测试评分为0.6
优点: 特别适合需要复杂逻辑推理和多轮交互的问题,能逐步逼近真实答案。
缺点: 迭代次数较多可能导致响应延迟,需要平衡准确率与效率。
十四、Proposition Chunking(命题分块)
命题分块——这是一种高级技术,可以将文档分解为原子的事实陈述,以便更准确地检索。与传统的按字符数划分文本不同,命题分块保留了单个事实的语义完整性。
命题分块通过以下方式提供更精确的检索:
- 1、将内容分解为原子的、自包含的事实
- 2、为检索创建更小、更细粒度的单元
- 3、支持查询和相关内容之间更精确的匹配
- 4、过滤掉低质量或不完整的命题

火山引擎开发者社区是火山引擎打造的AI技术生态平台,聚焦Agent与大模型开发,提供豆包系列模型(图像/视频/视觉)、智能分析与会话工具,并配套评测集、动手实验室及行业案例库。社区通过技术沙龙、挑战赛等活动促进开发者成长,新用户可领50万Tokens权益,助力构建智能应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献12条内容
已为社区贡献12条内容





所有评论(0)